ASTM D153-84(2014)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Specific Gravity of Pigments
Standard Test Methods for Specific Gravity of Pigments
ABSTRACT
These test methods cover three procedures for determining the specific gravity of pigments, as follows: Test Method A which is for routine testing of several samples simultaneously, Test Method B which is for tests requiring greater accuracy than Test Method A, and Test Method C which is for rapid and accurate testing of single samples. The specific gravity value obtained by these procedures may be used with the weight of a dry pigment to determine the volume occupied by the pigment in a coating formulation. For Test Method A, the following apparatus and materials shall be used: pycnometer, water bath, manometer, desiccator, vacuum pumps, thermometer, weighing bottle, and immersion liquid. For Test Method B, the following apparatus and materials shall be used: pycnometer, water bath, manometer, vacuum pump, thermometer, weighing bottle, bell jar, and bottle. For Test Method C, the following apparatus and materials shall be used: buret, flask, stopcocks, vacuum pump, manometer, thermometer, weighing bottle, and immersion liquid.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover three procedures for determining the specific gravity of pigments, as follows:
Test Method A—For Routine Testing of Several Samples Simultaneously.
Test Method B—For Tests Requiring Greater Accuracy than Test Method A.
Test Method C—For Rapid and Accurate Testing of Single Samples.
1.2 The specific gravity value obtained by these procedures may be used with the weight of a dry pigment to determine the volume occupied by the pigment in a coating formulation.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Sections 5, 11, and 15.
General Information
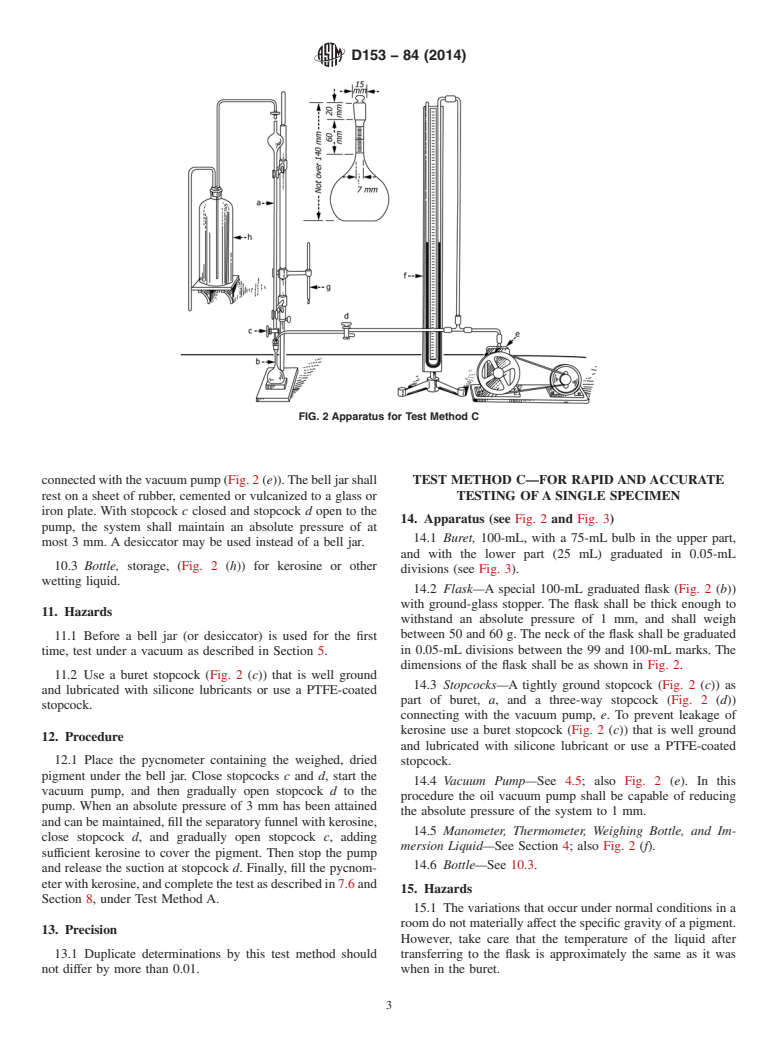
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D153 −84 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Methods for
1
Specific Gravity of Pigments
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D153; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope TEST METHOD A—FOR ROUTINE TESTING OF
SEVERAL SAMPLES SIMULTANEOUSLY
1.1 These test methods cover three procedures for determin-
ing the specific gravity of pigments, as follows:
4. Apparatus and Materials
Test Method A—For Routine Testing of Several Samples
4.1 Pycnometer—A pycnometer (Note 1) having a 50-mL
Simultaneously.
capacity.
Test Method B—For Tests Requiring Greater Accuracy than
Test Method A.
NOTE 1—The Weld type with the cap seal on the outside of the neck of
Test Method C—For Rapid and Accurate Testing of Single
the bottle is preferred because there is less danger of trapping air just
Samples. under the capillary tube than with types having the ground glass seal on
the inside of the neck.
1.2 The specific gravity value obtained by these procedures
4.2 Water Bath, maintained at 25 6 0.5°C and equipped
may be used with the weight of a dry pigment to determine the
with a stirring device.
volume occupied by the pigment in a coating formulation.
