ASTM C631-09(2020)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Bonding Compounds for Interior Gypsum Plastering
Standard Specification for Bonding Compounds for Interior Gypsum Plastering
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the minimum requirements for bonding compounds used in adhering interior gypsum plasters to structurally sound surfaces. The bonding compound should be a tinted film-forming material suitable for application by brush, roller, and spray. It shall have a non-oxidizing, non-toxic, and non-flammable composition, and have a smooth, homogeneous, and flexible consistency with no settling of the solids. It shall also be free of foreign matter, and shall not be noticeably affected by mild acid or alkali. The apparatus needed for the preparation of the compound are moist cabinet, forced drift type oven, freezer, balance, timing device, tamper, steel straight edge, metal-bladed spatula, paint brush, briquet testing machine, briquet molds, divider, and clips. Specimens shall be sampled, tested, and conform accordingly to the following performance requirements: bonding capability; degradation; high temperature stability; freeze-thaw stability, and bond strength.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers minimum requirements for bonding compounds for adhering interior gypsum plaster to structurally sound surfaces.
1.2 This specification also covers test methods for determining performance requirements and physical properties.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C631 −09 (Reapproved 2020)
Standard Specification for
Bonding Compounds for Interior Gypsum Plastering
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C631; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Moist Rooms, and Water Storage Tanks Used in the
Testing of Hydraulic Cements and Concretes
1.1 This specification covers minimum requirements for
bonding compounds for adhering interior gypsum plaster to
3. Terminology
structurally sound surfaces.
3.1 Definitions:
1.2 Thisspecificationalsocoverstestmethodsfordetermin-
3.1.1 Fordefinitionsrelatingtogypsumandrelatedbuilding
ing performance requirements and physical properties.
materials and systems, see Terminology C11.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical 4. Physical Properties
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
4.1 General—The bonding compound shall be a film
and are not considered standard.
forming, non-oxidizing, non-toxic, non-flammable composi-
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
tion suitable for application by brush, roller, and spray. The
testmethodsdescribedinthisspecification: This standard does
compound shall be tinted to show, by visual inspection, where
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
ithasbeenapplied.Thetintingmaterialshallnotshowthrough
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
the material being bonded. The surfaces to which bonding
standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environ-
compounds are applied shall be relatively smooth, clean, and
mental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
dry. Surface coatings shall be removed if their nature indicates
limitations prior to use. an unsatisfactory condition. Surfaces shall be prepared in
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
accordance with the manufacturer’s directions.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4.2 Consistency—The bonding compound shall be of a
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
homogeneous nature with no settling of the solids. The
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
compound shall be free of foreign matter, and when applied in
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
accordance with the manufacturer’s directions, shall cover
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
evenly.
4.3 Film Characteristics—A dry film of the bonding com-
2. Referenced Documents
pound shall be uniform and smooth and shall remain flexible.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Thefilmshallnotbenoticeablyaffectedbymildacidoralkali.
C11Terminology Relating to Gypsum and Related Building
Materials and Systems
5. Performance Requirements
C28/C28MSpecification for Gypsum Plasters
5.1 Bonding Capability—A dry film of bonding compound
C472Test Methods for Physical Testing of Gypsum, Gyp-
shall be capable of bonding gypsum plaster immediately after
sum Plasters and Gypsum Concrete
drying and ten days after drying when tested as specified in
C511Specification for Mixing Rooms, Moist Cabinets,
Section 12.
5.2 Degradation—Bonding compound that separates shall
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C11 on
beabletobere-mixedtoauniformconsistencywhentestedas
GypsumandRelatedBuildingMaterialsandSystemsandisthedirectresponsibility
specified in Section 10.
of Subcommittee C11.02 on Specifications and Test Methods for Accessories and
Related Products.
5.3 High Temperature Stability—The bond strength shall be
Current edition approved April 1, 2020. Published April 2020. Originally
not less than 20 psi (138 kPa) when tested as specified in
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as C631–09(2014).
