ASTM D4745-97
(Specification)Standard Specification for Filled Compounds of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Molding and Extrusion Materials
Standard Specification for Filled Compounds of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Molding and Extrusion Materials
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) filled molding compounds made with virgin PTFE resins defined in Specification D 4894, except Types I, IV, V, and VI.
Note 1—This specification can be used as a model for other PTFE compounds having particulate fillers that can survive the sintering temperatures of PTFE as can those listed in this specification. This specification is restricted to virgin PTFE for technical reasons. Recycled material cannot be processed successfully.
Note 2—The properties measured on commercially fabricated parts may differ from the listed values for samples prepared by the procedures given in this specification, depending on part geometry and processing parameters.
Note 3—There is no ISO equivalent to this specification.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.3 The following statement applies to the test method portion, Section 12, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 9.5 and Note 4 for a specific warning statement.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4745 – 97
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Specification for
Filled Compounds of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Molding and Extrusion Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4745; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope * D 1895 Test Methods for Apparent Density, Bulk Factor,
and Pourability of Plastic Materials
1.1 This specification covers polytetrafluoroethylene
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
(PTFE) filled molding compounds made with virgin PTFE
D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
resins defined in Specification D 4894, except Types I, IV, V,
D 4894 Specification for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
and VI.
Granular Molding and Extrusion Materials
NOTE 1—This specification can be used as a model for other PTFE
E 11 Specification for Wire-Cloth Sieves for Testing Pur-
compounds having particulate fillers that can survive the sintering
poses
temperatures of PTFE as can those listed in this specification. This
E 380 Practice for the Use of the International System of
specification is restricted to virgin PTFE for technical reasons. Recycled
Units (SI)
material cannot be processed successfully.
NOTE 2—The properties measured on commercially fabricated parts E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
may differ from the listed values for samples prepared by the procedures
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
given in this specification, depending on part geometry and processing
parameters.
3. Terminology
NOTE 3—There is no ISO equivalent to this specification.
3.1 Definitions—The terminology given in Terminology
1.2 The values stated in SI units as detailed in Practice
D 883 is applicable to this specification unless otherwise
E 380 are to be regarded as the standard and the practices of
specified.
E380 incorporated herein.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.3 The following statement applies to the test method
3.2.1 bulk density, n—the mass in kilograms per cubic
portion, Section 12, of this specification: This standard does
metre of resin compound measured under the conditions of the
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
test.
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
3.2.2 density, n—the mass per unit volume in air in milli-
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
grams per cubic metre (grams per cubic centimetre) of the
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
material at a temperature of 23 6 2°C (73.4 6 4°F).
to use. See 9.5 and Note 4 for a specific warning statement.
3.2.3 filled compound, n—blend of PTFE resin as the matrix
and particulate fillers, generally glass, other inorganic, metal-
2. Referenced Documents
lic, or polymeric materials that withstand the sintering tem-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
perature of PTFE (327 to 380°C).
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
3.2.4 free-flow resins (pelletized), n—generally made by
Insulating Materials for Testing
treatment of finely divided resins to produce free-flowing
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
agglomerates.
D 792 Test Methods for Specific Gravity (Relative Density)
3.2.5 lot, n—one continuous production run or a uniform
and Density of Plastics by Displacement
blend of two or more production runs of the compound.
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
3.2.6 pigmented compound, n—a compound in which a
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
pigment is added for colorant purposes only.
Plastics
3.2.7 standard flow resins (nonpelletized), n—finely divided
resin with an average particle size less than 100 μm.
3.3 Abbreviations—Abbreviations are in accordance with
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
Materials.
Current edition approved April 10, 1997. Published April 1998. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
published as D 4745 – 91. Last previous edition D 4745 – 91. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.03.
2 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
D 4745
Terminology D 1600. PTFE is the acronym for polytetrafluo- 6. Requirements
roethylene.
6.1 The PTFE compounds covered by this specification
shall be uniform (filler and resin particles evenly distributed)
4. Classification
and shall contain no foreign material.
4.1 This specification covers the following two types of
6.2 The PTFE compounds shall conform to the require-
PTFE compounds
ments prescribed in Tables 1-3 when tested by the procedures
4.1.1 Type I—Nonpelletized material, for general-purpose
specified herein. Table 1 and Table 3 list requirements for Type
compression molding.
