ASTM F1427-21
(Specification)Standard Consumer Safety Specification for Bunk Beds
Standard Consumer Safety Specification for Bunk Beds
SCOPE
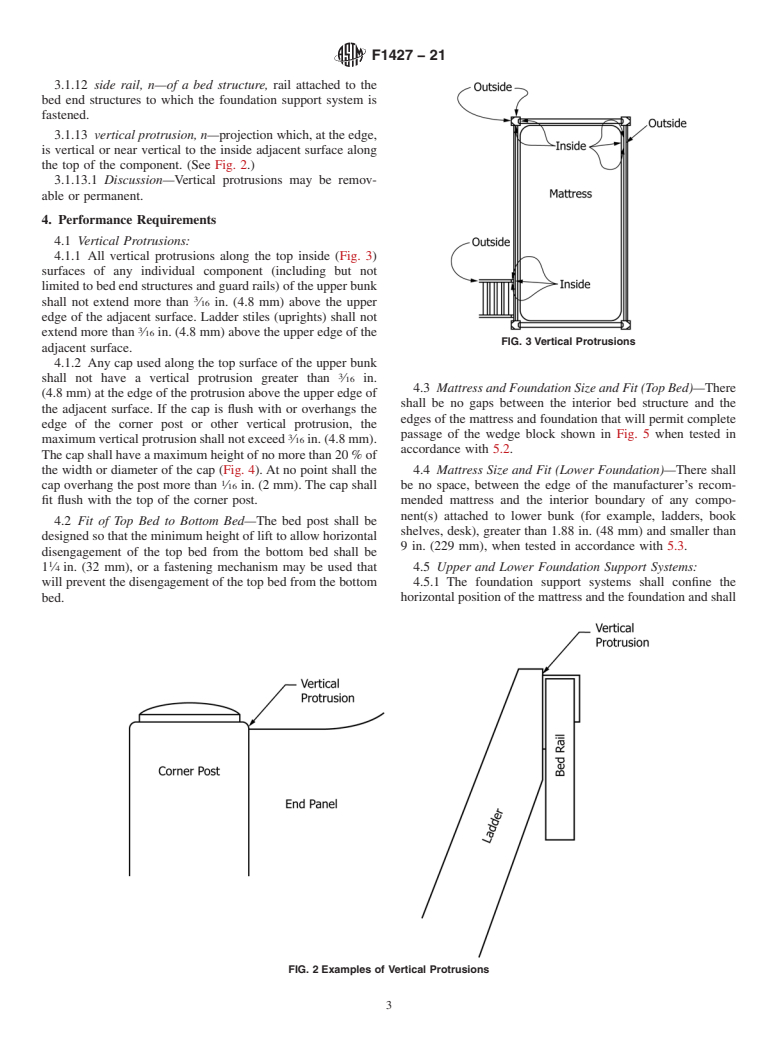
1.1 This consumer safety specification establishes minimum requirements for the design and performance of bunk beds. It also contains requirements for labeling and instructional material.
1.2 This consumer safety specification is intended to minimize accidents to children resulting from normal use and reasonably foreseeable misuse or abuse of bunk beds. This consumer safety specification is written within the current state of the art of bunk bed technology and does not address bunk beds that are blatantly misused or are used in a careless manner that disregards warning statements and safety instructions provided with each bunk bed.
1.3 For the purpose of this consumer safety specification, a bunk bed (hereinafter referred to as a bed) is defined as any structure that includes at least one sleeping surface in which the underside of any of its foundations is over 30 in. (762 mm) from the floor.
1.4 This consumer safety specification does not address bunk beds for institutional use (for example, in prisons, military facilities, dormitories, and so forth).
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units, as well as any specified ISO/ANSI standard hardware, are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 5, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1427 −21
Standard Consumer Safety Specification for
1
Bunk Beds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1427; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This consumer safety specification addresses bunk bed accidents that were identified by the U.S.
Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC).
The CPSC estimates that in 1989, about 34 000 bunk bed-related injuries were treated in U.S.
hospital emergency rooms, and about three fourths of those injured were under the age of 15. Most
of these injuries were minor and were associated with victims who fell from, bumped into, or jumped
from bunk beds. However, there are other less-obvious potentially serious hazards associated with
bunk beds. For example, from 1973 through November 1990, CPSC also received reports of 83 deaths
of children less than 15 years of age involving bunk beds. Seventy-four incidents, including 17 deaths,
involved children who reportedly became entrapped between the mattress and guardrail; 24 incidents,
including five deaths, involved children who reportedly became entrapped either between the mattress
and bed structure or in the bed end structure; and 18 incidents, including 16 deaths, involved young
children who reportedly became entrapped between the bed and the wall. The CPSC also received
reports of four deaths due to failure of the mattress support, 19 deaths due to falls from bunk beds,
twelve deaths due to strangulation when a belt, rope, or clothing became caught on the bed structure,
and ten deaths due to other or unknown causes.
