ASTM F2111-01a(2011)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Measuring Intergranular Attack or End Grain Pitting on Metals Caused by Aircraft Chemical Processes
Standard Practice for Measuring Intergranular Attack or End Grain Pitting on Metals Caused by Aircraft Chemical Processes
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
If not properly qualified, chemicals and chemical processes can attack metals used during aircraft maintenance and production. It is important to qualify only processes and chemical formulas that do not have any deleterious effects on aircraft metallic skins, fittings, components, and structures. This test procedure is used to detect and measure intergranular attack or pitting depth caused by aircraft maintenance chemical processes, hence, this test procedure is useful in selecting a process that will not cause intergranular attack or end grain pitting on aircraft alloys.
The purpose of this practice is to aid in the qualification or process conformance testing or production of maintenance chemicals for use on aircraft.
Actual aircraft processes in the production environment shall give the most representative results; however, the test results cannot be completely evaluated with respect to ambient conditions which normally vary from day to day. Additionally, when testing chemicals requiring dilutions, water quality and composition can play a role in the corrosion rates and mechanism affecting the results.
Some examples of maintenance and production chemicals include: organic solvents, paint strippers, cleaners, deoxidizers, water-based or semi-aqueous cleaners, or etching solutions and chemical milling solutions.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the procedures for testing and measuring intergranular attack (IGA) and end grain pitting on aircraft metals and alloys caused by maintenance or production chemicals.
1.2 The standard does not purport to address all qualification testing parameters, methods, critical testing, or criteria for aircraft production or maintenance chemical qualifications. Specific requirements and acceptance testing along with associated acceptance criteria shall be found where applicable in procurement specifications, materials specifications, appropriate process specifications, or previously agreed upon specifications.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F2111 − 01a (Reapproved 2011)
Standard Practice for
Measuring Intergranular Attack or End Grain Pitting on
Metals Caused by Aircraft Chemical Processes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2111; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.2 ASME Standard:
B46.1Surface Texture (Surface Roughness, Waviness, and
1.1 This practice covers the procedures for testing and
Lay)
measuring intergranular attack (IGA) and end grain pitting on
aircraftmetalsandalloyscausedbymaintenanceorproduction
3. Terminology
chemicals.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.2 The standard does not purport to address all qualifica-
3.1.1 longitudinal grain direction (L)—the dimension par-
tion testing parameters, methods, critical testing, or criteria for
allel to the rolling or extruded direction of the extrusion in the
aircraft production or maintenance chemical qualifications.
original shape.
Specific requirements and acceptance testing along with asso-
3.1.2 long transverse (LT)—the longest dimension perpen-
ciated acceptance criteria shall be found where applicable in
dicular to the rolling or extruded direction of the extrusion in
