ASTM A781/A781M-00
(Specification)Standard Specification for Castings, Steel and Alloy, Common Requirements, for General Industrial Use
Standard Specification for Castings, Steel and Alloy, Common Requirements, for General Industrial Use
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers a group of requirements that are mandatory requirements of the following steel casting specifications issued by ASTM. If the product specification specifies different requirements, the product specification shall prevail.ASTM Designation Title of SpecificationA27/A27M Steel Castings, Carbon, for General ApplicationA128/A128MSteel Castings, Austenitic ManganeseA148/A148MSteel Castings, High-Strength, for Structural PurposesA297/A297M Steel Castings, Iron Chromium and Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Heat Resistant for General ApplicationA447/A447M Steel Castings, Chromium-Nickel-Iron Alloy (25-12 Class), for High-Temperature Service A486/A486MSteel Castings, for Highway BridgesA494/A494MCastings, Nickel and Nickel Alloy A560/A560MCastings, Chromium-Nickel Alloy A743/A743MCastings, Iron-Chromium, Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Corrosion Resistant, for General Application A744/A744M Castings, Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Corrosion Resistant, for Severe ServiceA747/A747M Steel Castings, Stainless, Precipitation HardeningA890/A890M Castings, Iron-Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum Corrosion-Resistant, Duplex (Austenitic/Ferritic) for General ApplicationA915/A915MSteel Castings, Carbon and Alloy Chemical
1.2 This specification also covers a group of supplementary requirements that may be applied to the above specifications as indicated therein. These are provided for use when additional testing or inspection is desired and apply only when specified individually by the purchaser in the order.
1.3 The requirements of the individual material specification, and this general specification shall prevail in the sequence named.
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification. Inch-pound units are applicable for material ordered to Specification A781 and SI units for material ordered to Specification A781M.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: A 781/A 781M – 00 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Castings, Steel and Alloy, Common Requirements, for
General Industrial Use
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 781/A 781M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Specification A 781M.
1.1 This specification covers a group of requirements that
2. Referenced Documents
are mandatory requirements of the following steel casting
2.1 ASTM Standards:
specifications issued by ASTM. If the product specification
A 27/A27M Specification for Steel Castings, Carbon, for
specifies different requirements, the product specification shall
General Application
prevail.
A 128/A128M Specification for Steel Castings, Austenitic
ASTM
Manganese
Designation Title of Specification
A 27/A 27M Steel Castings, Carbon, for General Application
A 148/A148M Specification for Steel Castings, High
A 128/A 128M Steel Castings, Austenitic Manganese 2
Strength, for Structural Purposes
A 148/A 148M Steel Castings, High-Strength, for Structural Purposes
A 297/A297M Specification for Steel Castings, Iron-
A 297/A 297M Steel Castings, Iron Chromium and Iron-Chromium-Nickel,
Heat Resistant for General Application
Chromium and Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Heat Resistant, for
A 447/A 447M Steel Castings, Chromium-Nickel-Iron Alloy (25-12 Class),
General Application
for High-Temperature Service
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
A 486/A 486M Steel Castings, for Highway Bridges
A 494/A 494M Castings, Nickel and Nickel Alloy
of Steel Products
A 560/A 560M Castings, Chromium-Nickel Alloy
A 447/A 447M Specification for Steel Castings,
A 743/A 743M Castings, Iron-Chromium, Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Corro-
Chromium-Nickel-Iron Alloy (25-12 Class), for High-
sion Resistant, for General Application
A 744/A 744M Castings, Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Corrosion Resistant, for
Temperature Service
Severe Service
A 488/A 488M Practice for Steel Castings, Welding, Quali-
A 747/A 747M Steel Castings, Stainless, Precipitation Hardening
A 890/A 890M Castings, Iron-Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum Corrosion- fications of Procedures and Personnel
Resistant, Duplex (Austenitic/Ferritic) for General Applica-
A 494/A 494M Specification for Castings, Nickel and
tion
Nickel Alloy
A 915/A 915M Steel Castings, Carbon and Alloy Chemical
A 560/A 560M Specification for Castings, Chromium-
1.2 This specification also covers a group of supplementary
Nickel Alloy
requirements that may be applied to the above specifications as
A 609/A 609M Practice for Castings, Carbon, Low-Alloy,
indicated therein. These are provided for use when additional
and Martensitic Stainless Steel, Ultrasonic Examination
testing or inspection is desired and apply only when specified 2
Thereof
individually by the purchaser in the order.