1. Scope structurethatincludesatleastonesleepingsurfaceinwhichthe
underside of any of its foundations is over 30 in. (762 mm)
1.1 Thisconsumersafetyspecificationestablishesminimum
from the floor.
requirements for the design and performance of bunk beds. It
also contains requirements for labeling and instructional ma-
1.4 This consumer safety specification does not address
terial.
bunk beds for institutional use (for example, in prisons,
1.2 This consumer safety specification is intended to mini- military facilities, dormitories, and so forth).
mize accidents to children resulting from normal use and
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units, as well as any
reasonably foreseeable misuse or abuse of bunk beds. This
specified ISO/ANSI standard hardware, are to be regarded as
consumer safety specification is written within the current state
the standard. The values given in parentheses are for informa-
of the art of bunk bed technology and does not address bunk
tion only.
beds that are blatantly misused or are used in a careless manner
that disregards warning statements and safety instructions
1.6 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
provided with each bunk bed.
test methods portion, Section 5, of this specification: This
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
1.3 For the purpose of this consumer safety specification, a
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
bunk bed (hereinafter referred to as a bed) is defined as any
of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and
environmental practices and determine the applicability of
1
This consumer safety specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Commit-
regulatory limitations prior to use.
tee F15 on Consumer Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F15.30 on Bunk Beds.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
Current edition approved April 1, 2021. Published April 2021. Originally
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as F1427 – 19. DOI:
10.1520/F1427-21. ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1427−21
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- 3. Terminology
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.1.1 bed, n—for the purpose of this specification, a bunk
bed, as described in 3.1.5.
2. Referenced Documents
2
3.1.2 bed end structure, n—upright unit at the head and foot
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of the bed, to which the side rails attach.
D3359 Test Methods for Rating Adhesion by Tape Test
3
2.2 Federal Standards:
3.1.3 bed post, n—upright post at each corner of the bed
16CFRPart1303 BanofLead-ContainingPaintandCertain
stru
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F1427 − 19 F1427 − 21
Standard Consumer Safety Specification for
1
Bunk Beds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1427; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This consumer safety specification addresses bunk bed accidents that were identified by the U.S.
Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC).
The CPSC estimates that in 1989, about 34 000 bunk bed-related injuries were treated in U.S.
hospital emergency rooms, and about three fourths of those injured were under the age of 15. Most
of these injuries were minor and were associated with victims who fell from, bumped into, or jumped
from bunk beds. However, there are other less-obvious potentially serious hazards associated with
bunk beds. For example, from 1973 through November 1990, CPSC also received reports of 83 deaths
of children less than 15 years of age involving bunk beds. Seventy-four incidents, including 17 deaths,
involved children who reportedly became entrapped between the mattress and guardrail; 24 incidents,
including five deaths, involved children who reportedly became entrapped either between the mattress
and bed structure or in the bed end structure; and 18 incidents, including 16 deaths, involved young
children who reportedly became entrapped between the bed and the wall. The CPSC also received
reports of four deaths due to failure of the mattress support, 19 deaths due to falls from bunk beds,
twelve deaths due to strangulation when a belt, rope, or clothing became caught on the bed structure,
and ten deaths due to other or unknown causes.
1. Scope
1.1 This consumer safety specification establishes minimum requirements for the design and performance of bunk beds. It also
contains requirements for labeling and instructional material.
1.2 This consumer safety specification is intended to minimize accidents to children resulting from normal use and reasonably
foreseeable misuse or abuse of bunk beds. This consumer safety specification is written within the current state of the art of bunk
bed technology and does not address bunk beds that are blatantly misused or are used in a careless manner that disregards warning
statements and safety instructions provided with each bunk bed.
1.3 For the purpose of this consumer safety specification, a bunk bed (hereinafter referred to as a bed) is defined as any structure
that includes at least one sleeping surface in which the underside of any of its foundations is over 30 in. (762 mm) from the floor.
1.4 This consumer safety specification does not address bunk beds for institutional use (for example, in prisons, military facilities,
dormitories, and so forth).
1
This consumer safety specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F15 on Consumer Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F15.30
on Bunk Beds.
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2019April 1, 2021. Published December 2019April 2021. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 20132019
as F1427 – 13.F1427 – 19. DOI: 10.1520/F1427-19.10.1520/F1427-21.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1427 − 21
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units, as well as any specified ISO/ANSI standard hardware, are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 5, of this specification: This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D3359 Test Methods for Rating Adhesion by Tape Test
3
2.2 Federal Standards:
16 CFR Part 1
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.