ASTM E844-09
(Guide)Standard Guide for Sensor Set Design and Irradiation for Reactor Surveillance, E 706(IIC)
Standard Guide for Sensor Set Design and Irradiation for Reactor Surveillance, E 706(IIC)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
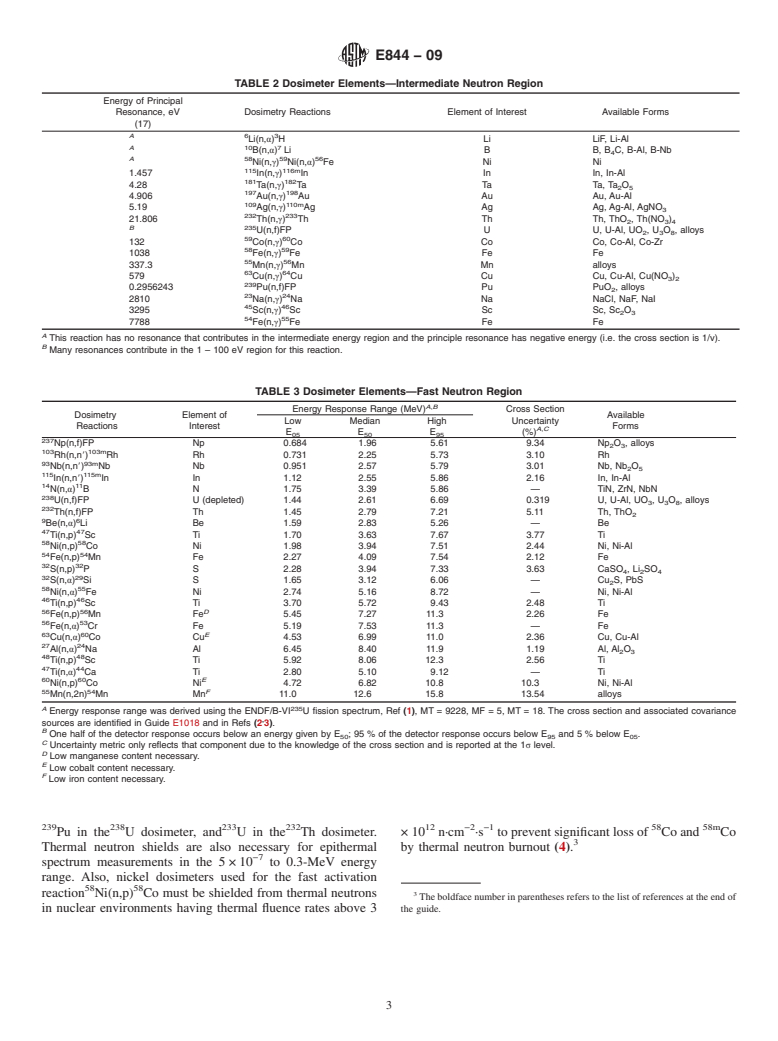
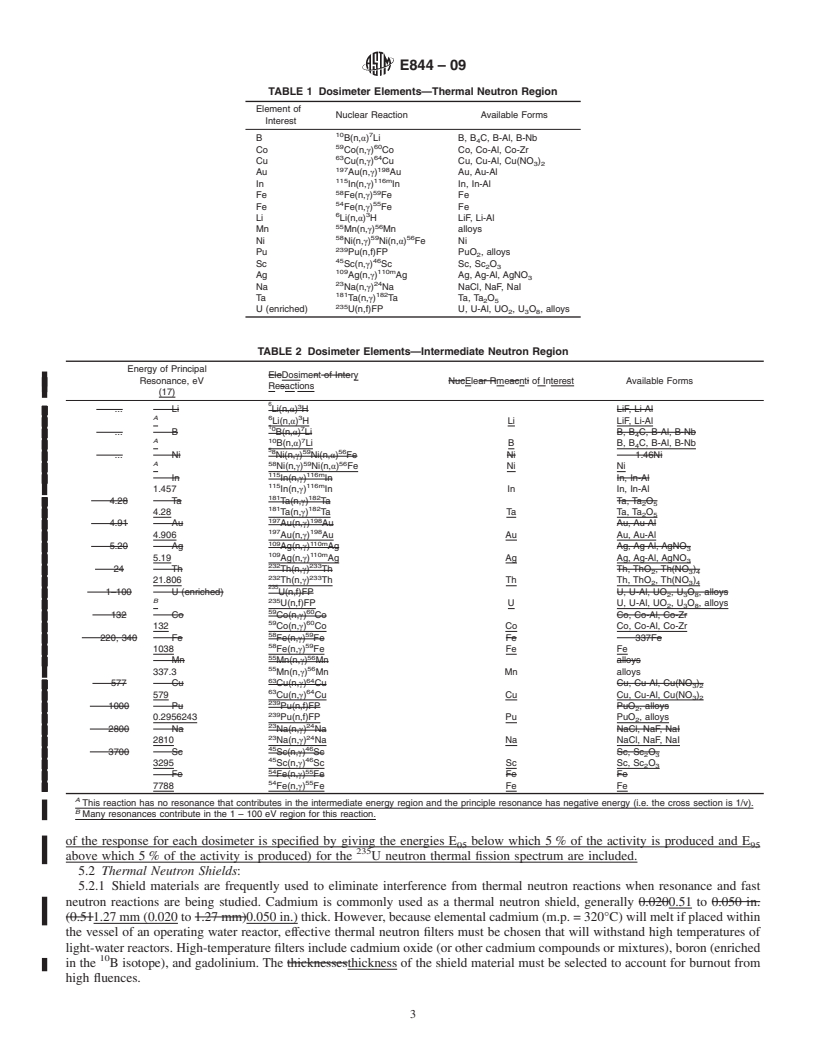
In neutron dosimetry, a fission or non-fission dosimeter, or combination of dosimeters, can be used for determining a fluence-rate, fluence, or neutron spectrum, or both, in nuclear reactors. Each dosimeter is sensitive to a specific energy range, and, if desired, increased accuracy in a fluence-rate spectrum can be achieved by the use of several dosimeters each covering specific neutron energy ranges.
A wide variety of detector materials is used for various purposes. Many of these substances overlap in the energy of the neutrons which they will detect, but many different materials are used for a variety of reasons. These reasons include available analysis equipment, different cross sections for different fluence-rate levels and spectra, preferred chemical or physical properties, and, in the case of radiometric dosimeters, varying requirements for different half-life isotopes, possible interfering activities, and chemical separation requirements.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers the selection, design, irradiation, post-irradiation handling, and quality control of neutron dosimeters (sensors), thermal neutron shields, and capsules for reactor surveillance neutron dosimetry.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E844 − 09
StandardGuide for
Sensor Set Design and Irradiation for Reactor Surveillance,
1
E 706 (IIC)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E844; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E2005Guide for Benchmark Testing of Reactor Dosimetry
in Standard and Reference Neutron Fields
1.1 This guide covers the selection, design, irradiation,
E2006GuideforBenchmarkTestingofLightWaterReactor
post-irradiation handling, and quality control of neutron do-