A 743/A 743M Specification for Castings, Iron-Chromium,
1.3 The requirements of the individual material specifica-
Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Corrosion-Resistant, for General
tion, and this general specification shall prevail in the sequence
Application
named.
A 744/A 744M Specification for Castings, Iron-
1.4 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
Chromium-Nickel, Corrosion Resistant, for Severe Ser-
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the 2
vice
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
A 747/A 747M Specification for Steel Castings, Stainless,
system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must 2
Precipitation Hardening
be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
A 751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for
two systems may result in nonconformance with the specifi- 3
Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
cation. Inch-pound units are applicable for material ordered to
A 800/A 800M Practice for Steel Castings, Austenitic Al-
Specification A 781 and SI units for material ordered to 2
loy, Estimating Ferrite Content Thereof
A 802/A 802M Practice for Steel Castings, Surface Accep-
tance Standards, Visual Examination
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel, and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.18 on Castings.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 2000. Published October 2000. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.02.
published as A 781 – 80. Last previous edition A 781/A 781M – 99a. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 781/A 781M
A 890/A 890M Specification for Castings, Iron- Samples for carbon analysis of carbon and alloy steel shall be
Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum Corrosion-Resistant, Du- taken no closer than ⁄4 in. to a cast surface, except that castings
plex (Austenitic/Ferritic) for General Application too thin for this shall be analyzed on representative material.
A 915/A 915M Specification for Steel Castings, Carbon The chemical composition thus determined shall meet the
and Alloy, Chemical Requirements Similar to Standard requirements specified in the applicable specification for the
Wrought Grades grade involved, or shall be subject to rejection by the pur-
A 919 Terminology Relating to Heat Treatment of Metals chaser, except that the chemical composition determined for
E 94 Guide for Radiographic Testing carbon and low alloy steel castings may vary from the specified
E 125 Reference Photographs for Magnetic Particle Indica- limits by the amounts shown in Table 1. The product analysis
tions on Ferrous Castings tolerances of Table 1 are not applicable as acceptance criteria
E 165 Test Method for Liquid Penetrant Examination for heat analysis by the casting manufacturer. When comparing
E 186 Reference Radiographs for Heavy-Walled (2 to 4 ⁄2- product and heat analysis for other than carbon and low alloy
in. (51 to 114-mm)) Steel Castings steels, the reproducibility Data R , in Test Methods E 353 or
E 280 Reference Radiographs for Heavy-Walled (4 ⁄2 to E 354, as applicable, shall be taken into consideration.
12-in. (114 to 305-mm)) Steel Castings 5.4 Unspecified Elements—When chemical analysis for el-
E 340 Test Method for Macroetching Metals and Alloys ements not specified for the grade ordered is desired, Supple-
E 353 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Stainless, mentary Requirement S13 may be specified.
Heat-Resisting, Maraging, and Other Similar Chromium- 5.4.1 Grade substitution, for stainless steel or nickel base
Nickel-Iron Alloys alloy castings, is not permitted. Grade substitution occurs when
E 354 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of High- the material supplied:
Temperature, Electrical, Magnetic, and Other Similar Iron, 1. contains an element, other than nitrogen, that is not
Nickel, and Cobalt Alloys specified in the ordered grade; and,
E 446 Reference Radiographs for Steel Castings Up to 2 in. 2. the amount of that element equals or exceeds the mini-
(51 mm) in Thickness mum requirement for the element in another grade for which it
E 709 Guide for Magnetic Particle Examination is specified.
