ISO 582:1979
(Main)Rolling bearings - Metric series - Chamfer dimension limits
Rolling bearings - Metric series - Chamfer dimension limits
Roulements — Séries métriques — Dimensions limites des arrondis
General Information
Relations
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 582:1979 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Rolling bearings - Metric series - Chamfer dimension limits". This standard covers: Rolling bearings - Metric series - Chamfer dimension limits
Rolling bearings - Metric series - Chamfer dimension limits
ISO 582:1979 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 21.100.20 - Rolling bearings. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 582:1979 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to SIST ISO 582:1995, ISO 582:1995. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
You can purchase ISO 582:1979 directly from iTeh Standards. The document is available in PDF format and is delivered instantly after payment. Add the standard to your cart and complete the secure checkout process. iTeh Standards is an authorized distributor of ISO standards.
Standards Content (Sample)
International Standard @ 582
~~
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANOARDlZATlON*MEXL1YHAPOllHAR OPrAHH3AUMR no CTAHllAPTH3AUMH.ORGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
U Rolling bearings - Metric series - Chamfer dimension
limits
Roulements - Séries métriques - Dimensions limites des arrondis
Second edition - 1979-10-15
- UDC 621.822.61.8 Ref. No. IS0 582-1979 (El
Lu
-
m Descriptors : bearings, rolling bearings, bevelling, shafts (machine elements), dimensions, limits
E
Price based on 4 pages
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national standards institutes (IS0 member bodies). The work of developing Inter-
national Standards is carried out through IS0 technical committees. Every member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been set up has the
right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council.
International Standard IS0 582 was developed by Technical Committee ISO/TC 4,
Rolling bearings, and was circulated to the member bodies in September 1978.
It has been approved by the member bodies of the following countries :
Hungary Romania
Australia
Austria India South Africa, Rep. of
Belgium Italy Sweden
Brazil Japan Switzerland
Canada Korea, Dem. P. Rep. of United Kingdom
Korea, Rep. of USA
Chile
China Libyan Arab Jamahiriya USSR
Czechoslovakia Mexico Yugoslavia
Netherlands
France
.-
Germany, F. R. Poland
No member body expressed disapproval of the document.
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition (i.e. IS0 582-1972)
Q International Organization for Standardization, 1979 O
Printed in Switzerland
IS0 582-1979 (E)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
Rolling bearings - Metric series - Chamfer dimension
limits
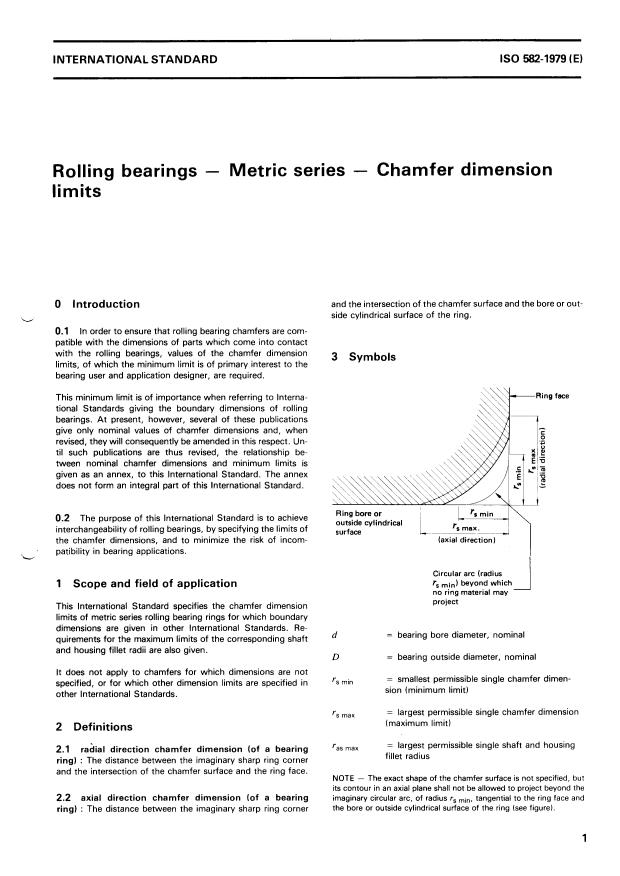
O Introduction and the intersection of the chamfer surface and the bore or out-
side cylindrical surface of the ring.
U
0.1 In order to ensure that rolling bearing chamfers are com-
patible with the dimensions of parts which come into contact
with the rolling bearings, values of the chamfer dimension
3 Symbols
limits, of which the minimum limit is of primary interest to the
bearing user and application designer, are required.
This minimum limit is of importance when referring to Interna-
tional Standards giving the boundary dimensions of rolling
bearings. At present, however, several of these publications
give only nominal values of chamfer dimensions and, when
revised, they will consequently be amended in this respect. Un-
til such publications are thus revised, the relationship be-
tween nominal chamfer dimensions and minimum limits is
given as an annex, to this International Standard. The annex
does not form an integral part of this International Standard.