Calculations
simeters (sensors), thermal neutron shields, and capsules for
reactor surveillance neutron dosimetry.
3. Terminology
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1 Definitions:
standard. Values in parentheses are for information only.
3.1.1 neutron dosimeter, sensor, monitor—a substance irra-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
diated in a neutron environment for the determination of
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
neutron fluence rate, fluence, or spectrum, for example: radio-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
metricmonitor(RM),solidstatetrackrecorder(SSTR),helium
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
accumulation fluence monitor (HAFM), damage monitor
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
(DM), temperature monitor (TM).
3.1.2 thermal neutron shield—a substance (that is,
2. Referenced Documents
cadmium, boron, gadolinium) that filters or absorbs thermal
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
neutrons.
E170Terminology Relating to Radiation Measurements and
3.2 For definitions or other terms used in this guide, refer to
Dosimetry
Terminology E170.
E261Practice for Determining Neutron Fluence, Fluence
Rate, and Spectra by Radioactivation Techniques
4. Significance and Use
E854Test Method for Application and Analysis of Solid
State Track Recorder (SSTR) Monitors for Reactor
4.1 In neutron dosimetry, a fission or non-fission dosimeter,
Surveillance, E706(IIIB)
or combination of dosimeters, can be used for determining a
E910Test Method for Application and Analysis of Helium
fluence-rate, fluence, or neutron spectrum, or both, in nuclear
Accumulation Fluence Monitors for Reactor Vessel
reactors.Eachdosimeterissensitivetoaspecificenergyrange,
Surveillance, E706 (IIIC)
and, if desired, increased accuracy in a fluence-rate spectrum
E1005Test Method for Application and Analysis of Radio-
canbeachievedbytheuseofseveraldosimeterseachcovering
metric Monitors for Reactor Vessel Surveillance, E 706
specific neutron energy ranges.
