ISO 703:1975
(Main)Conveyor belts — Troughability — Characteristic and method of test
Conveyor belts — Troughability — Characteristic and method of test
Courroies transporteuses — Aptitude à la mise en auge — Caractéristique et méthode d'essai
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD 703
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANOAROIZATION .METnLHAPOnHM OPrAHM3AUMR no CTAHLIAPTM3AUMM .ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Conveyor belts - Troughability - Characteristic and
method of test
Courroies transporteuses - Aptitude à la mise en auge - Caractéristique et méthode d'essai
First edition - 1975-05-01
I
w UDC 621.867.212.3/.5 : 620.11 Ref. No. IS0 703-1975 (E)
-
m IC
z
Descriptors : belts, conveyor belts, tests, bend tests, flexibility.
m
O
IC
s
Price based on 3 pages
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
FOREWORD
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation
of national standards institutes (IS0 Member Bodies). The work of developing
International Standards is carried out through IS0 Technical Committees. Every
Member Body interested in a subject for which a Technical Committee has been set
up has the right to be represented on that Committee. International organizations,
governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the Technical Committees are circulated
to the Member Bodies for approval before their acceptance as International
Standards by the IS0 Council.
Prior to 1972, the results of the work of the Technical Committees were published
as IS0 Recommendations; these documents are now in the process of being
transformed into International Standards. As part of this process, Technical
Committee ISO/TC 41 has reviewed IS0 Recommendation R 703 and found it
technically suitable for transformation. International Standard IS0 703 therefore
replaces IS0 Recommendation R 703-1968 to which it is technically identical.
IS0 Recommendation R 703 was approved by the Member Bodies of the following
countries :
Australia Egypt, Arab Rep. of South Africa, Rep. of
Austria Finland Spain
Belgium France Sweden
Brazil Germany Switzerland
Chile India Turkey
Czechoslovakia Italy United Kingdom
Denmark Japan Yugoslavia
The Member Body of the following country expressed disapproval of the
Recommendation on technical grounds :
Ireland
No Member Body disapproved the transformation of ISO/R 703 into an
International Standard.
O International Organization for Standardization, 1975
Printed in Switzerland
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
IS0 703-1975 (E)
I NTE RNATl ONA L STAN DARD
Conveyor belts - Troughability - Characteristic and
method of test
O INTRODUCTION
act vertically and the deflection of
The suspending forces
the test piece under gravity is unaffected by any other
A large number of conveyor belts work in the form of a
external force. The troughability is determined by
trough. If a belt is too stiff in the transverse direction, when
measuring the maximum deflection of the test piece under
empty it does not rest on the central idler roller. Its balance
its own weight and is expressed as the ratio of the
is then unstable and it is subject to lateral travel which may
deflection to the flat length of the test piece (i.e. the width
its destruction.
eventually cause
of the belt).
L
It is possible to make a section of the belt take on the shape
of a trough under its own weight, by suspending the section
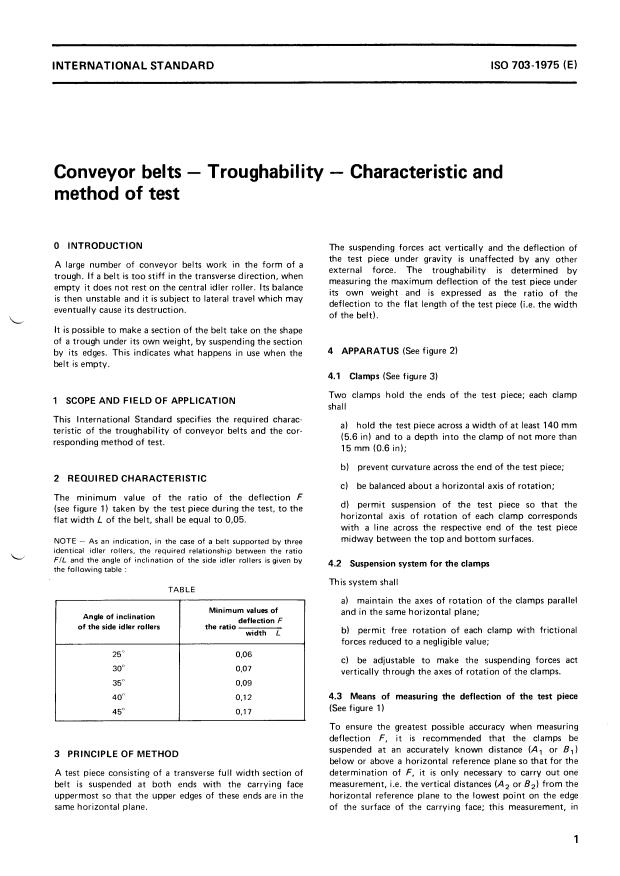
4 APPARATUS (See figure 2)
by its edges. This indicates what happens in use when the
belt is empty.
