ASTM B111/B111M-08
(Specification)Standard Specification for Copper and Copper-Alloy Seamless Condenser Tubes and Ferrule Stock
Standard Specification for Copper and Copper-Alloy Seamless Condenser Tubes and Ferrule Stock
ABSTRACT
This specification establishes the requirements for seamless tube and ferrule stock of copper and various copper alloys of a specified range of diameters, for use in surface condensers, evaporators, and heat exchangers. The specified coppers and copper alloys are UNS No. C10100, C10200, C10300, C10800, C12000, C12200, C14200, C19200, C23000, C28000, C44300, C44400, C44500, C60800, C61300, C61400, C68700, C70400, C70600, C70620, C71000, C71500, C71520, C71640, and C72200. The product shall be produced by processes such as casting, extrusion, drawing, annealing, straightening, trimming, and other processes which may produce a seamless tube in the specified condition. The coppers and copper alloys shall be specifically furnished in any one of the following tempers: annealed, light-drawn, hard-drawn, or hard drawn and end annealed. Tubes for ferrule stock shall be annealed sufficiently to be fully crystallized. Some tubes are suggested to be subjected to a stress-relieving thermal treatment subsequent to straightening. The products shall be subjected to expansion, flattening, and residual stress tests. The tensile and expansion requirements for the products are specified in accordance with the temper designation. The products shall also be subjected to mercurous nitrate, ammonia vapor, Eddy-current, hydrostatic, and pneumatic tests.