For this requirement, a grade is defined as an alloy described
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions: TABLE 1 Product Analysis Tolerances
3.1.1 The definitions in Test Methods and Definitions
A B C
Element Range, % Tolerances , Over
A 370, Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology A 751, and
Maximum or Under
Terminology A 919 are applicable to this specification and
Minimum Limit, %
those listed in 1.1.
C up to 0.65 0.03 3%C + 0.02
L
above 0.65 0.04
4. Materials and Manufacture
Mn up to 1 0.08 3%Mn + 0.01
L
above 1 0.09
4.1 Melting Process—The steel shall be made by open-
Si up to 0.60 0.22 3%Si − 0.01
L
hearth or electric furnace process with or without separate
above 0.60 0.15
P all 0.13 3%P + 0.005
refining such as argon-oxygen-decarburization (AOD) unless
L
S all 0.36 3%S + 0.001
L
otherwise specified in the individual specification.
Ni up to 2 0.10 3%Ni + 0.03
L
above 2 0.25
5. Chemical Composition
Cr up to 2 0.07 3%Cr + 0.04
L
above 2 0.18
5.1 Chemical Analysis—Chemical analysis of materials
Mo up to 0.6 0.04 3%Mo + 0.03
L
covered by this specification shall be in accordance with Test
above 0.6 0.06
V up to 0.25 0.23 3%V + 0.004
L
Methods, Practices, and Terminology A 751.
above 0.25 0.06
5.2 Heat Analysis—An analysis of each heat shall be made
W up to 0.10 0.08 3%W + 0.02
L
by the manufacturer to determine the percentages of the above 0.10 0.02
Cu up to 0.15 0.18 3%Cu + 0.02
L
elements specified in the individual specification for the grade
above 0.15 0.05
being poured. The analysis shall be made from a test sample
Al up to 0.10 0.08 3 %Al + 0.02
L
preferably taken during the pouring of the heat. When drillings above 0.10 0.03
are used, they shall be taken not less than ⁄4 in. [6.4 mm]
A
The range denotes the composition limits up to which tolerances are computed
beneath the surface. The chemical composition thus deter-
by the equation, and above which the tolerances are given by a constant.
mined shall conform to the requirements in the individual
B
The subscript for the elements in each equation indicates that the limits of the
L
specification for the grade being poured.
element specified by the applicable specification are to be inserted into the
equation to calculate the tolerance for the upper limit and the lower limit (if
5.3 Product Analysis—A product analysis may be made by
applicable), respectively. Examples of computing tolerances are presented in
the purchaser from material representing each heat, lot, or
footnote C.
C
casting. The analysis shall be made on representative material.
To illustrate the computation of the tolerance, consider the manganese
maximum of 0.70 for an 0.30 carbon grade 65–35 in Specification A 27. The
maximum permissible deviation is (0.08 3 0.70 + 0.01) = 0.066. Therefore, the
highest acceptable product analysis is 0.766. Similarly, for an 0.20 carbon grade
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.03.
70–40 in Specification A 27, the maximum manganese content is 1.40; thus, the
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05. highest acceptable product analysis is (1.40 + 0.09) = 1.49.
