ASTM D4508-06
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Chip Impact Strength of Plastics
Standard Test Method for Chip Impact Strength of Plastics
SCOPE
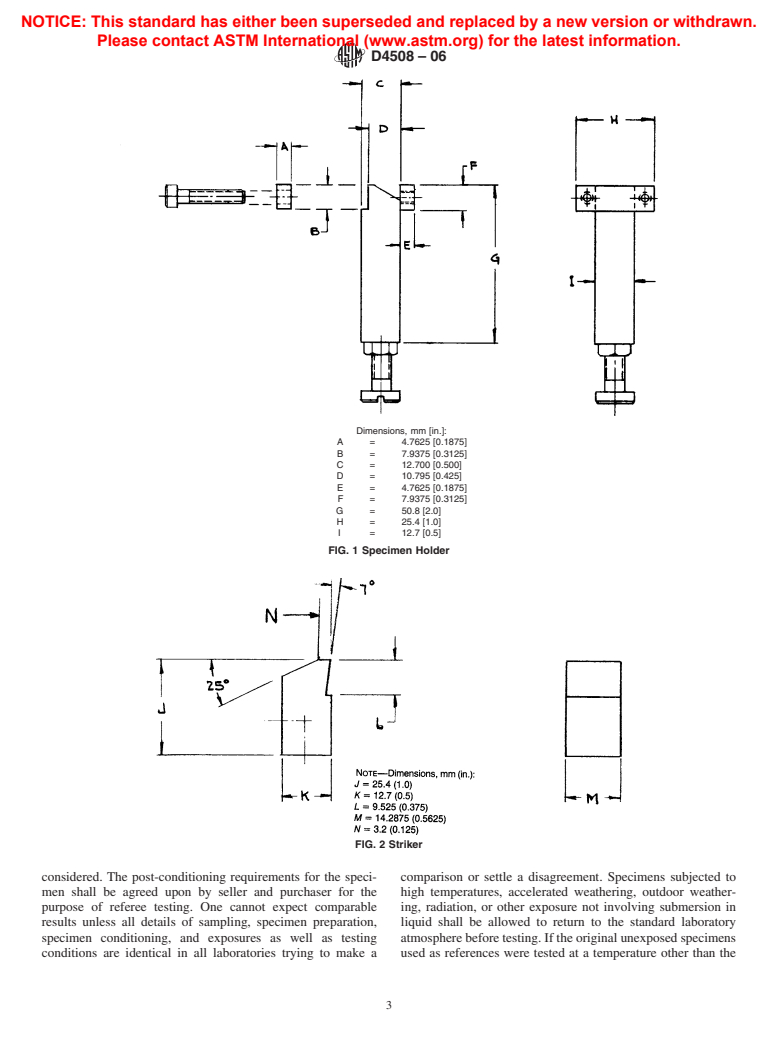
1.1 The purpose of this test method is to provide an impact test that can be performed on small specimens of plastics of different thicknesses. This test method is especially suited for observing the effects of microcracks caused by weathering, or by exposure to solvents or other hostile environments, on the surface of plastic materials. It is not meant to be used as a replacement for any existing impact test, but can be used to measure impact on coupons machined from finished parts that cannot be tested by the drop-weight, Izod, or Charpy method because of shape or thickness limitations.
1.2 The chip-impact test is run on small, flat, unnotched specimens using a standard pendulum-impact device. The test places the impacted surface in tension and, for notch-sensitive materials, is extremely sensitive to the presence of surface microcracks. Thus, for plastics that develop surface cracks when exposed outdoors, the chip-impact test is a severe test of the weathered impact strength.
1.3 Round-robin testing has indicated that materials that break at total energy values of less than 0.17 joules [1.5 in.-lbf] have within-laboratory coefficients of variation of approximately 30 %. Therefore, such values are considered out of the normal testing range for this test.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in brackets are for information only.
1.5 There is no ISO equivalent to this test method.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D4508 – 06
Standard Test Method for
1
Chip Impact Strength of Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4508; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D256 Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum
Impact Resistance of Plastics
1.1 The purpose of this test method is to provide an impact
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
test that can be performed on small specimens of plastics of
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
different thicknesses. This test method is especially suited for
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
observing the effects of microcracks caused by weathering, or
Plastics
by exposure to solvents or other hostile environments, on the
D4066 Classification System for Nylon Injection and Ex-
surface of plastic materials. It is not meant to be used as a
trusion Materials (PA)
replacement for any existing impact test, but can be used to
D5947 Test Methods for Physical Dimensions of Solid
measure impact on coupons machined from finished parts that
Plastics Specimens
cannot be tested by the drop-weight, Izod, or Charpy method
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
because of shape or thickness limitations.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.2 The chip-impact test is run on small, flat, unnotched
specimens using a standard pendulum-impact device. The test
3. Terminology
places the impacted surface in tension and, for notch-sensitive
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of plastic terms see Termi-
materials, is extremely sensitive to the presence of surface
nology D883 and for abbreviations see Terminology D1600.
microcracks. Thus, for plastics that develop surface cracks
There are no terms in this test method that require new or
when exposed outdoors, the chip-impact test is a severe test of
other-than-dictionary definitions.
the weathered impact strength.
1.3 Round-robin testing has indicated that materials that
4. Significance and Use
breakattotalenergyvaluesoflessthan0.17joules[1.5in.-lbf]
4.1 The chip-impact test is a variation of the Izod impact
have within-laboratory coefficients of variation of approxi-
test described in Test Methods D256.
mately 30%. Therefore, such values are considered out of the
4.2 The specimen geometry has been chosen to fit three
normal testing range for this test.
basic criteria as follows:
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
4.2.1 The specimen is relatively thin and is struck on the
standard.Thevaluesgiveninbracketsareforinformationonly.
broad surface so that the test result is sensitive to the condition
1.5 There is no ISO equivalent to this test method.
of the surface,
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.2.2 The specimen is relatively small for efficient utiliza-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
tion of space in accelerated testing media or devices and to
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
minimize amounts of material needed for testing, and
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.2.3 The specimen can be tested using a standard Izod
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
pendulum tester.
4.3 It has been found that a 12.7-mm [0.500-in.] wide strip
2. Referenced Documents
2
with a thickness in the range from 1.02 to 3.18 mm [0.040 to
2.1 ASTM Standards:
0.125 in.] meets the above criteria. Much experimental work
on 1.78-mm [0.070-in.] strips has demonstrated the utility of
the chip-impact test to track weather aging of a variety of
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD20onPlastics
materials.
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.10 on Mechanical Properties.
4.4 The distance (L) between clamping and impact points
Current edition approved March 15, 2006. Published March 2006. Originally
(striker height) will affect test results. Extensive experimental
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D4508-05. DOI:
10.1520/D4508-06.
work has established that a ratio of L = 2.182 h (where L is the
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
distance between clamping and impact points and h is the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
thickness of the specimen) will provide accurate and sensitive
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. chip-impact values. Increasing this ratio (that is, raising the
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copy
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.