Section 9.
DOI: 10.1520/C0631-09R20.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
5.4 Freeze-thaw Stability—The bond strength shall be not
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
less than 20 psi (138 kPa) when tested as specified in Section
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 11.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
C631 − 09 (2020)
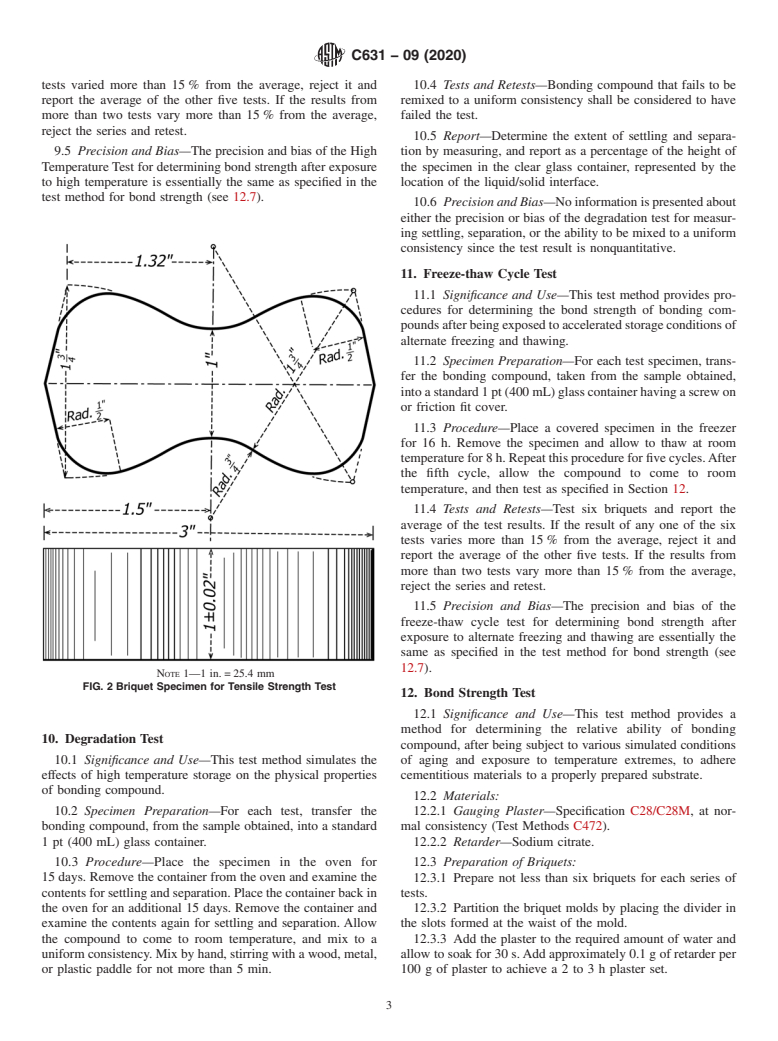
5.5 Bond Strength—Bond strength of a fresh sample or a 7.11 Briquet Molds—The molds for making test specimens
30-day-oldsampleshallbenotlessthan20psi(138kPa)when shall be made of metal not attacked by the plaster mortar and
tested as specified in Section 12. shall have sufficient material in the sides to prevent spreading
during molding. Gang molds, when used, shall be of the type
6. Sampling
shown in Fig. 1. The dimensions of the briquet molds shall
conform to the following requirements: width of mold, be-
6.1 Take a sample of not less than 1 kg from each shipment
tween inside faces, at waist line of the briquet, 1 in. (25.4 mm)
or consignment for analysis and tests. Except in special cases,
with permissible variations of 60.01 in. (0.25 mm) for molds
take the sample from not less than three separate containers,
in use and 60.005 in. (0.13 mm) for new molds; thickness of
chosen at random. In addition, take samples from containers
moldsmeasuredatthepointofgreatestthicknessoneitherside
that appear to be nonrepresentative, and test separately. Imme-
of the mold at the waist line, 1 in. (25.4 mm) with permissible
diately place the samples in airtight glass containers and
variations of+0.004 in. (0.10 mm) and−0.002 in. (0.05 mm)
transport to the testing laboratory in these containers. Take
for new molds and−0.02 in. (0.5 mm) for molds in use. The
precautions to reduce evaporation or drying to a minimum.
inside faces at the waist line shall have a vertical slot 0.03 in.
