ASTM D6500-00
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Diameter of Wool and Other Animal Fibers Using an Optical Fiber Diameter Analyser
Standard Test Method for Diameter of Wool and Other Animal Fibers Using an Optical Fiber Diameter Analyser
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure that uses an Optical Fiber Diameter Analyser (OFDA) for the determination of the average fiber diameter and the fiber diameter variation in wool and other animal fibers in their various forms.Note 1
This test method may also be applied to other fibers having a round cross section such as some polyamides, polyesters, and glass; it may also be applied to a limited number of polyacrylics and regenerated cellulose-type fibers.Note 2
In subsequent sections of this test method, the term "wool" also signifies other animal fibers where applicable.Note 3
For fineness specifications of wool, wool top, mohair, mohair top, alpaca, and cashmere, refer to Specifications D 3991, D 3992, D 2252, and Test Method D 2816, respectively.
1.2 The OFDA reports average fiber diameter and standard deviation of fiber diameter in micrometer units (m). The coefficient of variation of fiber diameter is reported as a percentage.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 6500 – 00
Standard Test Method for
Diameter of Wool and Other Animal Fibers Using an Optical
Fiber Diameter Analyser
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6500; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Instruments based on image analysis have been designed to reduce the level of operator skill
required and to speed up the measurement process while concurrently maintaining acceptable levels
of precision and accuracy.An additional advantage of image analysis instruments is the ability of the
operator to see the measurement points and to audit the process, if required, though this is not carried
out during routine measurement. As with projection microscope measurements, and the Sirolan-
Laserscan, the Optical Fiber DiameterAnalyser (OFDA) system covered by this test method provides
a count of readings grouped into diameter classes. Because the fiber snippets are measured
automatically by an optical and image processing system, controls are provided in the image
processing software to minimize the inclusion of multiple measurements on the same fiber and false
diameter readings that arise from non-fiber material.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This test method covers a procedure that uses an Optical 2.1 ASTM Standards:
Fiber Diameter Analyser (OFDA) for the determination of the D 123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
average fiber diameter and the fiber diameter variation in wool D 584 Test Method for Wool Content of Raw Wool—
and other animal fibers in their various forms. Laboratory Scale
D 1060 Practice for Core Sampling of Raw Wool in Pack-
NOTE 1—This test method may also be applied to other fibers having a
ages for Determination of Percentage of Clean Wool Fiber
roundcrosssectionsuchassomepolyamides,polyesters,andglass;itmay
Present
also be applied to a limited number of polyacrylics and regenerated
D 1776 Practice for Conditioning Textiles for Testing
cellulose-type fibers.
NOTE 2—In subsequent sections of this test method, the term “wool”
D 2130 Test Method for Diameter of Wool and Other
also signifies other animal fibers where applicable.
Animal Fibers by Microprojection
NOTE 3—For fineness specifications of wool, wool top, mohair, mohair 2
D 2252 Specification for Fineness of Types of Alpaca
top, alpaca, and cashmere, refer to Specifications D 3991, D 3992,
D 2816 Test Method for Cashmere Coarse–Hair Content in
D 2252, and Test Method D 2816, respectively.
Cashmere
1.2 The OFDA reports average fiber diameter and standard
D 3510 Test Method for Diameter of Wool and Other
deviation of fiber diameter in micrometer units (µm). The 3
Animal Fibers by Image Analyzer
coefficient of variation of fiber diameter is reported as a
D 3991 Specifications for Fineness of Wool or Mohair and
percentage. 4
Assignment of Grade
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
D 3992 Specifications for Fineness of Wool Top or Mohair
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 4
Top and Assignment of Grade
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 4
D 4845 Terminology Relating to Wool
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
2.2 Federal Standards:
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Official Standards of the United States for Grades of
1 2
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD13onTextiles, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.01.
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.13 on Wool and Wool Felt. Discontinued. See 1986 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.02.
Current edition approved March 10, 2000. Published June 2000. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 6500
Wool, Section 31.0 analysed to produce the mean and standard deviation of the
Measurement Method for Determining Grade of Wool, Sec- fiber diameter for the specimen. Full distribution data are also
tion 31.204 available in the form of a printed histogram.
