ASTM D5534-94(2005)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Vapor-Phase Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Hydraulic Fluids
Standard Test Method for Vapor-Phase Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Hydraulic Fluids
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Procedures such as Test Methods D 665 and D 3603 assess the ability of new or unused hydraulic fluid to prevent rusting on wetted steel surfaces but do not address the prevention of rusting in the vapor space above the fluid. This procedure addresses the latter question under one set of test conditions and need not be applicable to some service conditions. Since used fluids have not been cooperatively tested in this procedure, its utility for in-service monitoring has not been established.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the ability of hydraulic fluids to prevent the rusting of steel in the vapor phase over the hydraulic fluid and water.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D5534–94 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Test Method for
Vapor-Phase Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Hydraulic
Fluids
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5534; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope BS 970: 1955–EN3B Specification for wrought steels
1.1 This test method covers the ability of hydraulic fluids to
3. Summary of Test Method
prevent the rusting of steel in the vapor phase over the
3.1 This test method is divided into two parts:
hydraulic fluid and water.
3.1.1 Part A—Used only for fluids where water is the
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
continuous phase. Examples of such fluids include water-
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
glycol hydraulic fluids and high-water-content hydraulic fluids.
only.
Do not use PartAto evaluate invert emulsion hydraulic fluids.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.2 Part B—Used for both water-containing fluids and
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
completely water-free fluids such as petroleum based hydraulic
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
fluids, except phosphate esters. In Part B a small beaker of
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
water is present to provide water vapor to cause corrosion in
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
the absence of a vapor-phase inhibitor in the fluid. Part B is the
2. Referenced Documents appropriate procedure for evaluating invert emulsion hydraulic
fluids.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2 In both Part A and Part B, a steel specimen is attached
A108 Specification for Steel Bar, Carbon and Alloy, Cold-
to the underside of the cover of a beaker containing the fluid
Finished
undertest.Theapparatusandspecimenareidenticaltothoseof
A240/A240M Specification for Chromium and Chromium-
Test Method D3603. The fluid is brought to a test temperature
Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure
of 60°C (140°F).
Vessels and for General Applications
3.3 InPartB,thetestspecimenisexposedtothevaporfrom
D91 Test Method for Precipitation Number of Lubricating
the fluid for 30 min prior to the introduction of water.Abeaker
Oils
of water is then placed in the undercarriage of the cover.
D665 Test Method for Rust-Preventing Characteristics of
3.4 After 6 h, the apparatus is disassembled and the speci-
Inhibited Mineral Oil in the Presence of Water
men is rated visually for the presence of rust.
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
3.5 Since the apparatus and test conditions are identical,
D3603 Test Method for Rust-Preventing Characteristics of
Part A can be completed simultaneously with Test Method
Steam Turbine Oil in the Presence of Water (Horizontal
D3603 by adding the vapor-phase specimen to that procedure.
Disk Method)
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
4. Significance and Use
2.2 Other Standards:
3 4.1 Procedures such as Test Methods D665 and D3603
IP 60/80 Specification for Petroleum Spirit
assess the ability of new or unused hydraulic fluid to prevent
rusting on wetted steel surfaces but do not address the
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
prevention of rusting in the vapor space above the fluid. This
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
procedure addresses the latter question under one set of test
D02.N0 on Hydraulic Fluids.
conditions and need not be applicable to some service condi-
Current edition approved May 1, 2005. Published May 2005. Originally
approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D5534–94(1999). tions. Since used fluids have not been cooperatively tested in
DOI: 10.1520/D5534-94R05.
thisprocedure,itsutilityforin-servicemonitoringhasnotbeen
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
established.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3 4
Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London, WIG 7AR, Available from IHS Engineering/IHS International, 15 Inverness Way, East
U.K. Englewood, CO 80112.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D5534–94 (2005)
NOTE—All dimensions are in millimetres (inches).
FIG. 2 Beaker Cover
present even for PartA, to prevent vortexing. The holding rod,
appropriate for this apparatus, is depicted in Fig. 4.
NOTE—All dimensions are in millimetres (inches).
NOTE 3—Other holders suitable for supporting the specimen in Test
FIG. 1 Rusting Test Apparatus
MethodD3603arealsosuitableforsupportingthewaterbeakerinthistest
method. The undercarriage design is not considered to be critical.
5. Apparatus
5.4 Stirrer—Constructed entirely from stainless steel in the
form of an inverted T (Fig. 5). A flat blade 25.4 by 6.1 by 0.6
5.1 Oil Bath—Thermostatically controlled liquid bath ca-
mm(1by0.24by0.024in.)shallbeattachedtoa6.1mm(0.24
pable of maintaining a temperature in the oil sample of 60 6
1°C (140 6 2°F). The bath shall have holes to accommodate in.)rodinsuchawaythatthebladeissymmetricalwiththerod
and has its flat surface in the vertical pane.
the test beakers.
NOTE 1—ThebathusedforTestMethodD665canbeusedwithaslight NOTE 4—A suitable material is an 18 % chromium, 8 % nickel alloy
modification, that is, the centers of the beaker holes are moved from 6.4 steel conforming to Type 304 of SpecificationA240/A240M, or SAE No.
1 23
mm to 18.3 mm ( ⁄4 to ⁄32 in.) from the axis of the stirrers. 30304, or BS 970: Part 1: 1983: 302531.
NOTE 2—To indicate the temperature, a thermometer conforming to the
NOTE 5—Ifstainlesssteelisnotavailable,stirrersmadeofheatresistant
requirements of ASTM Thermometer 9C or 9F, or IP Thermometer 21C,
glass and having approximately the same dimensions as the stainless steel
as prescribed in Specification E1 should be used. 6
stirrers can be used.