Thoroughly mix the bonding compound in the container if
(0.75 mm) wide by 0.06 in. (1.5 mm) deep to accept the
there is a tendency for liquid phase separation.
divider. The briquet specimens shall conform to the dimen-
sional requirements shown in Fig. 2.
7. Apparatus
7.12 Divider—Sheet brass 0.02 in. (0.05 mm) thick, 1.1 in.
7.1 Moist Cabinet—Specification C511.
(27.8 mm) wide by 1 in. (25.4 mm) high.
7.2 Oven—A forced draft type oven, having a temperature
7.13 Clips for Briquet Testing Machine—The clips for
controlledat140 65°F(60 63°C)forhightemperaturetests
holding the tension test specimen shall be in accordance with
and 100 6 5°F (38 6 3°C) for drying of the briquets.
Fig. 3.
7.3 Freezer—A freezer having a controlled temperature
of–10 6 2°F (–23 6 1°C).
8. Conditioning
7.4 Balance—Abalancecapableofweighingatleast2500g
8.1 Room Temperature and Humidity—Maintain the air
at a precision of 0.1 g.
temperature in the vicinity of the mixing and testing area,
7.5 Timing Device—Astandard clock or watch with second 70 6 5 °F (21 6 3 °C). Maintain the relative humidity
hand.
at50 62%.
7.6 Tamper—A tamper made up of a nonabsorptive,
8.2 Temperature of the Mixing Water—72 62°F
nonabrasive, non-brittle material and having a cross section of (22 61°C).
⁄2 by 1 in. (13 by 25 mm) and approximately 5 to 6 in. (130 to
150 mm) long. The tamping face shall be flat and at right 9. High Temperature Test
angles to the length of the tamper.
9.1 Significance and Use—This test method provides pro-
7.7 Straight Edge—A steel straight edge not less than 4 in. cedures for evaluating the bond strength of adhesives after
(100mm)longandnotlessthan ⁄16in.(1.6mm)normorethan being exposed to accelerated aging at high temperature.
⁄8 in. (3.2 mm) in thickness.
9.2 Specimen Preparation—Foreachtestspecimen,transfer
7.8 Spatula—Aspatulawithametalblade6in.(150mm)in the bonding compound, taken from the sample obtained, into a
length and ⁄2 in. (13 mm) in width, with straight edges. standard 1 pt (400 mL) glass container.
7.9 Paint Brush—Astandard1in.(25mm)widebrush,with 9.3 Procedure—Place the specimen in the oven for 30 days.
natural or synthetic bristles. Remove the container, allow the compound to cool to room
temperature, mix the compound to a uniform consistency, and
7.10 Testing Machine—Any type that is of sufficient capac-
test as specified in Section 12.
ity and that is capable of applying the load continuously and
without shock at the rate of 0.05 in. (1.27 mm)/min, with 9.4 Test and Retests—Test six briquets and report the
provision for adjustment of the rate of loading. average of the test results. If the result of any one of the six
FIG. 1 Briquet Gang Mold
C631 − 09 (2020)
tests varied more than 15% from the average, reject it and 10.4 Tests and Retests—Bonding compound that fails to be
report the average of the other five tests. If the results from remixed to a uniform consistency shall be considered to have
more than two tests vary more than 15% from the average, failed the test.
reject the series and retest.
10.5 Report—Dete
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.