I. Table 2 and Table 3 reference requirements for Type II.
4.1.2 Type II—Pelletized or free-flowing material, for mold-
6.3 Other PTFE compounds are commercially available, but
ing, automatic molding, or ram extrusion.
are not described in this specification.
4.2 Thirteen grades of each type distinguished by the nature
of the filler(s) are listed in Tables 1-3.
7. Sampling
4.3 A one-line system may be used to specify materials
7.1 Sample the resin in accordance with the Sections cov-
covered by this specification. The system uses predefined cells
ering General Sampling Procedures in Practice D 1898. Ad-
to refer to specific aspects of this specification, as the following
equate statistical sampling prior to packaging shall be consid-
illustrates:
ered an acceptable alternative.
Specification
7.2 The producer shall take (and test) sufficient within-lot
Standard Number : Type : Grade : Class : Special
samples to ensure adequate in-process quality control and
Block : : : : Notes
:: : : :
continuing conformance to the property requirements of this
Example: Specification II 2
specification.
D4745–97
8. Number of Tests
4.3.1 For this example, the line callout would be Specifica-
tion D 4745 – 97, II 2, and would specify a pelletized or 8.1 Routine lot inspection tests shall consist of those carried
free-flowing filled composition of polytetrafluoroethylene that out to determine the requirements specified in Table 1 or Table
has all of the properties listed for that type, and grade in the 3 depending on type. Periodic tests shall include using all the
appropriate specified properties, tables, or both, in the specifi- tests to determine the requirements in Table 3, depending on
cation identified. A comma is used as the separator between the type.
standard number and the type. Separators are not needed 8.2 The requirements listed in Tables 1-3, as they apply, are
between the type, grade, and class. A provision for special sufficient to establish conformity of a material to this specifi-
notes is included so that other information can be provided cation. When the number of test specimens is not stated in the
when required. An example would be in Specification test method, single determinations may be made. If more than
D 3295 – 81a where dimensions and tolerances are specified single determinations are made on specimens from separate
for each AWG size within type and class. When special notes portions of the same sample, the results shall be averaged. The
are used, they should be preceded by a comma. single or average result shall conform to the requirements
prescribed in this specification.
5. Ordering Information
5.1 The filled compounds of PTFE may be ordered using the
9. Test Specimens
type, (see 4.1) and the grade (see reference Table 1 and Table
9.1 Test specimens shall be cut from billets molded in
3), or they may be ordered using the designation of the
accordance with the following procedures. An acceptable
suppliers.
alternate procedure for molding the test plaque is described in
Specification D 4894.
See the ASTM Form and Style Manual, available from ASTM Headquarters.
9.2 Test Billets:
TABLE 1 TFE Compounds, Type I, Standard Flow (Nonpelletized)
Molded Parts (Molded and Sintered)
Raw Resin
Density, min, SPG, max,
Type Grade Bulk Density, Tensile Strength
3 3 Elongation, min,
g/cm g/cm
min, g/L
%
min, MPa min, psi
1 15 % glass fiber 400 2.150 2.25 19.6 2840 250
2 25 % glass fiber 425 2.150 2.250 15.7 2270 200
3 35 % glass fiber 450 2.200 2.300 10.3 1500 150
4 5 % glass fiber and 5 % MoS 350 2.150 2.300 20.7 3000 250
5 15 % glass fiber and 5 % MoS 375 2.150 2.300 17.2 2500 200
6 10 % graphite 350 2.100 2.220 17.9 2600 225
7 15 % graphite 300 2.100 2.200 16.6 2400 100
8 25 % carbon and graphite 350 1.950 2.100 11.0 1600 80
9 32 % carbon and graphite 325 1.900 2.100 6.9 1000 50
10 40 % bronze 500 2.900 3.200 17.2 2500 175
11 60 % bronze 650 3.800 4.000 13.8 2000 140
12 55 % bronze and 5 % MoS 700 3.500 4.000 10.3 1500 80
13 50 % stainless steel 500 3.200 3.600 17.2 2500 150
D 4745
TABLE 2 TFE Compounds, Type II, Free-Flow (Pelletized)
Molded Parts (Molded and Sintered)
Raw Resin
SPG, max,
Type Grade Bulk Density, Density, min, g/cm Tensile Strength
Elongation, min,
g/cm
min, g/L
%
min, MPa min, psi
1 15 % glass fiber 625 2.150 2.25 17.2 2500 200
2 25 % glass fiber 625 2.150 2.250 12.4 1800 180
3 35 % glass fiber 650 2.200 2.300 8.3 1200 100
4 5 % glass fiber and 5 % MoS 575 2.150 2.300 17.2 2500 220
5 15 % glass fiber and 5 % MoS 600 2.150 2.300 13.8 2000 180
6 10 % graphite 600 2.100 2.220 13.8 2000 180
7 15 % graphite 550 2.100 2.200 10.3 1500 100
8 25 % carbon and graphite 500 1.950 2.100 8.3 1200 20
9 32 % carbon and graphite 500 1.900 2.100 6.9 1000 20
10 40 % bronze 750 2.900 3.200 13.8 2000 100
11 60 % bronze 900 3.800 4.000 10.3 1500 100
12 55 % bronze and 5 % MoS 900 3.500 4.000 6.9 1000 50
13 50 % stainless steel 850 3.200 3.600 13.8 2000 100
TABLE 3 Required Filler Content
9.2.3 Assemble the mold. Add the resin to the mold, taking
Mass, % Tolerance,6 ,% care not to fill within 13 mm (0.5 in.) of the top of the cavity.