A 781/A 781M
individually in a table of chemical requirements within any 6.2 Unless otherwise specified by the purchaser, when
specification listed within the scope of A 781/A 781M. mechanical properties are required by the product specifica-
tion, test coupons may be cast integrally with the castings, or
6. Tensile Requirements
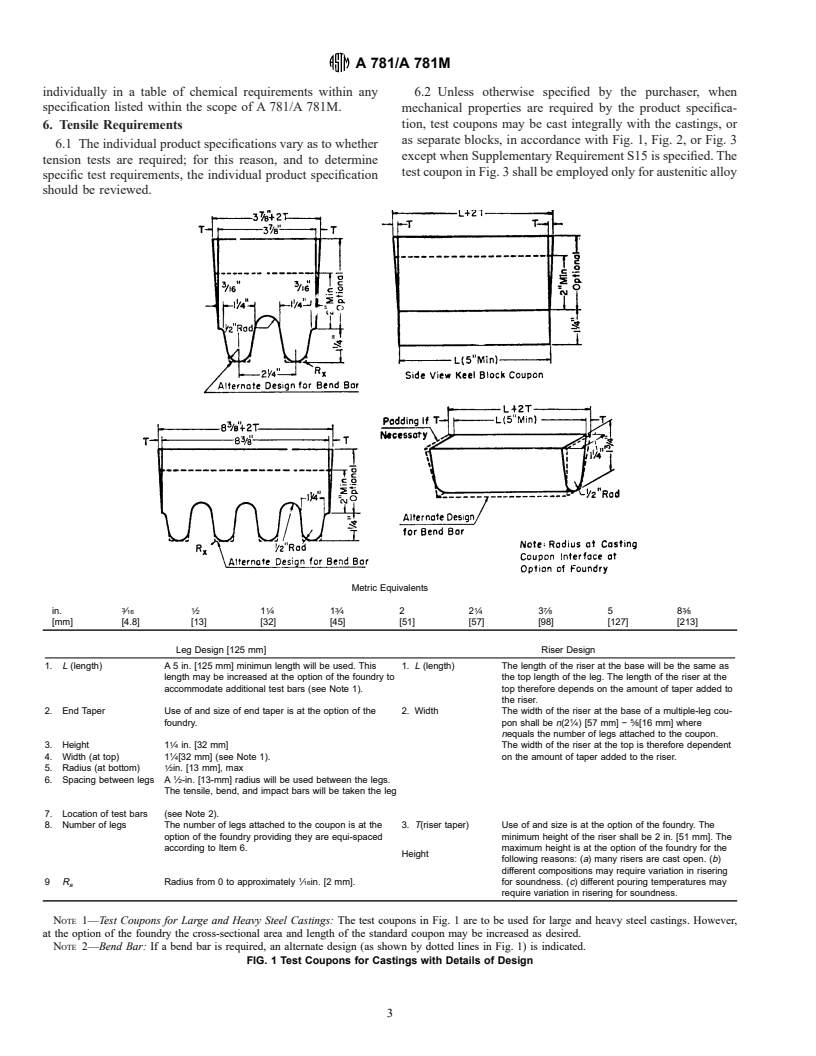
as separate blocks, in accordance with Fig. 1, Fig. 2, or Fig. 3
6.1 The individual product specifications vary as to whether
except when Supplementary Requirement S15 is specified. The
tension tests are required; for this reason, and to determine
test coupon in Fig. 3 shall be employed only for austenitic alloy
specific test requirements, the individual product specification
should be reviewed.
Metric Equivalents
3 1 1 3 1 7 3
in. ⁄16 ⁄2 1 ⁄4 1 ⁄4 2 2 ⁄4 3 ⁄8 5 8 ⁄8
[mm] [4.8] [13] [32] [45] [51] [57] [98] [127] [213]
Leg Design [125 mm] Riser Design
1. L (length) A 5 in. [125 mm] minimun length will be used. This 1. L (length) The length of the riser at the base will be the same as
length may be increased at the option of the foundry to the top length of the leg. The length of the riser at the
accommodate additional test bars (see Note 1). top therefore depends on the amount of taper added to
the riser.
2. End Taper Use of and size of end taper is at the option of the 2. Width The width of the riser at the base of a multiple-leg cou-
1 5
foundry. pon shall be n(2 ⁄4) [57 mm] − ⁄8[16 mm] where
nequals the number of legs attached to the coupon.