Official Standards of the United States for Grades of Wool
6 5. Significance and Use
Top, Section 31.1
Measurement Method for Determining Grade of Wool 5.1 This test method specifies sampling and testing proce-
Top, Section 31.301 dures for the measurement of average fiber diameter and
USDA Grade Standards for Grease Mohair and Mohair variation in diameter of animal fibers.
Top 5.2 This test method is considered satisfactory for accep-
2.3 IWTO Standards: tance testing of commercial shipments of wool and other
IWTO-8-66 Method of Determining Wool Fiber Diameter animal fibers in raw and sliver form because current estimates
by the Projection Microscope of between-laboratory precision are acceptable. In cases of
IWTO-12-93 Measurement of the Mean and Distribution of disagreement arising from differences in values reported by
Fibre Diameter Using a Sirolan-Laserscan Fibre Diameter two or more laboratories when using this test method for
Analyser acceptance testing, the statistical bias, if any, between the
IWTO-19-98 Determination of Wool Base and Vegetable
laboratories should be determined with each comparison being
Matter Base of Core Samples of Raw Wool based on the testing of specimens randomly drawn from one
IWTO-47-98 Measurement of the Mean and Distribution of
sample of material of the type being evaluated. Test Method
Fibre Diameter of Wool Using an Optical Fibre Diameter D 2130 shall be used as a referee test method.
Analyser (OFDA)
5.3 This test method may be used for determining compli-
ance with average fiber diameter and diameter variation to
3. Terminology
assign grades when determining conformance of shipments to
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of “wool” and other textile material specifications given in Specifications D 2252, D 3991,
terms used in this test method, refer to Terminologies D 4845 and D 3992, and Test Method D 2816.
and D 123. 5.4 Theproceduresfordeterminingmeanfiberdiameterand
3.1.1 average fiber diameter, n—the arithmetic mean width standard deviation of fiber diameter provided in this test
of a group of fibers. methodandinIWTOMethod47-98areinessentialagreement.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—In wool and other animal fibers, all
6. Apparatus, Materials, and Reagents
animal fibers, regardless of species, can be measured using the
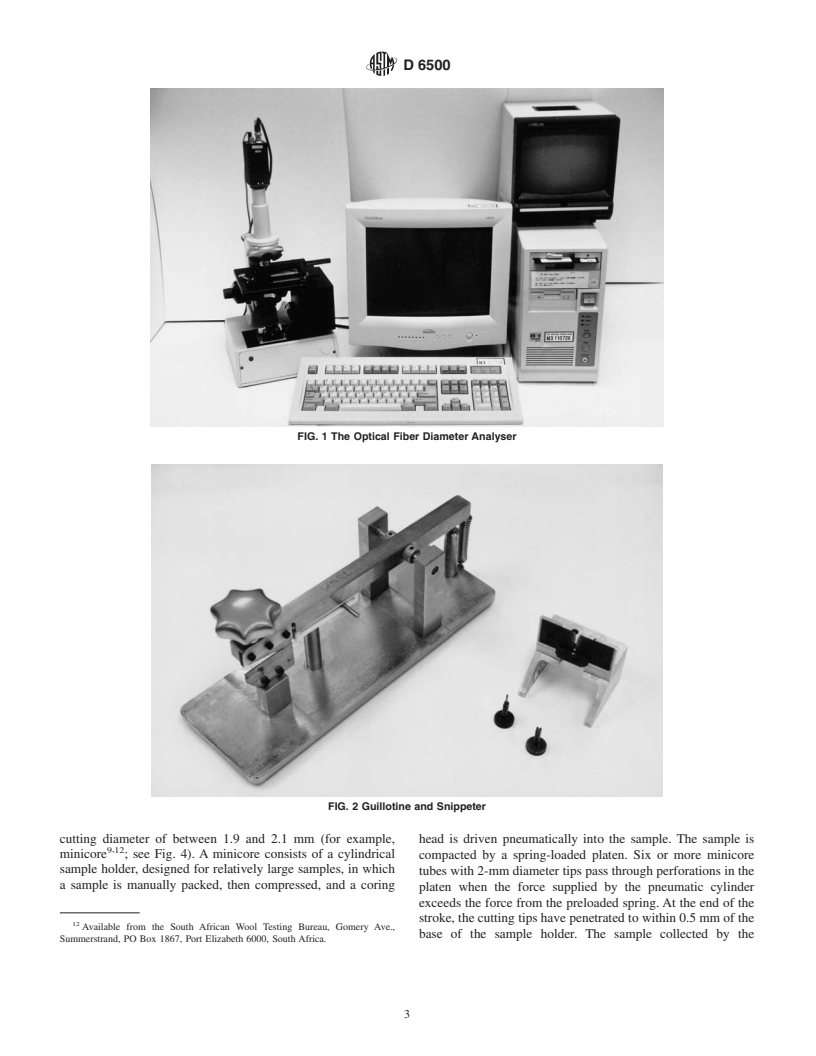
OFDA to determine average fiber diameter. 6.1 Optical Fiber Diameter Analyser , consisting of a trans-
3.1.2 grade, n—in wool and mohair, a numerical designa- mission light microscope, fitted with a stage (motor-driven and
tionusedinclassificationoffibersintheirraw,semi-processed, controlled by a computer), stroboscopic illumination that is
and processed forms based on average fiber diameter and synchronised with the stage movement, and a CCD camera; an
variation of fiber diameter. image acquisition and analysis hardware system; a means for
3.1.3 snippet, n—a wool or other animal fiber that has been controlling the interaction between the camera, stage motors
cut to a specified length. and illumination unit; a data acquisition and processing com-
puter, with optionally, control and reporting software; and, a
4. Summary of Test Method