Insert the top plug and apply hand pressure, making certain that
10to3 1
2 4 to 25 2
the pusher is centered in the mold. Place the mold in a
3 26to60 3
hydraulic press and remove the support ring or spacers. Do not
4 61to75 5
allow the two end plugs to bottom on the mold shell. Apply an
initial load to the mold of 3.45 MPa (500 psi) 6 10 % and hold
for 1 to 2 min. Increase the loading smoothly to the final
9.2.1 Prior to molding, screen the material through a
preforming pressure in 3 to 5 min. Use 35 MPa (5100 psi) for
2.0-mm hand sieve.
compounds containing 15 % by weight or less filler and 70
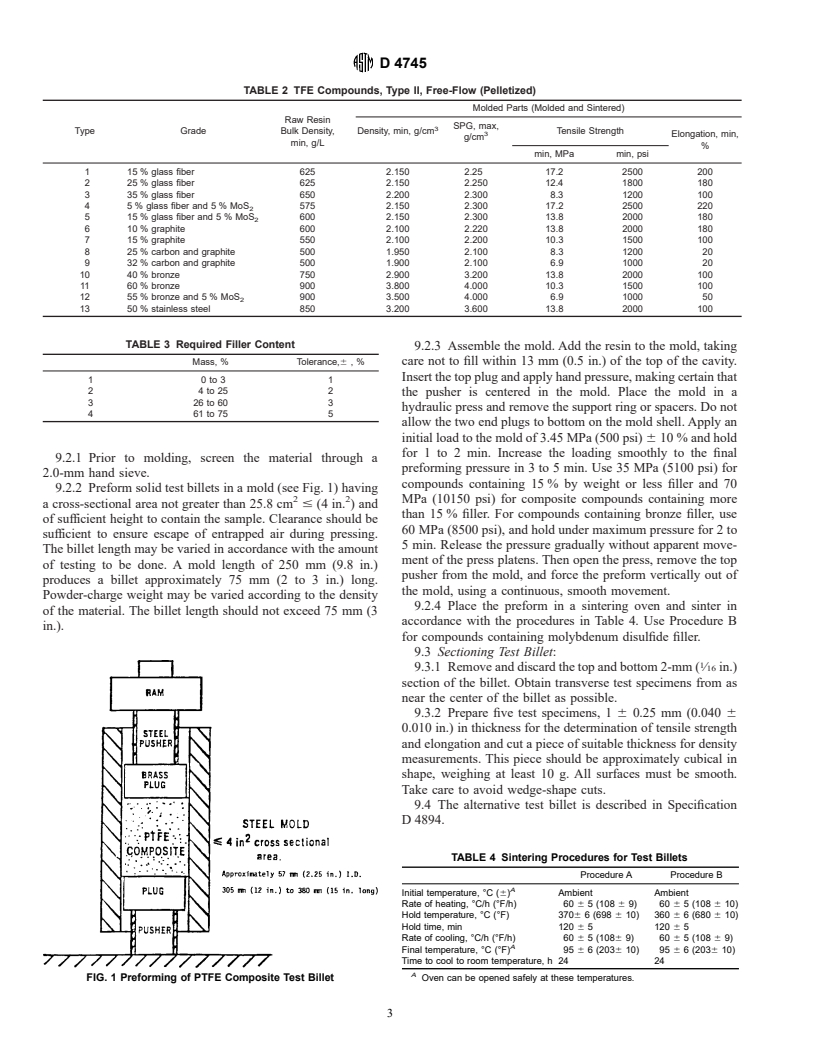
9.2.2 Preform solid test billets in a mold (see Fig. 1) having
2 2
MPa (10150 psi) for composite compounds containing more
a cross-sectional area not greater than 25.8 cm # (4 in. ) and
than 15 % filler. For compounds containing bronze filler, use
of sufficient height to contain the sample. Clearance should be
60 MPa (8500 psi), and hold under maximum pressure for 2 to
sufficient to ensure escape of entrapped air during pressing.