3. Height 1 ⁄4 in. [32 mm] The width of the riser at the top is therefore dependent
4. Width (at top) 1 ⁄4[32 mm] (see Note 1). on the amount of taper added to the riser.
5. Radius (at bottom) ⁄2in. [13 mm], max
6. Spacing between legs A ⁄2-in. [13-mm] radius will be used between the legs.
The tensile, bend, and impact bars will be taken the leg
7. Location of test bars (see Note 2).
8. Number of legs The number of legs attached to the coupon is at the 3. T(riser taper) Use of and size is at the option of the foundry. The
option of the foundry providing they are equi-spaced minimum height of the riser shall be 2 in. [51 mm]. The
according to Item 6. maximum height is at the option of the foundry for the
Height
following reasons: (a) many risers are cast open. (b)
different compositions may require variation in risering
9 R Radius from 0 to approximately ⁄16in. [2 mm]. for soundness. (c) different pouring temperatures may
s
require variation in risering for soundness.
NOTE 1—Test Coupons for Large and Heavy Steel Castings: The test coupons in Fig. 1 are to be used for large and heavy steel castings. However,
at the option of the foundry the cross-sectional area and length of the standard coupon may be increased as desired.
NOTE 2—Bend Bar: If a bend bar is required, an alternate design (as shown by dotted lines in Fig. 1) is indicated.
FIG. 1 Test Coupons for Castings with Details of Design
A 781/A 781M
Metric Equivalents
in. [mm] in. [mm]
1 1
⁄8 [3.2] 3 ⁄2 [88.9]
⁄2 [12.7] 4 [101.6]
1 1
1 ⁄16 [27.0] 4 ⁄16 [103.2]
1 ⁄2 [38.1] 5 [127.0]
3 [76.2] 11 [279.4]
NOTE—Pour through head; cover molten head with powdered charcoal, coke dust, etc., immediately after pouring, in order to keep head fluid as long
as possible.
FIG. 2 Test Block for Tension Test Specimen
NOTE—Coupons produced in this manner are suitable for austenitic alloys only. The mold may be preheated for pouring to produce a sound coupon.
FIG. 3 Cast-To-Shape Test Coupon for Tension Specimen
A 781/A 781M
castings with cross sections less than 2 ⁄2 in. requirements of the individual specification using procedures
and welders qualified in accordance with Practice A 488/
7. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
A 488M.
7.1 All castings shall be made in a workmanlike manner and
shall conform to the dimensions on drawings furnished by the
10. Inspection
purchaser before manufacture is started. If the pattern is
10.1 The manufacturer shall afford the purchaser’s inspector
supplied by the purchaser, the dimensions of the casting shall
all reasonable facilities necessary to satisfy that the material is
be as predicated by the pattern.
being produced and furnished in accordance with the appli-
8. Quality
c
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
Designation:A 781/A 781M–99a Designation: A 781/A 781M – 00
Standard Specification for
Castings, Steel and Alloy, Common Requirements, for
General Industrial Use
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationA781/A781M;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyear
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers a group of requirements that are mandatory requirements of the following steel casting
specificationsissuedbyASTM.Iftheproductspecificationspecifiesdifferentrequirements,theproductspecificationshallprevail.
ASTM
Designation Title of Specification
A 27/A 27M Steel Castings, Carbon, for General Application
A 128/A 128M Steel Castings, Austenitic Manganese
A 148/A 148M Steel Castings, High-Strength, for Structural Purposes
A 297/A 297M Steel Castings, Iron Chromium and Iron-Chromium-Nickel,
Heat Resistant for General Application
A 447/A 447M Steel Castings, Chromium-Nickel-Iron Alloy (25-12 Class),
for High-Temperature Service
A 486/A 486M Steel Castings, for Highway Bridges
A 494/A 494M Castings, Nickel and Nickel Alloy
A 560/A 560M Castings, Chromium-Nickel Alloy
A 743/A 743M Castings, Iron-Chromium, Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Corro-
sion Resistant, for General Application
A 744/A 744M Castings, Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Corrosion Resistant, for
Severe Service
A 747/A 747M Steel Castings, Stainless, Precipitation Hardening
A 890/A 890M Castings, Iron-Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum Corrosion-
Resistant, Duplex (Austenitic/Ferritic) for General Applica-
tion
A 915/A 915M Steel Castings, Carbon and Alloy Chemical
1.2 This specification also covers a group of supplementary requirements that may be applied to the above specifications as
indicated therein. These are provided for use when additional testing or inspection is desired and apply only when specified
individually by the purchaser in the order.