SCOPE
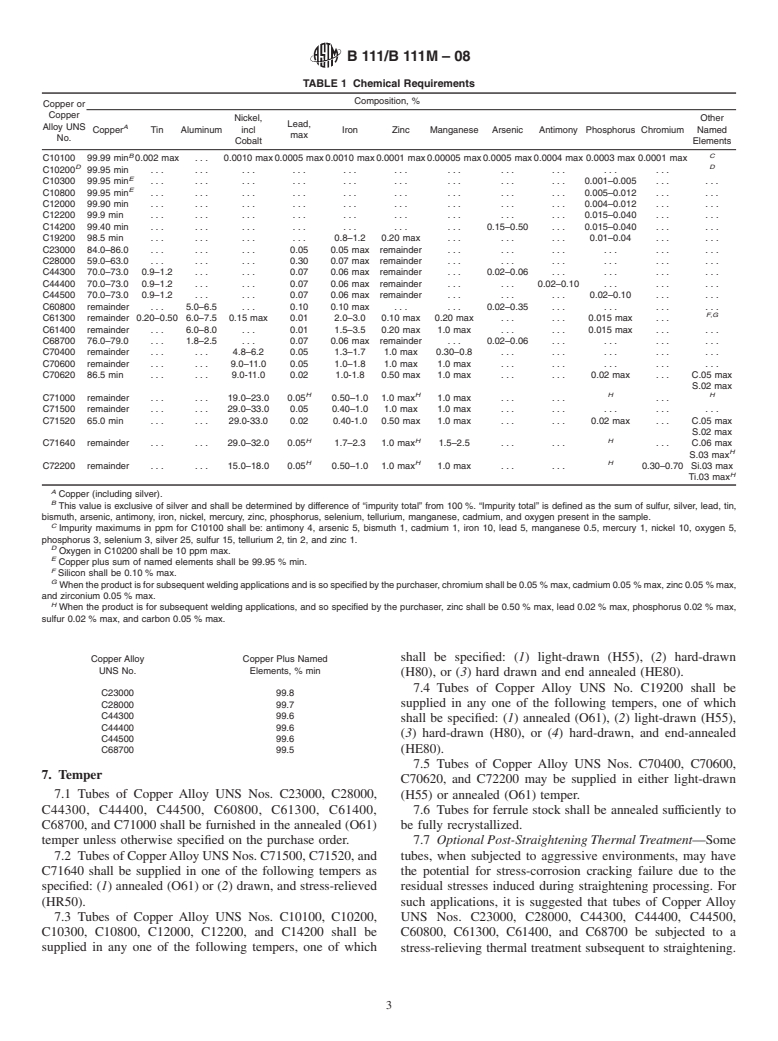
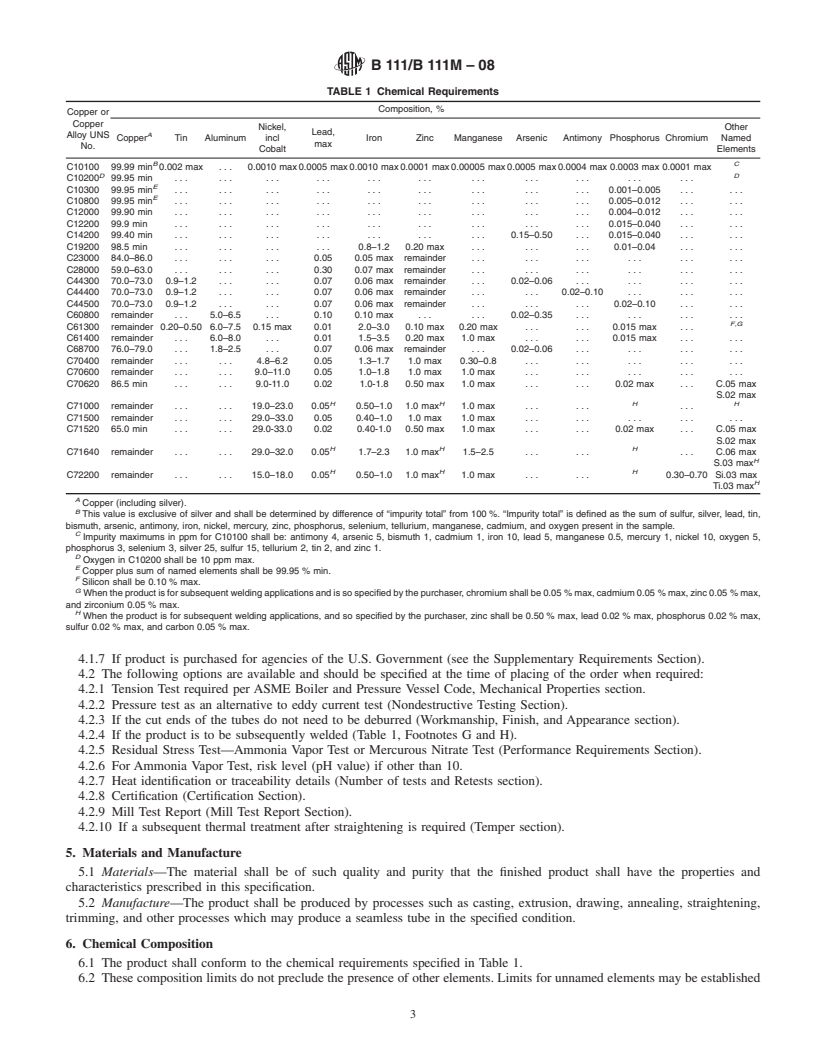
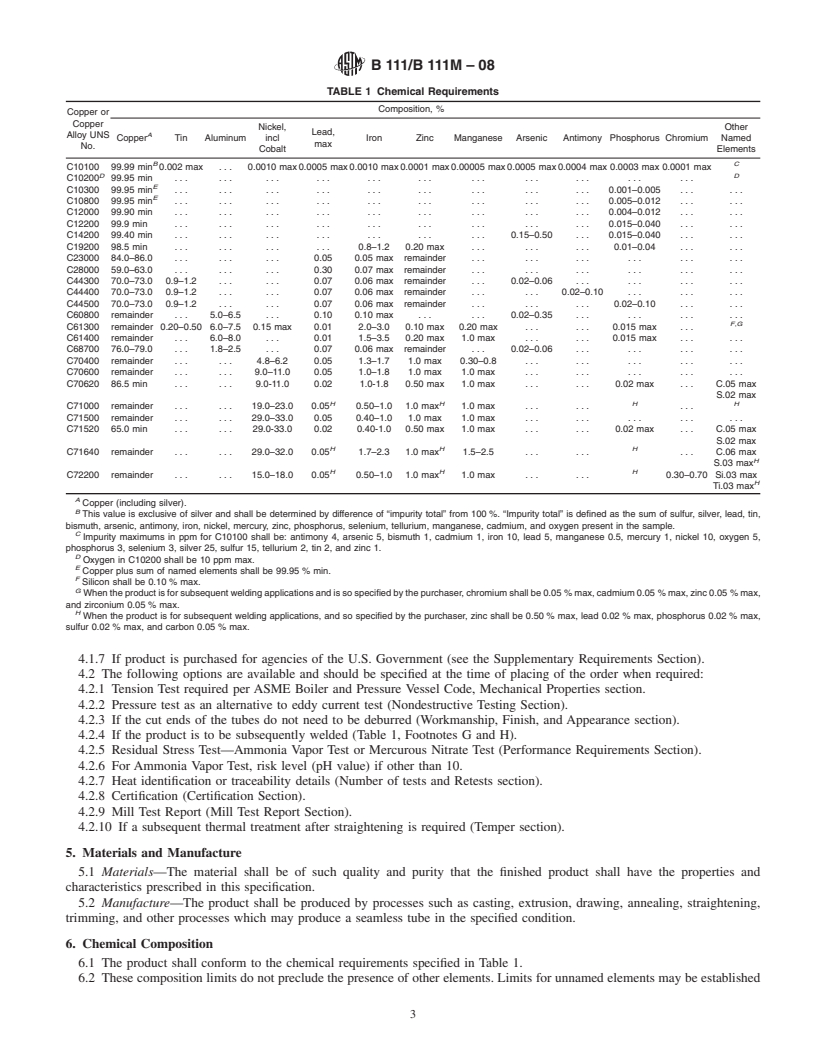
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for seamless tube and ferrule stock of copper and various copper alloys up to 31/8 in. [80 mm] inclusive, in diameter, for use in surface condensers, evaporators, and heat exchangers. The following coppers and copper alloys are specified: (Warning—Mercury is a definite health hazard in use and disposal. (See 12.1.))
Copper or
Copper
Alloy
UNS No. Previously
Used
Designation
Description C10100OFEOxygen-free electronic C10200OFAOxygen-free without residual deoxidants C10300. . .Oxygen-free, extra low phosphorus C10800. . .Oxygen-free, low phosphorus C12000DLPAPhosphorized, low residual phosphorus C12200DHPAPhosphorized, high residual phosphorus C14200DPAAPhosphorized, arsenical C19200. . .Phosphorized, 1 % iron C23000. . .Red Brass C28000. . .Muntz Metal C44300. . .Admiralty Metals, B, C, and D C44400 C44500 C60800 . . . Aluminum Bronze C61300. . .. . . C61400. . .Aluminum Bronze, D C68700. . .Aluminum Brass, B C70400. . .95-5 Copper-Nickel C70600. . .90-10 Copper-Nickel C70620. . .90-10 Copper-Nickel—Welding Grade C71000. . .80-20 Copper-Nickel C71500. . .70-30 Copper-Nickel C71520. . .70-30 Copper-Nickel—Welding Grade C71640. . .Copper-nickel-iron-manganese C72200. . .. . .
A Designations listed in Classification B 224.
1.2 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 19, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B 111/B 111M – 08
Standard Specification for
Copper and Copper-Alloy Seamless Condenser Tubes and
1
Ferrule Stock
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 111/B 111M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
C70620 . . . 90-10 Copper-Nickel—Welding Grade
C71000 . . . 80-20 Copper-Nickel
2
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for
C71500 . . . 70-30 Copper-Nickel
seamless tube and ferrule stock of copper and various copper
C71520 . . . 70-30 Copper-Nickel—Welding Grade
1 C71640 . . . Copper-nickel-iron-manganese
alloys up to 3 ⁄8 in. [80 mm] inclusive, in diameter, for use in
C72200 . . . . . .
surface condensers, evaporators, and heat exchangers. The
A
Designations listed in Classification B 224.
following coppers and copper alloys are
1.2 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-
3
specified: (Warning—Mercury is a definite health hazard in
pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The
use and disposal. (See 12.1.))
values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents;
Copper or
therefore,eachsystemshallbeusedindependentlyoftheother.