4.3 Manometer, open- or closed-tube (see Part f of the
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
apparatus for Test Method C), made of glass tubing 6 mm in
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
diameter, fitted with rubber pressure tubing attached to a
only.
T-joint leading to the desiccator and the pump. For the
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
open-tube type 860 mm of mercury shall be used. The
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
difference in levels of the mercury in the manometer when the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
system is in operation, subtracted from the barometer reading
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
taken at the same time, shall be considered the absolute
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
pressure of the system in millimetres of mercury.
statements, see Sections 5, 11, and 15.
4.4 Desiccator, glass, constructed with heavy walls to with-
stand a vacuum of one atmosphere, and with an opening at the
2. Referenced Documents
side.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.5 VacuumPumps—Alaboratory water vacuum-type pump
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
(Note 2), to remove the greater portion of air in the desiccator,
and an oil vacuum-type pump, motor-driven, and capable of
3. Purity of Reagents
reducing the absolute pressure of the system to 3 mm.
3.1 PurityofWater—Reference to water shall be understood
NOTE 2—The water vacuum pump may be omitted if the rate of
to mean reagent water as defined by Type II of Specification
evacuation with the oil pump can be controlled so as to avoid a rapid
D1193.
ebullition of entrapped air and possible loss of specimen.
4.6 Thermometer, having a range from 0 to 60°C, and
graduated in 0.1°C divisions.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on
4.7 WeighingBottle, wide-mouth cylindrical glass (about 30
Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and are the direct
responsibility of Subcommittee D01.31 on Pigment Specifications.
mm in height and 70 mm in diameter), provided with a
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2014. Published December 2014. Originally
ground-glass stopper.
approved in 1923. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D153 – 84 (2008).
DOI: 10.1520/D0153-84R14.
4.8 Immersion Liquid—Kerosine has been found to be a
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
good wetting vehicle for most pigments, and shall be used
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
generally as the immersion liquid. Refined, white kerosine of
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. narrow evaporation and boiling range shall be used.With some
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D153−84 (2014)
pigments that are not wetted well with kerosine, other immer- pigments very rapidly, then this action gradually decreases and
sion liquids such as glycerin, ethylene glycol, finally stops. The time required for complete removal of air
tetrahydronaphthalene, etc., may be substituted.
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D153 − 84 (Reapproved 2008) D153 − 84 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Methods for
1
Specific Gravity of Pigments
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D153; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover three procedures for determining the specific gravity of pigments, as follows:
Test Method A—For Routine Testing of Several Samples Simultaneously.
Test Method B—For Tests Requiring Greater Accuracy than Test Method A.
Test Method C—For Rapid and Accurate Testing of Single Samples.
1.2 The specific gravity value obtained by these procedures may be used with the weight of a dry pigment to determine the
volume occupied by the pigment in a coating formulation.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Sections 5, 11, and 15.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
3. Purity of Reagents
3.1 Purity of Water—Reference to water shall be understood to mean reagent water as defined by Type II of Specification
D1193.
TEST METHOD A—FOR ROUTINE TESTING OF SEVERAL SAMPLES SIMULTANEOUSLY
4. Apparatus and Materials
4.1 Pycnometer—A pycnometer (Note 1) having a 50-mL capacity.
NOTE 1—The Weld type with the cap seal on the outside of the neck of the bottle is preferred because there is less danger of trapping air just under
the capillary tube than with types having the ground glass seal on the inside of the neck.
4.2 Water Bath, maintained at 25 6 0.5°C and equipped with a stirring device.
4.3 Manometer, open- or closed-tube (see Part f of the apparatus for Test Method C), made of glass tubing 6 mm in diameter,
fitted with rubber pressure tubing attached to a T-joint leading to the desiccator and the pump. For the open-tube type 860 mm of
mercury shall be used. The difference in levels of the mercury in the manometer when the system is in operation, subtracted from
the barometer reading taken at the same time, shall be considered the absolute pressure of the system in millimetres of mercury.
4.4 Desiccator, glass, constructed with heavy walls to withstand a vacuum of one atmosphere, and with an opening at the side.
4.5 Vacuum Pumps—A laboratory water vacuum-type pump (Note 2), to remove the greater portion of air in the desiccator, and
an oil vacuum-type pump, motor-driven, and capable of reducing the absolute pressure of the system to 3 mm.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and are the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.31 on Pigment Specifications.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2008Dec. 1, 2014. Published February 2008December 2014. Originally approved in 1923. Last previous edition approved in 20032008
as D153 – 84 (2003).(2008). DOI: 10.1520/D0153-84R08.10.1520/D0153-84R14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D153 − 84 (2014)
NOTE 2—The water vacuum pump may be omitted if the rate of evacuation with the oil pump can be controlled so as to avoid a rapid ebullition of
entrapped air and possible loss of specimen.
4.6 Thermometer, having a range from 0 to 60°C, and graduated in 0.1°C divisions.
4.7 Weighing Bottle, wide-mouth cylindrical glass (about 30 mm in height and 70 mm in diameter), provided with a
ground-glass stopper.
4.8 Immersion Liquid—Kerosine has been found to be a good wetting vehicle for most pigments, and shall be used generally
as the immersion liq
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.