ASTM D7237-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Free Cyanide with Flow Injection Analysis (FIA) Utilizing Gas Diffusion Separation and Amperometric Detection
Standard Test Method for Free Cyanide with Flow Injection Analysis (FIA) Utilizing Gas Diffusion Separation and Amperometric Detection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Cyanide and hydrogen cyanide are highly toxic. Regulations have been established to require the monitoring of cyanide in industrial and domestic wastes and surface waters.
It is useful to determine the aquatic free cyanide to establish an index of toxicity when a wastewater is introduced into the natural environment at a given pH and temperature.
This test method is applicable for natural water, saline waters, and wastewater effluent.
SCOPE
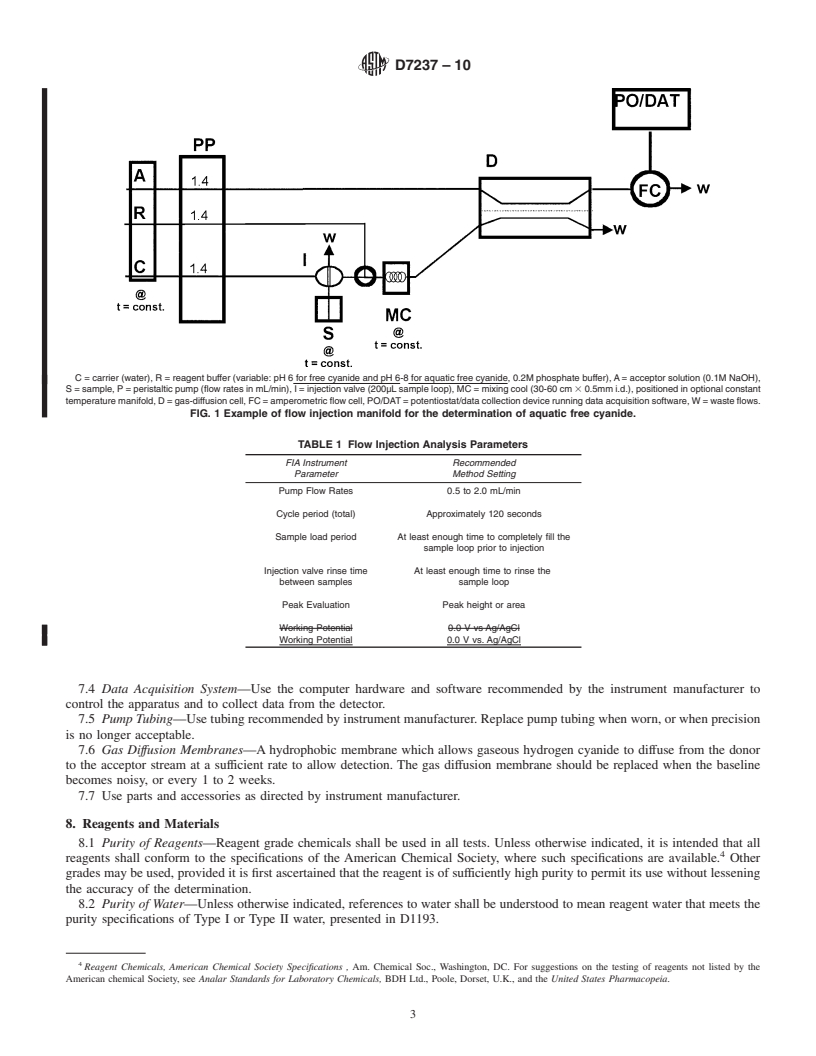
1.1 This test method is used to establish the concentration of free cyanide in an aqueous wastewater or effluent. The test conditions of this method are used to measure free cyanide (HCN and CN-) and cyanide bound in the metal-cyanide complexes that are easily dissociated into free cyanide ions at the pH of 6. Free cyanide is determined at pH 6 at room temperature. The aquatic free cyanide can be determined by matching the pH to the water in the receiving environment in the range of pH 6 to 8. The extent of HCN formation is less dependent on temperature than the pH; however, the temperature can be regulated if deemed necessary for aquatic free cyanide to further simulate the actual aquatic environment.
1.2 The free cyanide method is based on the same instrumentation and technology that is described in standard test method D6888, but employs milder conditions (pH 6-8 buffer versus HCl or H2SO4 in the reagent stream), and does not utilize ligand displacement reagents.
1.3 The aquatic free cyanide measured by this procedure should be similar to actual levels of HCN in the original aquatic environment. This in turn may give a reliable index of toxicity to aquatic organisms.
1.4 This procedure is applicable over a range of approximately 2 to 500 μg/L (parts per billion) free cyanide. Sample dilution may increase cyanide recoveries depending on the cyanide speciation; therefore, it is not recommended to dilute samples. Higher concentrations can be analyzed by increasing the range of calibration standards or with a lower injection volume. In accordance with Guide E1763 and Practice D6512 the lower scope limit was determined to be 9 μg/L for chlorinated gold leaching barren effluent water.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in 8.6 and Section 9.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D7237 −10
StandardTest Method for
Free Cyanide with Flow Injection Analysis (FIA) Utilizing
1
Gas Diffusion Separation and Amperometric Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7237; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 Thistestmethodisusedtoestablishtheconcentrationof
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
free cyanide in an aqueous wastewater or effluent. The test
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
conditions of this method are used to measure free cyanide
- bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
(HCN and CN ) and cyanide bound in the metal-cyanide
statements are given in 8.6 and Section 9.
complexes that are easily dissociated into free cyanide ions at
the pH of 6. Free cyanide is determined at pH 6 at room
2. Referenced Documents
temperature. The aquatic free cyanide can be determined by
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
matching the pH to the water in the receiving environment in
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
the range of pH 6 to 8. The extent of HCN formation is less
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
dependent on temperature than the pH; however, the tempera-
D1293 Test Methods for pH of Water
ture can be regulated if deemed necessary for aquatic free
D2036 Test Methods for Cyanides in Water
cyanide to further simulate the actual aquatic environment.