1.3 Therequirementsoftheindividualmaterialspecification,andthisgeneralspecificationshallprevailinthesequencenamed.
1.4 Thevaluesstatedineitherinch-poundunitsorSIunitsaretoberegardedseparatelyasstandard.Withinthetext,theSIunits
are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used
independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
Inch-pound units are applicable for material ordered to Specification A781 and SI units for material ordered to Specification
A781M.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A27/A27M Specification for Steel Castings, Carbon, for General Application
A128/A128M Specification for Steel Castings, Austenitic Manganese
A148/A148M Specification for Steel Castings, High Strength, for Structural Purposes
A297/A297M Specification for Steel Castings, Iron-Chromium and Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Heat Resistant, for General
Application
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A447/A447M Specification for Steel Castings, Chromium-Nickel-Iron Alloy (25-12 Class), for High-Temperature Service
A488/A488M Practice for Steel Castings, Welding, Qualifications of Procedures and Personnel
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA-1A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel, and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.18 on Castings.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1999.2000. Published October 1999.2000. Originally published as A781–80. Last previous edition A781/A781M–99a.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.02.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 781/A 781M – 00
A494/A494M Specification for Castings, Nickel and Nickel Alloy
A560/A560M Specification for Castings, Chromium-Nickel Alloy
A609/A609M Practice for Castings, Carbon, Low-Alloy, and Martensitic Stainless Steel, Ultrasonic Examination Thereof
A743/A743M Specification for Castings, Iron-Chromium, Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Corrosion-Resistant, for General Appli-
cation
A744/A744M Specification for Castings, Iron-Chromium-Nickel, Corrosion Resistant, for Severe Service
A747/A747M Specification for Steel Castings, Stainless, Precipitation Hardening
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
A800/A800M Practice for Steel Castings, Austenitic Alloy, Estimating Ferrite Content Thereof
A802/A802M Practice for Steel Castings, Surface Acceptance Standards, Visual Examination
A890/A890M Specification for Castings, Iron-Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum Corrosion-Resistant, Duplex (Austenitic/
Ferritic) for General Application
A915/A915M Specification for Steel Castings, Carbon and Alloy, Chemical Requirements Similar to Standard Wrought
Grades
A919 Terminology Relating to Heat Treatment of Metals
E94 Guide for Radiographic Testing
E125 Reference Photographs for Magnetic Particle Indications on Ferrous Castings
E165 Test Method for Liquid Penetrant Examination
E186 Reference Radiographs for Heavy-Walled (2 to 4 ⁄2-in. (51 to 114-mm)) Steel Castings
E280 Reference Radiographs for Heavy-Walled (4 ⁄2 to 12-in. (114 to 305-mm)) Steel Castings
E340 Test Method for Macroetching Metals and Alloys
E353 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Stainless, Heat-Resisting, Maraging, and Other Similar Chromium-Nickel-Iron
Alloys
E354 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of High-Temperature, Electrical, Magnetic, and Other Similar Iron, Nickel, and
Cobalt Alloys
E446 Reference Radiographs for Steel Castings Up to 2 in. (51 mm) in Thickness
E709 Guide for Magnetic Particle Examination
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 ThedefinitionsinTestMethodsandDefinitionsA370,TestMethods,Practices,andTerminologyA751,andTerminology
A919 are applicable to this specification and those listed in 1.1.
4. Materials and Manufacture
4.1 Melting Process—The steel shall be made by open-hearth or electric furnace process with or without separate refining such
as argon-oxygen-decarburization (AOD) unless otherwise specified in the individual specification.
5. Chemical Composition
5.1 Chemical Analysis—ChemicalanalysisofmaterialscoveredbythisspecificationshallbeinaccordancewithTestMethods,
Practices, and Terminology A751.
