ASTM B135-08a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Seamless Brass Tube
Standard Specification for Seamless Brass Tube
ABSTRACT
This specification covers seamless round and rectangular including square copper alloy tube in straight lengths. The tempers of drawn tube shall be designated as light-drawn, drawn, and hard-drawn. Light-drawn temper shall be used only when a tube of some stiffness but yet capable of being bent is needed. Drawn temper, which is most commonly used where there is no specific requirement for high strength on the one hand, shall be utilized for general purposes and or for bending qualities on the other. Hard-drawn temper shall be used only where there is need for a tube as strong as is commercially feasible for the sizes indicated. For any combination of diameter and wall thickness not covered under hard-drawn temper, the values given for drawn temper shall be used. Expansion test shall be performed on the rounded tube and shall show no cracking or rupture visible to the unaided eye. Both annealed and drawn tempers shall withstand, after proper cleaning, an immersion in standard mercurous nitrate solution for a certain amount of time without cracking. Materials shall then be removed from the solution and shall be wiped free of excess mercury and shall then be examined for cracks. The specimen shall undergo the eddy-current testing which is the standard nondestructive test. The specimen shall undergo the pneumatic test which subjects the tube to an internal air pressure making sure that it must not show evidence of leakage. The test method used shall provide for easy visual detection of any leakage, such as by immersion of the tube under water or by the pressure differential method. Annealed tube shall be either bright annealed or acid cleaned after final annealing operations.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers seamless round and rectangular including square copper alloy tube in straight lengths. Ten alloys are specified having the following nominal compositions:
CopperPreviously Nominal Composition, % AlloyUsed UNSDesigna- No. tionACopper ZincLeadTin C22000790.010.0 ...... C23000185.015.0 ...... C26000270.030.0 ...... C27000965.035.0 ...... C27200863.037.0 ...... C27400...62.537.5 ...... C28000560.040.0 ...... C33000366.033.5 0.5... C33200466.032.4 1.6... C37000660.039.0 1.0... C44300...71.527.5 ...1.00
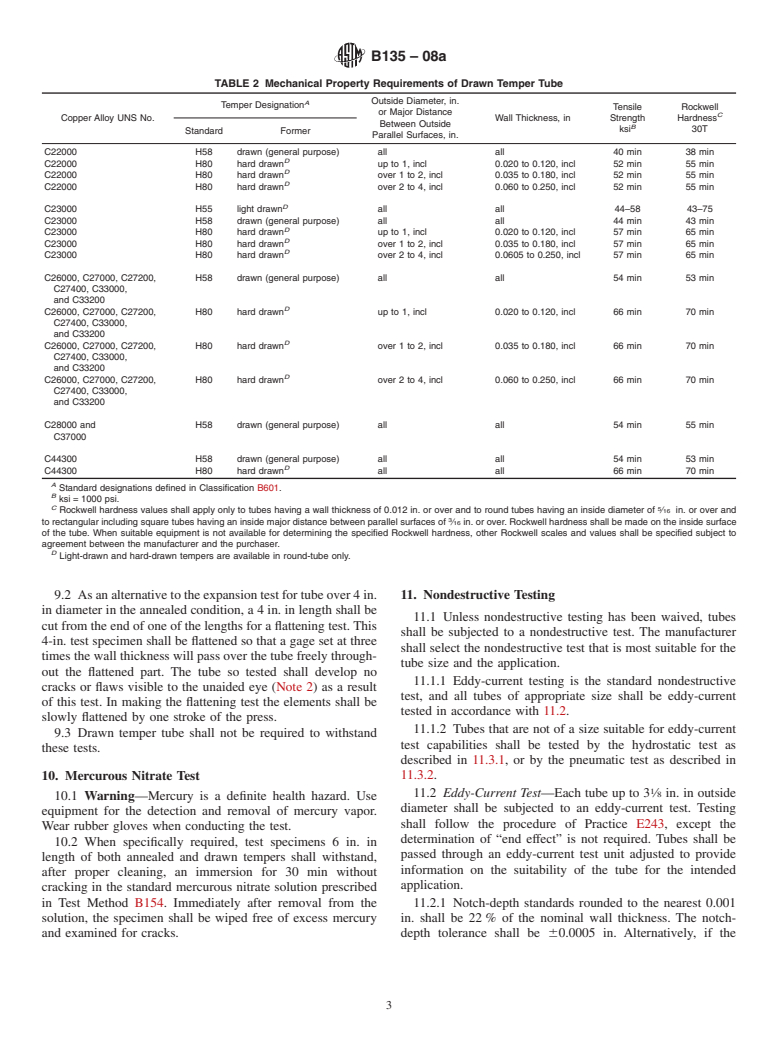
A Alloy Designations of Specification B 135 – 63, which was published in the 1966 Book of ASTM Standards, Part 5.