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
1.2 The free cyanide method is based on the same instru-
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
mentation and technology that is described in standard test
D3856 Guide for Management Systems in Laboratories
method D6888, but employs milder conditions (pH 6-8 buffer
Engaged in Analysis of Water
versus HCl or H SO in the reagent stream), and does not
2 4
D4841 Practice for Estimation of Holding Time for Water
utilize ligand displacement reagents.
Samples Containing Organic and Inorganic Constituents
1.3 The aquatic free cyanide measured by this procedure
D5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
should be similar to actual levels of HCN in the original
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
aquatic environment. This in turn may give a reliable index of
D6512 Practice for Interlaboratory Quantitation Estimate
toxicity to aquatic organisms.
D6696 Guide for Understanding Cyanide Species
D6888 Test Method for Available Cyanide with Ligand
1.4 This procedure is applicable over a range of approxi-
Displacement and Flow InjectionAnalysis (FIA) Utilizing
mately 2 to 500 µg/L (parts per billion) free cyanide. Sample
Gas Diffusion Separation and Amperometric Detection
dilution may increase cyanide recoveries depending on the
D7365 Practice for Sampling, Preservation and Mitigating
cyanide speciation; therefore, it is not recommended to dilute
Interferences in Water Samples for Analysis of Cyanide
samples. Higher concentrations can be analyzed by increasing
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
the range of calibration standards or with a lower injection
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
volume. In accordance with Guide E1763 and Practice D6512
E1763 Guide for Interpretation and Use of Results from
the lower scope limit was determined to be 9 µg/L for
Interlaboratory Testing of Chemical Analysis Methods
chlorinated gold leaching barren effluent water.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3. Terminology
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1 Definitions:
standard.
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
to Terminology D1129 and Guide D6696.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water
andisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.06onMethodsforAnalysisfor
2
Organic Substances in Water. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved May 1, 2010. Published June 2010. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2006. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as D7237 – 06. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D7237-10. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 -------
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D7237–06 Designation: D7237 – 10
Standard Test Method for
Aquatic Free Cyanide with Flow Injection Analysis (FIA)
Utilizing Gas Diffusion Separation and Amperometric
1
Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7237; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1This test method is used to establish the concentration of aquatic “free” cyanide in an aqueous wastewater or effluent. The
*
test conditions of this method are used to measure free cyanide (HCN and CN
1.1 This test method is used to establish the concentration of free cyanide in an aqueous wastewater or effluent. The test
-
conditions of this method are used to measure free cyanide (HCN and CN) and cyanide bound in the metal-cyanide complexes
that are easily dissociated into free cyanide ions at the pH of the aquatic environment ranging from pH 6 to pH 8. The extent of
HCN formation is less dependent on temperature than the pH; however, the temperature can be regulated if deemed necessary to
further simulate the actual aquatic environment.
1.2The aquatic free cyanide method is based on the same instrumentation and technology that is described in standard test
method ) and cyanide bound in the metal-cyanide complexes that are easily dissociated into free cyanide ions at the pH of 6. Free
cyanide is determined at pH 6 at room temperature. The aquatic free cyanide can be determined by matching the pH to the water
in the receiving environment in the range of pH 6 to 8. The extent of HCN formation is less dependent on temperature than the
pH; however, the temperature can be regulated if deemed necessary for aquatic free cyanide to further simulate the actual aquatic
environment.
1.2 The free cyanide method is based on the same instrumentation and technology that is described in standard test method
D6888, but employs milder conditions (pH 6-8 buffer versus HCl or H SO in the reagent stream), and does not utilize ligand
2 4
displacement reagents.
1.3 The aquatic free cyanide measured by this procedure should be similar to actual levels of HCN in the original aquatic
environment. This in turn may give a reliable index of toxicity to aquatic organisms.
1.4 This procedure is applicable over a range of approximately 2 to 500 µg/L (parts per billion) aquatic free cyanide. Sample
dilution may increase cyanide recoveries depending on the cyanide speciation; therefore, it is not recommended to dilute samples.
Higher concentrations can be analyzed by increasing the range of calibration standards or with a lower injection volume. In
accordance with Guide E1763 and Practice D6512 the lower scope limit was determined to be 9 µg/Lfor chlorinated gold leaching
barren effluent water.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 8.6 and Section 9.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D1293 Test Methods for pH of Water
D2036 Test Methods for Cyanides in Water
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
D3370Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD19onWaterandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.06onMethodsforAnalysisofOrganic
Substances in Water.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2006. Published February 2006. DOI: 10.1520/D7237-06.on Methods for Analysis for Organic Substances in Water.
CurrenteditionapprovedMay1,2010.PublishedJune2010.Originallyapprovedin2006.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2006asD7237 – 06.DOI:10.1520/D7237-10.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this stand
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.