5.2 Heat Analysis—An analysis of each heat shall be made by the manufacturer to determine the percentages of the elements
specifiedintheindividualspecificationforthegradebeingpoured.Theanalysisshallbemadefromatestsamplepreferablytaken
during the pouring of the heat. When drillings are used, they shall be taken not less than ⁄4 in. [6.4 mm] beneath the surface. The
chemicalcompositionthusdeterminedshallconformtotherequirementsintheindividualspecificationforthegradebeingpoured.
5.3 Product Analysis—Aproduct analysis may be made by the purchaser from material representing each heat, lot, or casting.
The analysis shall be made on representative material. Samples for carbon analysis of carbon and alloy steel shall be taken no
closer than ⁄4 in. to a cast surface, except that castings too thin for this shall be analyzed on representative material.The chemical
composition thus determined shall meet the requirements specified in the applicable specification for the grade involved, or shall
be subject to rejection by the purchaser, except that the chemical composition determined for carbon and low alloy steel castings
may vary from the specified limits by the amounts shown inTable 1.The product analysis tolerances ofTable 1 are not applicable
as acceptance criteria for heat analysis by the casting manufacturer. When comparing product and heat analysis for other than
carbon and low alloy steels, the reproducibility Data R , in Test Methods E353 or E354, as applicable, shall be taken into
consideration.
5.4 Unspecified Elements—When chemical analysis for elements not specified for the grade ordered is desired, Supplementary
Requirement S13 may be specified.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.03.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05.
A 781/A 781M – 00
TABLE 1 Product Analysis Tolerances
A B C
Element Range, % Tolerances , Over
Maximum or Under
Minimum Limit, %
C upto0.65 0.03 3%C + 0.02
L
above 0.65 0.04
Mn up to 1 0.08 3%Mn + 0.01
L
above 1 0.09
Si up to 0.60 0.22 3%Si − 0.01
L
above 0.60 0.15
P all 0.13 3%P + 0.005
L
S all 0.36 3%S + 0.001
L
Ni up to 2 0.10 3%Ni + 0.03
L
above 2 0.25
Cr up to 2 0.07 3%Cr + 0.04
L
above 2 0.18
Mo up to 0.6 0.04 3%Mo + 0.03
L
above 0.6 0.06
V upto0.25 0.23 3%V + 0.004
L
above 0.25 0.06
W upto0.10 0.08 3%W + 0.02
L
above 0.10 0.02
Cu up to 0.15 0.18 3%Cu + 0.02
L
above 0.15 0.05
Al up to 0.10 0.08 3%Al + 0.02
L
above 0.10 0.03
A
Therangedenotesthecompositionlimitsuptowhichtolerancesarecomputed
by the equation, and above which the tolerances are given by a constant.
B
Thesubscript fortheelementsineachequationindicatesthatthelimitsofthe
L
element specified by the applicable specification are to be inserted into the
equation to calculate the tolerance for the upper limit and the lower limit (if
applicable), respectively. Examples of computing tolerances are presented in
footnote C.
C
To illustrate the computation of the tolerance, consider the manganese
maximum of 0.70 for an 0.30 carbon grade 65–35 in Specification A 27. The
maximum permissible deviation is (0.08 3 0.70 + 0.01) = 0.066. Therefore, the
highest acceptable product analysis is 0.766. Similarly, for an 0.20 carbon grade
70–40 in Specification A 27, the maximum manganese content is 1.40; thus, the
highest acceptable product analysis is (1.40 + 0.09) = 1.49.
5.4.1 Grade substitution, for stainless steel or nickel base alloy castings, is not permitted. Grade substitution occurs when the
material supplied:
1. contains an element, other than nitrogen, that is not specified in the ordered grade; and,
2. the amount of that element equals or exceeds the minimum requirement for the element in another grade for which it is
specified.
For this requirement, a grade is defined as an alloy described individually in a table of chemical requirements within any
specification listed within the scope of A 781/A 781M.