Copper Previously
Combining values from the two systems may result in non-
Alloy Used
UNS No. Designation Description
conformance with the standard.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
C10100 OFE Oxygen-free electronic
A
test methods portion, Section 19, of this specification: This
C10200 OF Oxygen-free without residual deoxidants
C10300 . . . Oxygen-free, extra low phosphorus
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
C10800 . . . Oxygen-free, low phosphorus
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
A
C12000 DLP Phosphorized, low residual phosphorus
A
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
C12200 DHP Phosphorized, high residual phosphorus
A
C14200 DPA Phosphorized, arsenical
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
C19200 . . . Phosphorized, 1 % iron
tions prior to use.
C23000 . . . Red Brass
C28000 . . . Muntz Metal
2. Referenced Documents
C44300 . . . Admiralty Metals, B, C, and D
C44400
2.1 The following documents in the current issue of the
C44500
Annual Book of ASTM Standards form a part of this specifi-
C60800 . . . Aluminum Bronze
C61300 . . . . . .
cation to the extent referenced herein:
C61400 . . . Aluminum Bronze, D 4
2.2 ASTM Standards:
C68700 . . . Aluminum Brass, B
B 153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and
C70400 . . . 95-5 Copper-Nickel
C70600 . . . 90-10 Copper-Nickel
Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing
B 154 Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper
Alloys
B 170 Specification for Oxygen-Free Electrolytic Copper—
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper
Refinery Shapes
and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe
B 224 Classification of Coppers
and Tube.
Current edition approved April 1, 2008. Published April 2008. Originally B 846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
approved in 1937. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as B 111/B 111M – 04.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specifi-
cation SB-111 in Section II of the Code.
3 4
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E 527) is a simple For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
of a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
composition variations of the base alloy. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B 111/B 111M – 08
B 858 Test Method for Ammonia Vapor Test for Determin- 4.2.1 Tension Test required per ASME Boiler and Pressure
ing Susceptibility to Stress Corrosion Cracking in Copper Vessel Code, Mechanical Properties section.
Alloys 4.2.2 Pressure test as an alternative to eddy current test
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials (Nondestructive Testing Section).
E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Mate- 4.2.3 If the cut ends of the tubes do not need to be de
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B111/B111M–04 Designation: B 111/B 111M – 08
Standard Specification for
Copper and Copper-Alloy Seamless Condenser Tubes and
1
Ferrule Stock
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 111/B 111M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for seamless tube and ferrule stock of copper and various copper alloys up
1
to 3 ⁄8 in. [80 mm] inclusive, in diameter, for use in surface condensers, evaporators, and heat exchangers. The following coppers
3
and copper alloys are specified: (Warning—Mercury is a definite health hazard in use and disposal. (See 12.1.))
Copper or
Copper Previously
Alloy Used
UNS No. Designation Description
C10100 OFE Oxygen-free electronic
A
C10200 OF Oxygen-free without residual deoxidants
C10300 . . . Oxygen-free, extra low phosphorus
C10800 . . . Oxygen-free, low phosphorus
A
C12000 DLP Phosphorized, low residual phosphorus
A
C12200 DHP Phosphorized, high residual phosphorus
A
C14200 DPA Phosphorized, arsenical
C19200 . . . Phosphorized, 1 % iron
C23000 . . . Red Brass
C28000 . . . Muntz Metal
C44300 . . . Admiralty Metals, B, C, and D
C44400
C44500
C60800 . . . Aluminum Bronze
C61300 . . . . . .
C61400 . . . Aluminum Bronze, D
C68700 . . . Aluminum Brass, B
C70400 . . . 95-5 Copper-Nickel
C70600 . . . 90-10 Copper-Nickel
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B05 on Copper and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe and
Tube.
´2
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2004. Published October 2004. Originally approved in 1937. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as B111–98 .
Current edition approved April 1, 2008. Published April 2008. Originally approved in 1937. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as B 111/B 111M – 04.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specification SB-111 in Section II of the Code.
3
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E 527) is a simple expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition of
a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate composition variations of the base alloy.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B 111/B 111M – 08
C70620 . . . 90-10 Copper-Nickel—Welding Grade
C71000 . . . 80-20 Copper-Nickel
C71500 . . . 70-30 Copper-Nickel
C71520 . . . 70-30 Copper-Nickel—Welding Grade
C71640 . . . Copper-nickel-iron-manganese
C72200 . . . . . .