Ring bore or
0.2 The purpose of this International Standard is to achieve
outside cylindrical
interchangeability of rolling bearings, by specifying the limits of
surface
(axial direction)
the chamfer dimensions, and to minimize the risk of incom-
~ patibility in bearing applications.
W
I
Circular arc (radius
rs beyond which
1 Scope and field of application
no ring material may
project
This International Standard specifies the chamfer dimension
limits of metric series rolling bearing rings for which boundary
dimensions are given in other International Standards. Re-
d = bearing bore diameter, nominal
quirements for the maximum limits of the corresponding shaft
and housing fillet radii are also given.
D = bearing outside diameter, nominal
It does not apply to chamfers for which dimensions are not
= smallest permissible single chamfer dimen-
rs min
specified, or for which other dimension limits are specified in
Sion (minimum limit)
other International Standards.
= largest permissible single chamfer dimension
rs max
(maximum limit)
2 Definitions
= largest permissible single shaft and housing
‘as max
2.1 radial direction ch
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION*ME)K/3YHAPO/lHAR OPrAHHJAUHR il0 CTAH/lAPTH3AUHH~RGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Roulements - Séries métriques - Dimensions limites des
L
arrondis
Rolling bearings - Metric series - Chamfer dimension limits
Deuxième édition - 1979-10-15
- CDU 621.822.6/ .8 Réf. no : IS0 582-1979 (FI
k
m PI Descripteurs : palier, roulement, biseautage, arbre de machine, dimension, limite
c!
n
s Prix basé sur 4 pages
Avant-propos
L'ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d'organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I'ISO). L'élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I'ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I'ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I'ISO.
La Norme internationale IS0 582 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 4,
Roulements, et a été soumise aux comités membres en septembre 1978.
Les comités membres des pays suivants l'ont approuvée :
Corée, Rép. de Roumanie
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d'
Allemagne, R. F. France Royaume-Uni
Australie Hongrie Suède
Inde Suisse
Autriche
Belgique Italie Tchécoslovaquie
Brésil URSS
Japon
Canada Jamahiriya arabe libyenne USA
Chili Mexique Yougoslavie
Chine Pays-Bas
Corée, Rép. dém. p. de Pologne
Aucun comité membre ne l'a désapprouvée.
Cette deuxième édition annule et remplace la première édition (IS0 582-1972).
O Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1979 0
Imprimé en Suisse
IS0 582-1979 (FI
NORM E I NTER NAT1 ON ALE
Roulements - Séries métriques - Dimensions limites des
arrondis
O Introduction 2.2 dimension axiale de l'arrondi : Distance mesurée de
L
l'arête vive virtuelle à l'intersection de la surface de l'arrondi
0.1 Pour coter correctement les arrondis d'un roulement et
avec l'alésage ou avec la surface extérieure cylindrique de la
les pièces qui viennent en contact avec lui, il est nécessaire de bague.
connaître la valeur des dimensions limites des arrondis et,
notamment, la dimension minimale qui intéresse en tout pre-
mier lieu l'utilisateur de roulements et celui qui en étudie les
3 Symboles
applications.
.\ ' ' ]-Face de la bague
Cette dimension minimale sert de référence entre la présente
Norme internationale et les diverses publications IS0 qui don-
nent les dimensions d'encombrement des roulements. Toute-
fois, plusieurs de ces publications indiquent encore la dimen-
sion nominale des arrondis; elles seront, par conséquent, mises
à jour lors d'une prochaine révision. D'ici là, il a semblé utile de
donner en annexe, la correspondance existant entre les dimen-
sions nominales et minimales des arrondis. Cette annexe ne fait
pas partie intégrante de la présente Norme internationale.
Alésageousurface ~
0.2 Le but de la présente Norme internationale est d'assurer
extérieure cylindrique ,
l'interchangeabilité des roulements du point de vue de leurs
--- Lrmax ~ 2
de la bague
(direction axiale)
arrondis en précisant leurs dimensions limites et de réduire les
W
risques d'erreur de cotation dans les applications des roule-
ments.
Arc de cercle
(de rayon r, mini
au maximum de matière
1 Objet et domaine d'application
d = diamètre nominal d'alésage
La présente Norme internationale fixe les dimensions limites
des arrondis des bagues de roulements, séries métriques, figu- D = diamètre extérieur nominal du roulement
rant dans les publications EO. Elle définit également le rayon
= plus petite dimension isolée admise de
maximal correspondant des congés d'arbre et de logement.
rs min
l'arrondi
La présente Norme internationale ne s'applique pas aux arron-
dis des roulements dont les dimensions ne sont pas normali- = plus grande dimension isolée admise de
rs max
sées, ou pour lesquels d'autres dimensions limites sont don- l'arrondi
nées dans les publications IS0 y relatives.
= rayon isolé maximal admis des congés
'as rnax
d'arbre et de logement
2 Définitions
NOTE - La forme exacte de la surface de l'arrondi n'est pas fixée;
cependant, sa trace dans un plan axial doit se
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...