6. Tensile Requirements
6.1 Theindividualproductspecificationsvaryastowhethertensiontestsarerequired;forthisreason,andtodeterminespecific
test requirements, the individual product specification should be reviewed.
6.2 Unless otherwise specified by the purchaser, when mechanical properties are required by the product specification, test
coupons may be cast integrally with the castings, or as separate blocks, in accordance with Fig. 1, Fig. 2, or Fig. 3 except when
Supplementary Requirement S15 is specified. The test coupon in Fig. 3 shall be employed only for austenitic alloy castings with
cross sections less than 2 ⁄2 in.
7. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
7.1 All castings shall be made in a workmanlike manner and shall conform to the dimensions on drawings furnished by the
purchaser before manufacture is started. If the pattern is supplied by the purchaser, the dimensions of the casting shall be as
predicated by the pattern.
8. Quality
8.1 The surface of the casting shall be free of adhering sand, scale, cracks, and hot tears as determined by visual examination.
Information on the relationship of mechanical properties determined on test coupons obtained as specified in 6.2 with those obtained from the casting may be found in
“The Steel Casting Handbook,” Fifth Edition, Steel Founders’ Society of America, pp. 15–35 through 15–43, 1980.
A 781/A 781M – 00
Metric Equivalents
3 1 1 3 1 7 3
in. ⁄16 ⁄2 1 ⁄4 1 ⁄4 2 2 ⁄4 3 ⁄8 5 8 ⁄8
[mm] [4.8] [13] [32] [45] [51] [57] [98] [127] [213]
Leg Design [125 mm] Riser Design
1. L (length) A 5 in. [125 mm] minimun length will be used. This 1. L (length) The length of the riser at the base will be the same as
length may be increased at the option of the foundry to the top length of the leg. The length of the riser at the
accommodate additional test bars (see Note 1). top therefore depends on the amount of taper added to
the riser.
2. End Taper Use of and size of end taper is at the option of the 2. Width The width of the riser at the base of a multiple-leg cou-
1 5
foundry. pon shall be n(2 ⁄4) [57 mm] − ⁄8 [16 mm] where
nequals the number of legs attached to the coupon.
3. Height 1 ⁄4 in. [32 mm] The width of the riser at the top is therefore dependent
on the amount of taper added to the riser.
4. Width (at top) 1 ⁄4 [32 mm] (see Note 1).
5. Radius (at bottom) ⁄2 in. [13 mm], max
6. Spacing between legs A ⁄2-in. [13-mm] radius will be used between the legs.
The tensile, bend, and impact bars will be taken the leg
7. Location of test bars (see Note 2).
8. Number of legs The number of legs attached to the coupon is at the 3. T(riser taper) Use of and size is at the option of the foundry. The
option of the foundry providing they are equi-spaced minimum height of the riser shall be 2 in. [51 mm]. The
according to Item 6. maximum height is at the option of the foundry for the
Height
following reasons: (a) many risers are cast open. (b)
different compositions may require variation in risering
9 R Radius from 0 to approximately ⁄16 in. [2 mm]. for soundness. (c) different pouring temperatures may
s
require variation in risering for soundness.
NOTE 1—Test Coupons for Large and Heavy Steel Castings: The test coupons in Fig. 1 are to be used for large and heavy steel castings. However,
at the option of the foundry the cross-sectional area and length of the standard coupon may be increased as desired.
NOTE 2—Bend Bar: If a bend bar is required, an alternate design (as shown by dotted lines in Fig. 1) is indicated.
FIG. 1 Test Coupons for Castings with Details of Design
Other surface discontinuities shall meet the visual acceptance standards specified in the order. Practice A802/A802M or other
visual standards may be used to define acceptable surface discontinuities and finish. Unacceptable visual surface discontinuities
shall be removed and their removal verified by visual examination of the resultant cavities.
8.2 When additional inspection is desired, Supplementary Requirements S1, S2, S3, S4, or S5 may be specified.
9. Repair
9.1 Repairbyw
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.