1.2 This specification is the inch-pound companion to Specification B 135M; therefore, no SI equivalents are presented in the specification.
1.3 Warning—Mercury has been designated by EPA and many state agencies as a hazardous material that can cause central nervous system, kidney, and liver damage. Mercury, or its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury-containing products. See the applicable product Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for details and EPA’s website (http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm) for additional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury or mercury-containing products, or both, in your state may be prohibited by state law. (See 10.1.)
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B135 – 08a
Standard Specification for
1
Seamless Brass Tube
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B135; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.1 This specification covers seamless round and rectangu-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
lar including square copper alloy tube in straight lengths. Ten
alloys are specified having the following nominal composi-
2. Referenced Documents
tions:
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Copper Previously Nominal Composition, %
B153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and
Alloy Used
UNS Designa-
Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing
2 A
No. tion Copper Zinc Lead Tin
B154 Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper
Alloys
C22000 7 90.0 10.0 . .
C23000 1 85.0 15.0 . .
B251 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought
C26000 2 70.0 30.0 . .
Seamless Copper and Copper-Alloy Tube
C27000 9 65.0 35.0 . .
B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper
C27200 8 63.0 37.0 . .
C27400 . 62.5 37.5 . .
and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
C28000 5 60.0 40.0 . .
E243 Practice for Electromagnetic (Eddy-Current) Exami-
C33000 3 66.0 33.5 0.5 .
nation of Copper and Copper-Alloy Tubes
C33200 4 66.0 32.4 1.6 .
C37000 6 60.0 39.0 1.0 .
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
C44300 . 71.5 27.5 . 1.00
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
A
Alloy Designations of Specification B135 – 63, which was published in the
1966 Book of ASTM Standards, Part 5.
3. Terminology
1.2 This specification is the inch-pound companion to
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Specification B135M; therefore, no SI equivalents are pre-
3.1.1 capable of—the test need not be performed by the
sented in the specification.
producer of the material. However, if subsequent testing by the
1.3 Warning—Mercury has been designated by EPA and
purchaser establishes that the material does not meet these
many state agencies as a hazardous material that can cause
requirements, the material shall be subject to rejection.
central nervous system, kidney, and liver damage. Mercury, or
its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to
4. Ordering Information
materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and
4.1 Orders for material under the specification shall include
mercury-containing products. See the applicable product Ma-
the following information:
terial Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for details and EPA’s website
4.1.1 Alloy (Section 1),
(http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm) for additional informa-
4.1.2 Temper (Section 7),
tion. Users should be aware that selling mercury or mercury-
4.1.3 Whether tension tests are required (for drawn tempers
containingproducts,orboth,inyourstatemaybeprohibitedby
2 only (see 8.1)),
state law. (See 10.1.)
4.1.4 Dimensions: diameter or distance between parallel