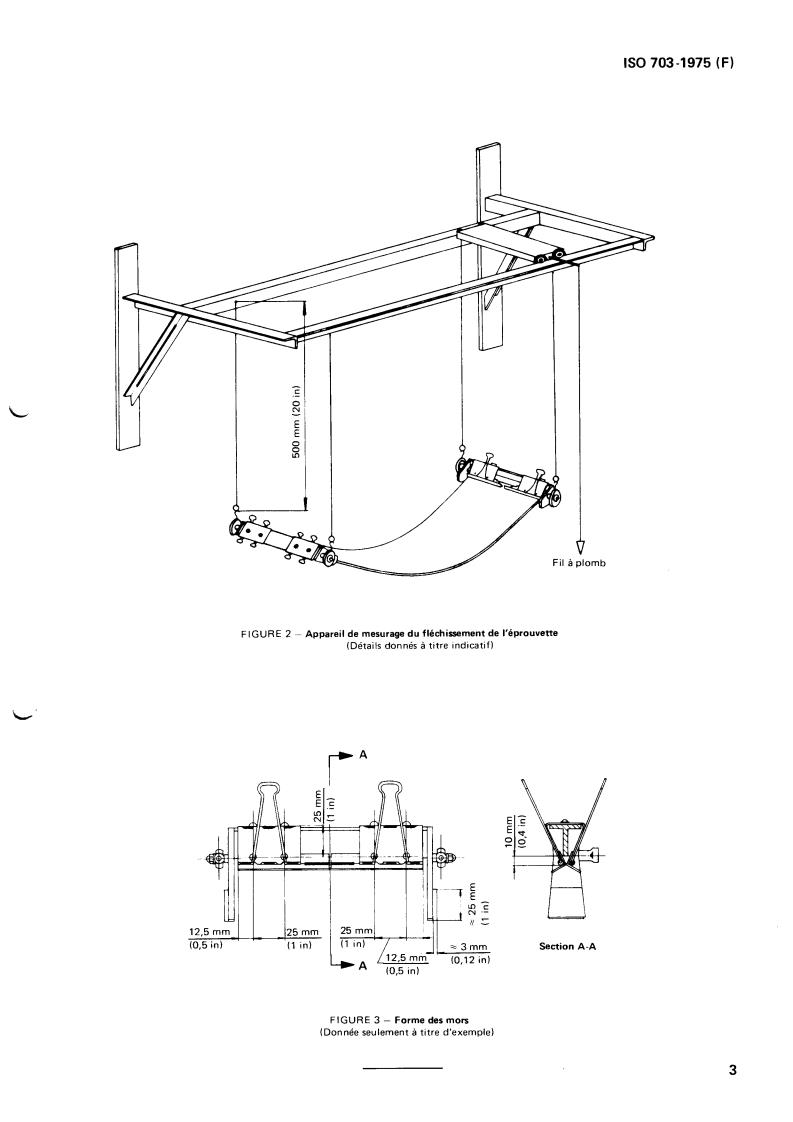
4.1 Clamps (See figure 3)
Two clamps hold the ends of the test piece; each clamp
1 SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION
shall
This International Standard specifies the required charac-
a) hold the test piece across a width of at least 140 mm
teristic of the troughability of conveyor belts and the cor-
(5.6 in) and to a depth into the clamp of not more than
responding method of test.
15 mm (0.6 in);
b) prevent curvature across the end of the test piece;
2 REQUIRED CHARACTERISTIC
c) be balanced about a horizontal axis of rotation;
The minimum value of the ratio of the deflection F
d) permit suspension of the test piece so that the
(see figure 1) taken by the test piece during the test, to the
horizontal axis of rotation of each clamp corresponds
flat width L of the belt, shall be equal to 0,05.
with a line across the respective end of t
...
@ 703
NORME INTERNATIONALE
‘*E&
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION -MEXnYHAPOnHAX OPrAH€43AUIII II0 CiAHLIAPTiISAUiIA .ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Courroies transporteuses - Aptitude à la mise en auge -
L
Caractéristique et méthode d’essai
Conveyor belts - Troughability - Characteristic and method of test
Première édition - 1975-05-01
CDU 621.867.212.3/.5 : 620.11 Réf. no : IS0 703-1975 (FI
Descripteurs : courroie. courroie transporteuse, essai, essai de flexion, flexibilité
m
O
O
2
Prix basé sur 3 pages
r.
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
IS0 703-1975 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Courroies transporteuses - Aptitude à la mise en auge -
Caractéristique et méthode d'essai
Les forces de suspension agissent verticalement et le
O INTRODUCTION
fléchissement de l'éprouvette sous l'effet de la pesanteur
Un grand nombre de courroies transporteuses travaillent en
n'est affecté par aucune autre force extérieure. L'aptitude à
forme d'auge. Si une courroie est trop raide dans le sens
la mise en auge est déterminée en mesurant le fléchissement
transversal, elle ne s'appuie pas, à vide, sur le rouleau
maximal de l'éprouvette sous son propre poids, et elle est
médian. Elle se trouve alors en équilibre instable et se
exprimée par rapport à la longueur à plat de l'éprouvette
déporte latéralement, ce qui peut provoquer sa destruction.
(c'est-à-dire à la largeur de la courroie).
L
On peut, en suspendant par les bords un troncon de
à celui-ci une forme d'auge SOUS son
courroie, faire prendre
propre poids, ce aui donne une indication sur la position
4 APPAREILLAGE (Voir figure 2)
que prendrait en service, à vide, la courroie par rapport aux
augets.
4.1 Mors (Voir figure 3)
Deux mors soutiennent les extrémités de l'éprouvette;
1 OBJET ET DOMAINE D'APPLICATION
chaque mors doit
La présente Norme Internationale spécifie la caractéristique
a) maintenir l'éprouvette sur une largeur d'au moins
requise d'aptitude des courroies transporteuses à la mise en
140 mm (5.6 in) et sur une profondeur dans le mors
auge, et la méthode d'essai correspondante.
n'excédant pas
...


Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.