A
Designations listed in Classification B 224.
1.2 Units—Values —The values stated in either inch-poundSI units or SIinch-pound units are to be regarded separately as
standard.Within the text, SI units are shown in brackets.The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore,
each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with
the standard.
1.3 Thefollowingsafetyhazardscaveatpertainsonlytothetestmethodsportion,Section19,ofthisspecification: This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 The following documents in the current issue of the Annual Book of ASTM Standards form a part of this specification to
the extent referenced herein:
4
2.2 ASTM Standards:
B 153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing
B 154 Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper and Copper Alloys
B 170 Specification for Oxygen-Free Electrolytic Copper—Refinery Shapes
B 224 Classification of Coppers
B 846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
B 858 Test Method for Ammonia Vapor Test for Determining Susceptibility to Stress Corrosion Cracking in Copper Alloys
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E8M Test Methods for Tension T
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B111/B111M–04 Designation: B 111/B 111M – 08
Standard Specification for
Copper and Copper-Alloy Seamless Condenser Tubes and
1
Ferrule Stock
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 111/B 111M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for seamless tube and ferrule stock of copper and various copper alloys up
1
to 3 ⁄8 in. [80 mm] inclusive, in diameter, for use in surface condensers, evaporators, and heat exchangers. The following coppers
3
and copper alloys are specified: (Warning—Mercury is a definite health hazard in use and disposal. (See 12.1.))
Copper or
Copper Previously
Alloy Used
UNS No. Designation Description
C10100 OFE Oxygen-free electronic
A
C10200 OF Oxygen-free without residual deoxidants
C10300 . . . Oxygen-free, extra low phosphorus
C10800 . . . Oxygen-free, low phosphorus
A
C12000 DLP Phosphorized, low residual phosphorus
A
C12200 DHP Phosphorized, high residual phosphorus
A
C14200 DPA Phosphorized, arsenical
C19200 . . . Phosphorized, 1 % iron
C23000 . . . Red Brass
C28000 . . . Muntz Metal
C44300 . . . Admiralty Metals, B, C, and D
C44400
C44500
C60800 . . . Aluminum Bronze
C61300 . . . . . .
C61400 . . . Aluminum Bronze, D
C68700 . . . Aluminum Brass, B
C70400 . . . 95-5 Copper-Nickel
C70600 . . . 90-10 Copper-Nickel
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B05 on Copper and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe and
Tube.
e2
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2004. Published October 2004. Originally approved in 1937. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as B111–98 .
Current edition approved April 1, 2008. Published April 2008. Originally approved in 1937. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as B 111/B 111M – 04.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specification SB-111 in Section II of the Code.
3
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E 527) is a simple expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition of
a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate composition variations of the base alloy.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B 111/B 111M – 08
C70620 . . . 90-10 Copper-Nickel—Welding Grade
C71000 . . . 80-20 Copper-Nickel
C71500 . . . 70-30 Copper-Nickel
C71520 . . . 70-30 Copper-Nickel—Welding Grade
C71640 . . . Copper-nickel-iron-manganese
C72200 . . . . . .
A
Designations listed in Classification B 224.
1.2 Units—Values —The values stated in either inch-poundSI units or SIinch-pound units are to be regarded separately as
standard.Within the text, SI units are shown in brackets.The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore,
each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with
the standard.
1.3 Thefollowingsafetyhazardscaveatpertainsonlytothetestmethodsportion,Section19,ofthisspecification: This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 The following documents in the current issue of the Annual Book of ASTM Standards form a part of this specification to
the extent referenced herein:
4
2.2 ASTM Standards:
B 153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing
B 154 Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper and Copper Alloys
B 170 Specification for Oxygen-Free Electrolytic Copper—Refinery Shapes
B 224 Classification of Coppers
B 846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
B 858 Test Method for Ammonia Vapor Test for Determining Susceptibility to Stress Corrosion Cracking in Copper Alloys
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E 8M Test Methods for Tension
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.