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
surfaces and wall thickness (see 11.2 and 11.3),
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.1.5 Length (see 12.4),
4.1.6 Mercurous nitrate test, if required (Section 10),
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper 4.1.7 Total length of each size,
and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe
4.1.8 Hydrostatic pressure test, when specified, and
and Tube.
4.1.9 Pneumatic test, when specified.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2008. Published November 2008. Originally
approved in 1940. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as B135 – 08. DOI:
10.1520/B0135-08A.
2 3
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E527) is a simple For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
of a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
composition variations of the base alloy. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B135 – 08a
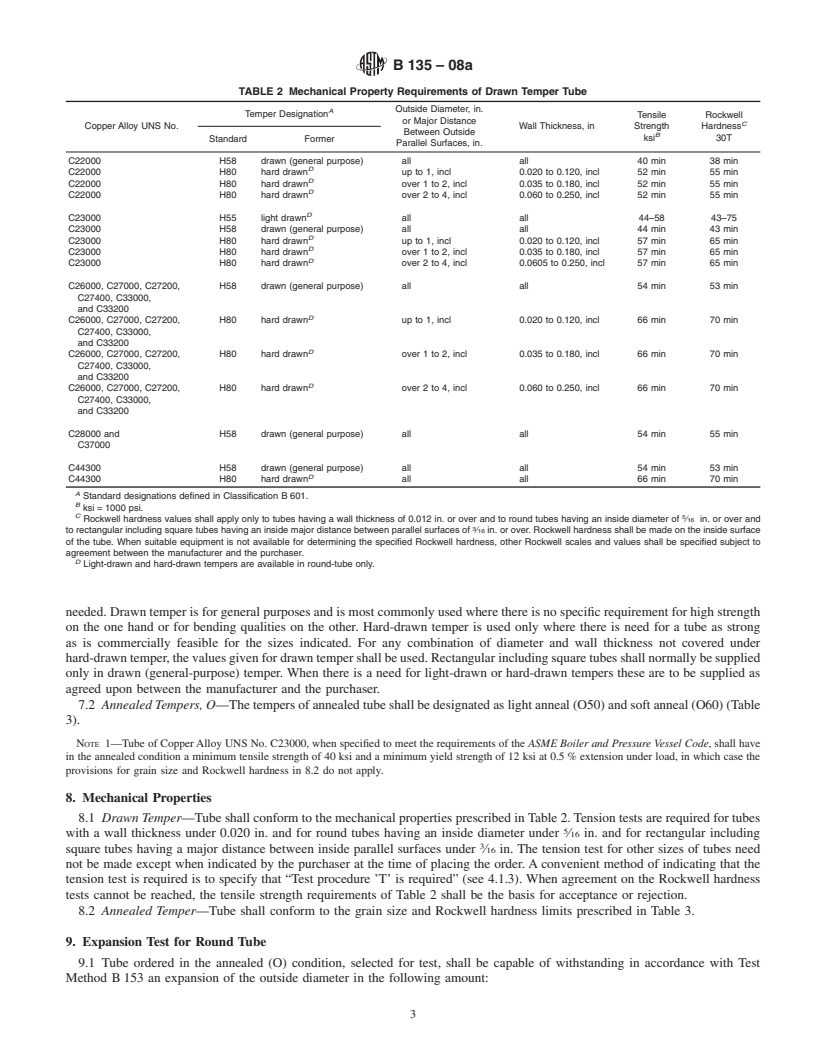
5. General Requirements these are to be supplied as agreed upon between the manufac-
turer and the purchaser.
5.1 Material furnished under this spec
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B135–08 Designation: B 135 – 08a
Standard Specification for
1
Seamless Brass Tube
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 135; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers seamless round and rectangular including square copper alloy tube in straight lengths. Ten alloys
are specified having the following nominal compositions:
Copper Previously Nominal Composition, %
Alloy Used
UNS Designa-
2 A
No. tion Copper Zinc Lead Tin
C22000 7 90.0 10.0 . .
C23000 1 85.0 15.0 . .
C26000 2 70.0 30.0 . .
C27000 9 65.0 35.0 . .
C27200 8 63.0 37.0 . .
C27400 . 62.5 37.5 . .
C28000 5 60.0 40.0 . .
C33000 3 66.0 33.5 0.5 .
C33200 4 66.0 32.4 1.6 .
C37000 6 60.0 39.0 1.0 .
C44300 . 71.5 27.5 . 1.00
A
Alloy Designations of Specification B 135 – 63, which was published in the 1966 Book of ASTM Standards, Part 5.
1.2 This specification is the inch-pound companion to Specification B 135M; therefore, no SI equivalents are presented in the
specification.
1.3 Warning—Mercury has been designated by EPA and many state agencies as a hazardous material that can cause central
nervous system, kidney, and liver damage. Mercury, or its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution
should be taken when handling mercury and mercury-containing products. See the applicable product Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS) for details and EPA’s website (http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm) for additional information. Users should be aware
2
that selling mercury or mercury-containing products, or both, in your state may be prohibited by state law. (See 10.1.)
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1The following documents of the issue in effect on date of material purchase form a part of this specification to the extent
referenced herein:
2.2
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B 153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing
B 154 Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper Alloys
B 251 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Seamless Copper and Copper-Alloy Tube
B 601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper AlloysWrought and Cast
E 243 Practice for Electromagnetic (Eddy-Current) Examination of Copper and Copper-Alloy Tubes
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B05 on Copper and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe and
Tube.
Current edition approved AprilOct. 1, 2008. Published AprilNovember 2008. Originally approved in 1940. Last previous edition approved in 20022008 as B 135 – 028.