video monitor, capable of displaying each image frame in real
4.1 This test method describes procedures for sampling time, for audit purposes. See Fig. 1.
wool in various physical forms, the reduction of the sample to 6.2 Glass Microscope Slides , of float glass, sufficiently
small test specimens, and measurement of the diameter of a robusttowithstandrepeatedhandlinghavingdimensions70by
number of fibers from the test specimens using the OFDA. 70 by 2 mm.Two identical slides are taped together so that one
Snippetscomprisingatestspecimencutfromthevariousforms supports the fiber samples with the other serving as a cover
of wool are cleaned where required, conditioned, and spread slide. Slides that are scratched on their inside surfaces are
uniformly over the surface of a microscope slide.Acover slide unsuitable as they may lend to erroneous measurements.
is placed over the specimen and the slide placed on a 6.3 Cleaning and Conditioning Apparatus and Facilities,
microscope stage, that is moved under computer control. The suitable for cleaning and drying the subsamples in accordance
slide is stepped through the field of view of a low-power withTest Method D 584 and conditioning them as described in
microscope objective. At each step, the video system is Practice D 1776.
instructed to capture and analyze a fiber image frame. Each 6.4 Apparatus for Snippet Preparation, having either two
diameter measurement is allocated to a diameter class and, at parallel cutting edges between 1.8 and 2.0 mm apart (for
9,10 11
the completion of the slide, the class contents are statistically example, guillotine or snippeter ; see Figs. 2 and 3), or a
5 9
Federal Register, Vol 30, No. 161, August 20, 1965, pp. 10829-10833. Available from BSC Electronics Pty, Ltd., 1A Thurso Rd., Myaree, Western
Federal Register, Vol 33, No. 248, December 21, 1968, pp. 19073-19076. Australia, 6154.
7 10
Federal Register, Vol 36, No. 129, July 3, 1971, pp. 12681-12658. Available from Symtech Systems and Technology, I-85 and Bryant Rd., PO
Available from the International Wool Textile Organization, International Wool Box 2627, Spartanburg, SC 29304.
Secretariat, Commercial Development Department, Valley Drive, Ilkley, Yorkshire Available from CSIRO, Division of Wool Technology, PO Box 21, Belmont,
LS29, 8PB, England, UK. VIC 3216, Australia.
D 6500
FIG. 1 The Optical Fiber Diameter Analyser
FIG. 2 Guillotine and Snippeter
cutting diameter of between 1.9 and 2.1 mm (for example, head is driven pneumatically into the sample. The sample is
9,12
minicore ; see Fig. 4). A minicore consists of a cylindrical compacted by a spring-loaded platen. Six or more minicore
sample holder, designed for relatively large samples, in which
tubes with 2-mm diameter tips pass through perforations in the
a sample is manually packed, then compressed, and a coring
platen when the force supplied by the pneumatic cylinder
exceeds the force from the preloaded spring. At the end of the
stroke, the cutting tips have penetrated to within 0.5 mm of the
Available from the South African Wool Testing Bureau, Gomery Ave.,
base of the sample holder. The sample collected by the
Summerstrand, PO Box 1867, Port Elizabeth 6000, South Africa.