5 min. Release the pressure gradually without apparent move-
The billet length may be varied in accordance with the amount
ment of the press platens. Then open the press, remove the top
of testing to be done. A mold length of 250 mm (9.8 in.)
pusher from the mold, and force the preform vertically out of
produces a billet approximately 75 mm (2 to 3 in.) long.
the mold, using a continuous, smooth movement.
Powder-charge weight may be varied according to the density
9.2.4 Place the preform in a sintering oven and sinter in
of the material. The billet length should not exceed 75 mm (3
accordance with the procedures in Table 4. Use Procedure B
in.).
for compounds containing molybdenum disulfide filler.
9.3 Sectioning Test Billet:
9.3.1 Remove and discard the top and bottom 2-mm ( ⁄16 in.)
section of the billet. Obtain transverse test specimens from as
near the center of the billet as possible.
9.3.2 Prepare five test specimens, 1 6 0.25 mm (0.040 6
0.010 in.) in thickness for the determination of tensile strength
and elongation and cut a piece of suitable thickness for density
measurements. This piece should be approximately cubical in
shape, weighing at least 10 g. All surfaces must be smooth.
Take care to avoid wedge-shape cuts.
9.4 The alternative test billet is described in Specification
D 4894.
TABLE 4 Sintering Procedures for Test Billets
Procedure A Procedure B
A
Initial temperature, °C (6) Ambient Ambient
Rate of heating, °C/h (°F/h) 60 6 5 (108 6 9) 60 6 5 (108 6 10)
Hold temperature, °C (°F) 3706 6 (698 6 10) 360 6 6 (680 6 10)
Hold time, min 120 6 5 120 6 5
Rate of cooling, °C/h (°F/h) 60 6 5 (1086 9) 60 6 5 (108 6 9)
A
Final temperature, °C (°F) 95 6 6 (2036 10) 95 6 6 (2036 10)
Time to cool to room temperature, h 24 24
A
FIG. 1 Preforming of PTFE Composite Test Billet Oven can be opened safely at these temperatures.
D 4745
9.5 Safety Warning—At normal processing temperatures,
F 5 grams per liter of the filler.
PTFE liberates vapors that may be harmful. Provide adequate
U 5 grams per liter of the unfilled PTFE.
ventilation in areas where PTFE compounds are exposed to
E 5 equivalent filler content (% by volume).
elevated temperatures. Avoid contaminating smoking materials
12.1.6 The percent by volume of filler in a finished piece is
with PTFE compounds.
lower than that in the powder compounds due to the increase in
volume of PTFE that results from the change in crystalline
10. Conditioning Test Specimens
content that occurs during sintering.
10.1 For density and tensile properties the test specimens
12.2 Filler Content (Alternate Method):
shall be conditioned in accordance with Procedure A of
12.2.1 Scope—This burn-out procedure for filler content
Practice D 618 for a period of at least 4 h prior to test.
may be used as alternate to the split tube furnace method of
12.1. The procedure shall be carried out in an inert atmosphere,
11. Test Conditions
especially when fillers that react with PTFE and oxygen in the
11.1 Tests shall be conducted at 25 6 2°C (77 6 3.6°F)
air are present. This reaction produces volatile products that
instead of the standard laboratory temperature of 23 6 2°C
cause incorrect results.
(73.4 6 3.6°F) unless otherwise specified in the test methods
12.2.2 Equipment—Thermogravimetric a
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.