procurement specifications, materials specifications, appropri-
the original shape.
ate process specifications, or previously agreed upon specifi-
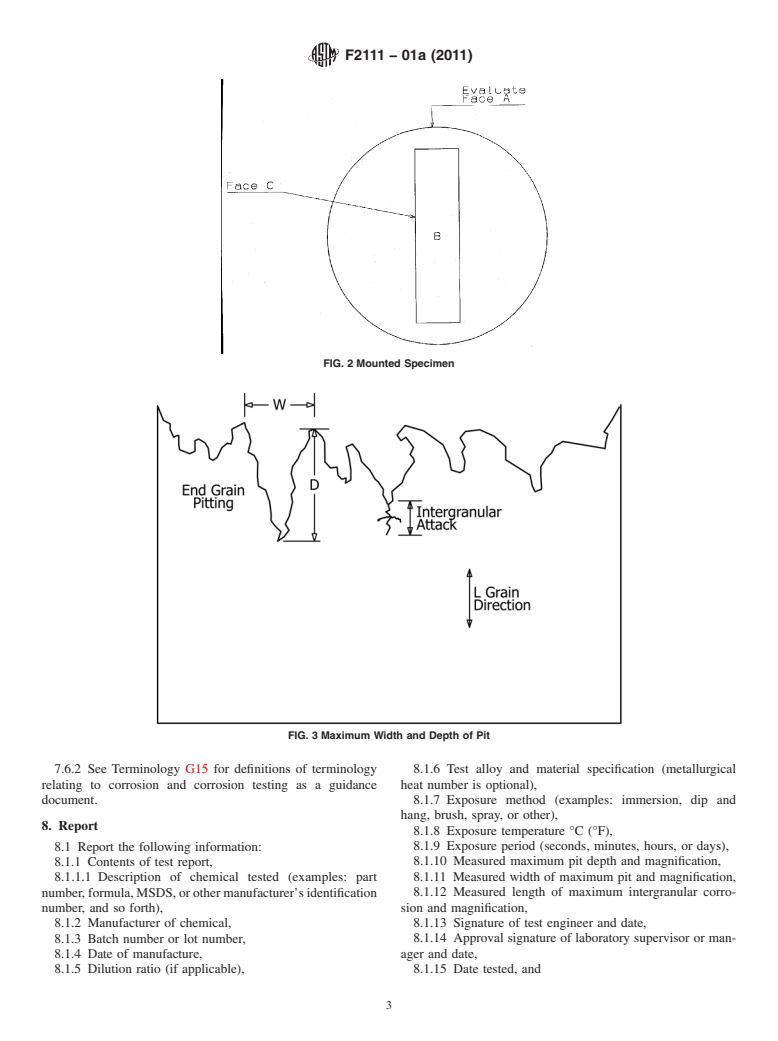
3.1.3 pit—a depression or cavity with a width to depth ratio
cations.
of <6 to 1.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1.4 short transverse (ST)—the shortest dimension perpen-
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
dicular to the rolling or extruded direction of the extrusion in
only.
the original shape.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.5 surface roughness (R )—filtered mean line µin. (µm)
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
a
as defined in ASME B46.1, Surface Texture.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4. Significance and Use
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1 If not properly qualified, chemicals and chemical pro-
2. Referenced Documents
cesses can attack metals used during aircraft maintenance and
2.1 ASTM Standards:
production. It is important to qualify only processes and
E3Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
chemical formulas that do not have any deleterious effects on
G1Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corro-
aircraft metallic skins, fittings, components, and structures.
sion Test Specimens
This test procedure is used to detect and measure intergranular
G15Terminology Relating to Corrosion and CorrosionTest-
attackorpittingdepthcausedbyaircraftmaintenancechemical
ing (Withdrawn 2010)
processes, hence, this test procedure is useful in selecting a
G46Guide for Examination and Evaluation of Pitting Cor-
process that will not cause intergranular attack or end grain
rosion
pitting on aircraft alloys.
4.2 The purpose of this practice is to aid in the qualification
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F07 on Aerospace
or process conformance testing or production of maintenance
and Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.07 on Qualifica-
chemicals for use on aircraft.
tion Testing of Aircraft Cleaning Materials.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2011. Published August 2012. Originally 4.2.1 Actual aircraft processes in the production environ-
approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as F2111–01a (2005).
ment shall give the most representative results; however, the
DOI: 10.1520/F2111-01AR11.
test results cannot be completely evaluated with respect to
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on International Headquarters, Three Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
www.astm.org. www.asme.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F2111 − 01a (2011)
ambient conditions which normally vary from day to day. representative-like alloy parts through all operations including
Additionally,whentestingchemicalsrequiringdilutions,water precleaning,postrinsing,andsoforth,forthetimenecessaryto
quality and composition can play a role in the corrosion rates
remove the amount of metal specified by process or to achieve
and mechanism affecting the results. process specified cleanliness.
4.2.2 Some examples of maintenance and production
7.2 For chemicals normally used at room temperature for
chemicals include: organic solvents, paint strippers, cleaners,
periods of less than 8 h, use 40.6 6 1°C (105 6 1.8°F) for an
deoxidizers, water-based or semi-aqueous cleaners, or etching
exposure
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.