2
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E 527) is a simple expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition of
a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate composition variations of the base alloy.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
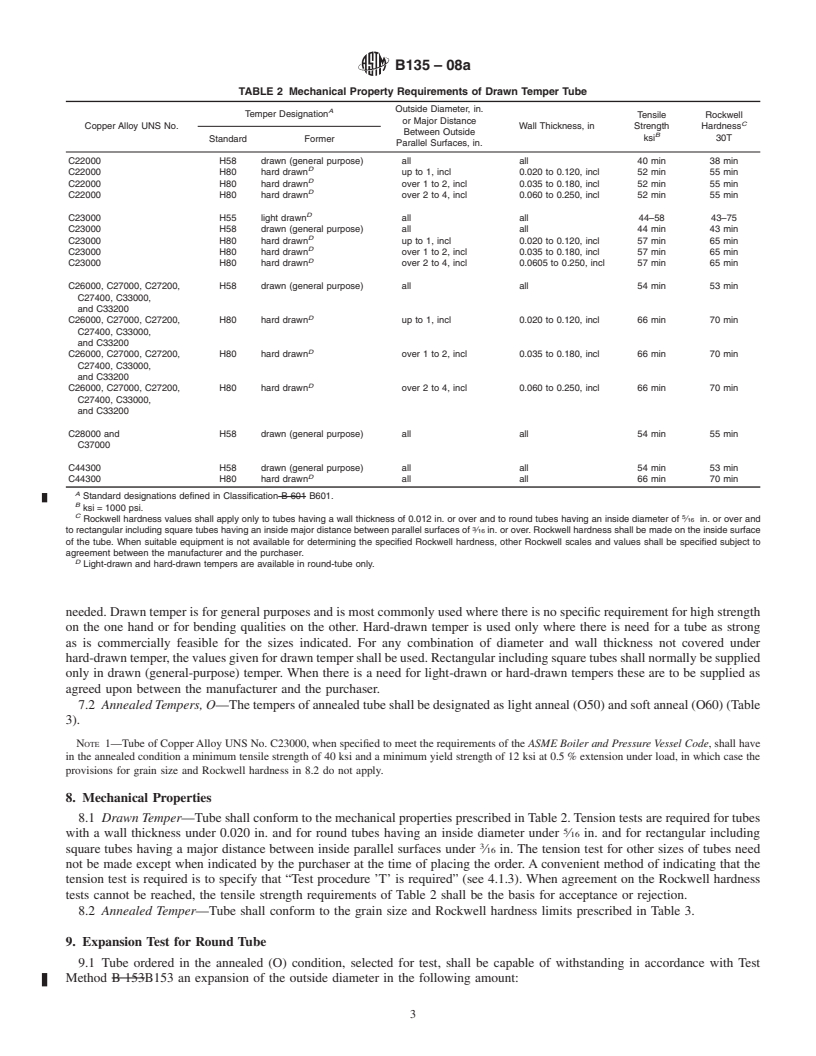
B 135 – 08a
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 capable of—the test need not be performed by the producer of the material. However, if subsequent testing by the
purchaser establishes that the material does not meet these requirements, the material shall be subject to rejection.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 Orders for material under the specification shall include the following information:
4.1.1 Alloy (Section 1),
4.1.2 Temper (Section 7),
4.1.3 Whether tension tests are required (for drawn tempers only (see 8.1)),
4.1.4
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B 135–08 Designation: B135 – 08a
Standard Specification for
1
Seamless Brass Tube
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B135; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers seamless round and rectangular including square copper alloy tube in straight lengths. Ten alloys
are specified having the following nominal compositions:
Copper Previously Nominal Composition, %
Alloy Used
UNS Designa-
2 A
No. tion Copper Zinc Lead Tin
C22000 7 90.0 10.0 . .
C23000 1 85.0 15.0 . .
C26000 2 70.0 30.0 . .
C27000 9 65.0 35.0 . .
C27200 8 63.0 37.0 . .
C27400 . 62.5 37.5 . .
C28000 5 60.0 40.0 . .
C33000 3 66.0 33.5 0.5 .
C33200 4 66.0 32.4 1.6 .
C37000 6 60.0 39.0 1.0 .
C44300 . 71.5 27.5 . 1.00
A
Alloy Designations of Specification B135 – 63, which was published in the 1966 Book of ASTM Standards, Part 5.
1.2 This specification is the inch-pound companion to Specification B135M; therefore, no SI equivalents are presented in the
specification.
1.3 Warning—Mercury has been designated by EPA and many state agencies as a hazardous material that can cause central
nervous system, kidney, and liver damage. Mercury, or its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution
should be taken when handling mercury and mercury-containing products. See the applicable product Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS) for details and EPA’s website (http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm) for additional information. Users should be aware
2
that selling mercury or mercury-containing products, or both, in your state may be prohibited by state law. (See 10.1.)
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1The following documents of the issue in effect on date of material purchase form a part of this specification to the extent
referenced herein:
2.2
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing
B154 Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper Alloys
B251 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Seamless Copper and Copper-Alloy Tube
B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper AlloysWrought and Cast
E243 Practice for Electromagnetic (Eddy-Current) Examination of Copper and Copper-Alloy Tubes
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B05 on Copper and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe and
Tube.
Current edition approvedAprilOct. 1, 2008. PublishedAprilNovember 2008. Originally approved in 1940. Last previous edition approved in 20022008 as B135 – 08. DOI:
10.1520/B0135-08A.
2
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E 527E527) is a simple expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition
of a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate composition variations of the base alloy.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B135 – 08a
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 capable of—the test need not be performed by the producer of the material. However, if subsequent testing by the
purchaser establishes that the material does not meet these requirements, the material shall be subject to rejection.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 Orders for material under the specification shall include the following information:
4.1.1 Alloy (Section 1),
4.1.2 Temper (Section 7),
4.1.3 Whether tension tests are required (for drawn tempers only (se
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.