D 6500
FIG. 3 Guillotine
FIG. 4 Minicoring Device
minicore tubes is automatically expelled into a collection 6.7 Slide Preparer capable of uniformly spreading a por-
device upon retraction of the coring head.
tion of the cleaned, conditioned snippet sample over the
6.5 Heavy-Duty Sectioning Device , comprised of a metal
surface of a clean glass slide at a predetermined, controlled
plate with slot and compressing key and equipped with a
density. For the OFDA, the optimum obscured areas, that is,
propulsion mechanism by which the fiber bundle may be
the ratio of fiber to the total field area, is between 15 and 25 %.
extruded for sectioning. The instrument is designed to hold a
There are different versions of slide preparers (spreaders)
sliver or top or equivalent bulk of fibers, yarn, or fabric (see
available and it must be ensured that the same slide preparer is
Fig. 1 of Test Method D 2130). Alternatively, this instrument
usedforbothcalibrationandroutineOFDAmeasurements.See
can be used to generate the snippets.
Fig. 5.
6.6 Safety Razor Blades, single-edge or double-edge (if
6.8 Box for Compressing Loose Fibers, 300 by 150 by 375
used with blade holder).
mm deep, inside dimensions, equipped with a floating top that
has 16 randomly spaced holes 20 mm in diameter over its area.
The sample may be firmly compressed by applying pressure on
Available from MICO Instruments, 1944 Main St., PO Box 451, Marshfield
Hills, MA 02051-0451. the top. The top is held in place by two rods extending through
D 6500
FIG. 5 Slide Spreader
holes in the side of the box and over the top. The coring tube 6.12 Calibration Standards—Used for instrument calibra-
is thrust through the holes in the top to sample the wool. tion. For wool, use current Interwoollabs IH Standard Tops
and for mohair, use current International Mohair Association
6.9 Pressure Coring Tube, 13-mm inside-diameter metal
Standard Tops .
tube, approximately 760 mm long, reamed and tapped on one
end to hold a sharp 10 or 13-mm cutting tip. The tube is fitted
7. Sampling
with a “T” cross bar about 500 mm long.
7.1 Loose Fibers—The method of obtaining a representa-
6.10 Core Extruder, 6-mm wood dowel or aluminum rod
tive sample of wool differs according to circumstances. The
slightly longer than the coring tube to push the sample from
sampling procedures and major circumstances encountered are
tube.
as follows:
6.11 Solvents—Petroleum spirit (boiling range 40 to 70°C)
7.1.1 Lots of Packaged, Grease, Pulled, or Scoured Wool—
and 1,1,1, trichloroethane. When the preparation method calls
Take core samples as directed in Practice D 1060. Clean or
for the cleaning of sliver subsamples, one of these two solvents
scour the raw wool sample as directed in Test Method D 584.
shall be used. Warning—Both solvents have associated haz-
ards in terms of volatility, toxicity, and, in the case of
petroleum spirit, flammability. In both cases, care should be
Available from Interwoollabs Secretariat, Boite 14 Rue de Luxembourg 19/21,
takeninstorage,handling,use,anddisposalinaccordancewith
1040 Brussels, Belgium.
the appropriate safety procedures. Refer to manufacturers’
Available from International Mohair Association, Mohair House, 68 The
material safety data sheets (MSDS). Grove, Ilkley, West Yorkshire, LS29 9PA, England, UK.
D 6500
If a representative portion of the scoured wool core sample 8.2.1 Test 1 test specimen from each bulk subsample and 2
resulting from the test for clean wool fiber present is available, specimens from each sliver and top subsample. Prepare ap-
it may be used for fiber diameter determination. If core proximately 25-mg test specimens by cutting enough fiber
sampling is not feasible, take at random, by hand, at least 50 snippets to measure the diameters of at least 2000 fiber
handfuls of wool from not less than 10 % of the packages. The segments for each test specimen
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.