(IIIA)
4.2 Awide variety of detector materials is used for various
E1018Guide for Application of ASTM Evaluated Cross
purposes. Many of these substances overlap in the energy of
Section Data File, Matrix E706 (IIB)
the neutrons which they will detect, but many different
E1214Guide for Use of Melt Wire Temperature Monitors
materials are used for a variety of reasons. These reasons
for Reactor Vessel Surveillance, E 706 (IIIE)
include available analysis equipment, different cross sections
fordifferentfluence-ratelevelsandspectra,preferredchemical
or physical properties, and, in the case of radiometric
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E10 on Nuclear
Technology and Applicationsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee dosimeters, varying requirements for different half-life
E10.05 on Nuclear Radiation Metrology.
isotopes, possible interfering activities, and chemical separa-
Current edition approved June 1, 2009. Published June 2009. Originally
tion requirements.
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as E844–03. DOI:
10.1520/E0844-09.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 5. Selection of Neutron Dosimeters and Thermal Neutron
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Shields
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 5.1 Neutron Dosimeters:
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E844 − 09
5.1.1 The choice of dosimeter material depends largely on 5.1.7 In thermal reactors the correction for neutron self
the dosimetry technique employed, for example, radiometric shielding can be appreciable for dosimeters that have highly
monitors, helium accumulation monitors, track recorders, and absorbing resonances (see 6.1.1).
damagemonitors.Atthepresenttime,thereisawidevarietyof 5.1.8 Dosimeters that produce activa
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:E 844–86 (Reapproved 1991) Designation: E844 – 09
Standard Guide for
Sensor Set Design and Irradiation for Reactor Surveillance,
1
E 706 (IIC)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E844; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (ϵ) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide covers the selection, design, irradiation, post-irradiation handling, and quality control of neutron dosimeters
(sensors), thermal neutron shields, and capsules for reactor surveillance neutron dosimetry.
1.2 The values stated in inch-poundSI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values givenValues in parentheses are for
information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E170 Terminology Relating to Radiation Measurements and Dosimetry
E261 Practice for Determining Neutron Fluence, Fluence Rate, Fluence, and Spectra by Radioactivation Techniques
E854 Test Method for Application and Analysis of Solid State Track Recorder (SSTR) Monitors for Reactor Surveillance, E
2
706(IIIB) E706(IIIB)
E910 Test Method forApplication andAnalysis of HeliumAccumulation Fluence Monitors for ReactorVessel Surveillance, E
2
706(IIIC) E706 (IIIC)
2
E1005 Test Method forApplication andAnalysis of Radiometric Monitors for Reactor Vessel Surveillance, E 706(IIIA) Test
Method for Application and Analysis of Radiometric Monitors for Reactor Vessel Surveillance, E 706 (IIIA)
E1018 Guide for Application of ASTM Evaluated Cross Section Data File, Matrix E706 (IIB)
E706(IIID)Analysis of Damage Monitors for Reactor Vessel Surveillance 1214 Guide for Use of Melt Wire Temperature
Monitors for Reactor Vessel Surveillance, E 706 (IIIE)
3
E706(IIIE)Analysis of Temperature Monitors for Reactor Vessel Surveillance 2005 Guide for Benchmark Testing of Reactor
Dosimetry in Standard and Reference Neutron Fields
3
E706(IIE)Benchmark Testing of Reactor Vessel Dosimetry 2006 Guide for Benchmark Testing of Light Water Reactor
Calculations
3. Terminology Definitions
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 neutron dosimeter, sensor, monitor—a substance irradiated in a neutron environment for the determination of neutron
fluencerate,fluence,orspectrum,forexample:radiometricmonitor(RM),solidstatetrackrecorder(SSTR),heliumaccumulation
fluence monitor (HAFM), damage monitor (DM), temperature monitor (TM).
3.1.2 thermal neutron shield—a substance (that is, cadmium, boron, gadolinium) that filters or absorbs thermal neutrons.
3.3For3.2 For definitions or other terms used in this guide, refer to Terminology E 170E170.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 In neutron dosimetry, a fission or non-fission dosimeter, or combination of dosimeters, can be used for determining a
fluence-rate, fluence, or neutron spectrum, or both, in nuclear reactors. Each dosimeter is sensitive to a specific energy range, and,
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E-10 E10 on Nuclear Technology and Applications and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E10.05
on Nuclear Radiation Metrology.
ϵ2
Current edition approved Oct. 31, 1986. Published December 1986. Originally published as E 844–81. Last previous edition E 844–81 .
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2009.PublishedJune2009.Originallyapprovedin1981.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2003asE844–03.DOI:10.1520/E0844-09.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
, Vol 12.02.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E844 – 09
if desired, increased accuracy in a fluxence-rate spectrum can be achieved by the use of several dosimeters each covering specific
neutron energy ranges.
4.2 A wide variety of detector materials is used for various purposes. Many of these substances overlap in the energy of the
neutrons which they will detect, but many different materials are used for a variety of rea
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.