5.2 Beaker—400-mL, Berzelius-type, tall-form heat resis-
5.5 Stirring Apparatus—Any convenient form of stirring
tant glass beaker, approximately 127 mm (5 in.) in height
apparatus capable of maintaining a speed of 1000 6 50 rpm.
measured from the inside bottom center and approximately 70
5.6 Grinding and Polishing Equipment—150- and 240- grit
mm (2 ⁄4 in.) in inside diameter measured at the middle, and
metalworking aluminum oxide abrasive cloth, closed coat on a
without pourout (see Fig. 1).
jeans backing, a suitable chuck (Fig. 6) for holding the
5.3 Beaker Cover (Fig. 2) and Specimen Holder (Fig.
specimen, and a means of rotating the specimen at a speed of
3)—Flat beaker cover of 4.8 mm ( ⁄16 in.) methyl methacrylate
1700 to 1800 rpm.
resin or other fluid-resistant material, kept in position by a
5.7 Water Beaker for Part B—Flat-bottomed beaker made
suitablegroove.Threeholes,7.9mm( ⁄16in.)indiameter,shall
from 30 mm (1.2 in.) outside diameter standard wall glass
be provided.Two are located on any diameter of the cover, one
tubing, 50 mm (2.0 in.) high. It should fit snugly in the
for a stirrer 18.3 mm ( ⁄32 in.) from the cover’s center, and the
undercarriage of the specimen holder.
other for the vapor-phase test specimen 7.9 mm ( ⁄16 in.) from
the center on the opposite side. The third hole, for a thermom-
6. Reagents and Materials
eter, is located 27 mm (1 ⁄16 in.) from the center on a diameter
6.1 Cleaning Agents—One of the following shall be used.
perpendicular to that of the other two holes. The undercarriage
is a Test Method D3603 specimen holder suitably attached to
6.1.1 ASTM Precipitation Naphtha, conforming to Test
the beaker cover, used here to support the water beaker (see
Method D91.(Warning—Precipitation naphtha is flammable
5.7)usedinPartB.Onesuitableundercarriage(theoneusedin
and a health hazard.)
the round-robin) is shown in Fig. 1. An undercarriage must be
5 6
British Standard 2, 1965 Section 5, or equivalent, may be used. Borosilicate glass is satisfactory for this purpose.
D5534–94 (2005)
NOTE—All dimensions are in millimetres (inches).
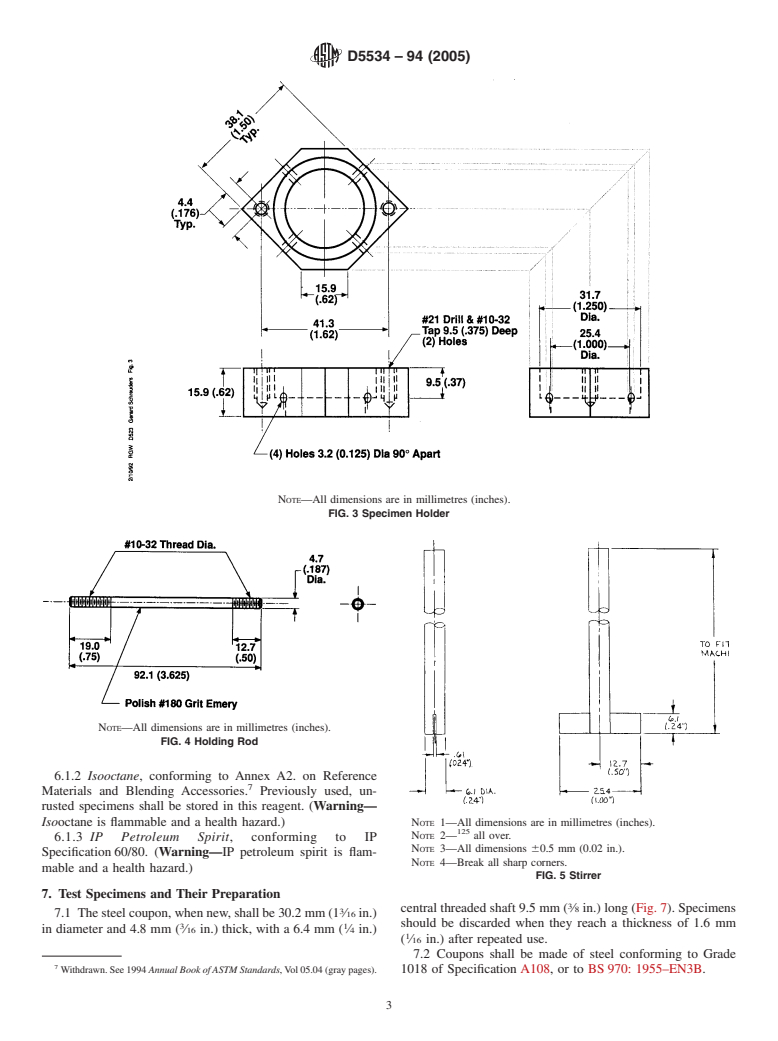
FIG. 3 Specimen Holder
NOTE—All dimensions are in millimetres (inches).
FIG. 4 Holding Rod
6.1.2 Isooctane, conforming to Annex A2. on Reference
Materials and Blending Accessories. Previously used, un-
rusted specimens shall be stored in this reagent. (Warning—
Isooctane is flammable and a health hazard.) NOTE 1—All dimensions are in millimetres (inches).
NOTE 2— all over.
6.1.3 IP Petroleum Spirit, conforming to IP
NOTE 3—All dimensions 60.5 mm (0.02 in.).
Specification 60/80. (Warning—IP petroleum spirit
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.