ASTM F3042-13(2018)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Nonferrous Hex Socket, Slotted Headless, and Square Head Set Screws
Standard Specification for Nonferrous Hex Socket, Slotted Headless, and Square Head Set Screws
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for nonferrous socket set screws sizes 0.125 (#5) through 2.000 in., square head set screws sizes 0.190 (#10) through 1.500 in., and slotted headless set screws 0.125 (#5) through 0.750 in. in diameter manufactured from a number of nonferrous alloys in use in the marine industry and the U.S. Navy subject to seawater wetting and salt atmosphere but that also may be used in other applications. It is recommended that copper-based alloys not be used in attempting to prevent mechanical components from rotating, such as locking shafts, because of the low hardness of the alloys. Some alloys or sizes or both of set screws may not be readily available. Manufacturers or suppliers should be contacted before design development or anticipated procurement.
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
Note 1: A complete metric companion to Specification F3042 will be developed—F3042M; therefore, no metric equivalents are shown in this specification.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F3042 −13 (Reapproved 2018)
Standard Specification for
Nonferrous Hex Socket, Slotted Headless, and Square Head
Set Screws
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F3042; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for nonfer- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
rous socket set screws sizes 0.125 (#5) through 2.000 in., B154Test Method for Mercurous Nitrate Test for Copper
squareheadsetscrewssizes0.190(#10)through1.500in.,and Alloys
slotted headless set screws 0.125 (#5) through 0.750 in. in E18Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
diameter manufactured from a number of nonferrous alloys in terials
use in the marine industry and the U.S. Navy subject to E29Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
seawaterwettingandsaltatmospherebutthatalsomaybeused Determine Conformance with Specifications
in other applications. It is recommended that copper-based E53Test Method for Determination of Copper in Unalloyed
alloys not be used in attempting to prevent mechanical com- Copper by Gravimetry
ponents from rotating, such as locking shafts, because of the E54Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Special Brasses
low hardness of the alloys. Some alloys or sizes or both of set and Bronzes (Withdrawn 2002)
screws may not be readily available. Manufacturers or suppli- E55Practice for Sampling Wrought Nonferrous Metals and
ers should be contacted before design development or antici- Alloys for Determination of Chemical Composition
pated procurement. E62Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and
CopperAlloys(PhotometricMethods)(Withdrawn2010)
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-pound units are to be
E75Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-Nickel
regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are
and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys (Withdrawn 2010)
included in this standard.
E76Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel-Copper
NOTE 1—Acomplete metric companion to Specification F3042 will be
Alloys (Withdrawn 2003)
developed—F3042M; therefore, no metric equivalents are shown in this
specification.
E120Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Titanium and
Titanium Alloys (Withdrawn 2003)
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
E165Practice for Liquid Penetrant Examination for General
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Industry
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
E350Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Carbon Steel,
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
Low-Alloy Steel, Silicon Electrical Steel, Ingot Iron, and
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Wrought Iron
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
E354 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of High-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
Temperature,Electrical,Magnetic,andOtherSimilarIron,
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Nickel, and Cobalt Alloys
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
E384Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Mate-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
rials
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
E478Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of CopperAlloys
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F16 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Fasteners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.04 on Nonferrous contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Fasteners. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2018. Published September 2018. Originally the ASTM website.
approved in 2013. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as E3042–13. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/F3042-13. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F3042 − 13 (2018)
E1409TestMethodforDeterminationofOxygenandNitro- 4.2 Example—50 000 pieces, 0.250-20 × 0.375 cone point,
gen in Titanium and TitaniumAlloys by Inert Gas Fusion nickel copper socket set screw, stress relieved, ASTM
F788/F788MSpecification for Surface Discontinuities of F3042–13.
Bolts, Screws, and Studs, Inch and Metric Series
5. Materials and Manufacture
F1470Practice for Fastener Sampling for Specified Me-
5.1 Materials:
chanical Properties and Performance Inspection
5.1.1 The screws shall be manufactured from material
2.2 ASME Standards:
havingachemicalcompositionconformingtotherequirements
ASME B1.1Unified Inch Screw Threads (UN and UNR
in Table 1 and capable of developing the required mechanical
Thread Form)
properties for the specified alloy in the finished fastener.
ASME B18.3Socket Cap, Shoulder and Set Screws, Hex
5.1.2 The starting condition of the raw material shall be at
and Spline Keys (Inch Series)
the discretion of the fastener manufacturer but shall be such
ASME B18.6.2Slotted Head Cap Screws, Square Head Set
that the finished products conform to all of the specified
Screws, and Slotted Headless Set Screws Inch Series
requirements.
2.3 SAE Standards:
AMS2485Coating, Black Oxide
5.2 Manufacture:
AMS2487Anodic Treatment of Titanium and Titanium
5.2.1 Forming—The screw may be forged, cold or hot
Alloys Solution pH 12.4 Maximum
formed,ormachinedfromsuitablematerialattheoptionofthe
AMS2488Anodic Treatment—Titanium and Titanium Al-
supplier to meet requirements.
loys Solution pH 13 or Higher
5.2.2 Condition—The fasteners shall be furnished in the
J2656Fastener Part Standard—Hexagon Socket, Square
following conditions:
Head, and Slotted Headless Set Screws—Inch Dimen-
Alloy Condition
sioned Copper (all alloys) As formed or stress relieved at
6 manufacturer’s option
2.4 Federal Standards and Specifications:
Nickel alloys:
QQ-N-286Nickel-Copper-AluminumAlloy, Wrought (UNS
400 and 405 As formed or stress relieved at
manufacturer’s option
N05500)
500 Solution annealed and aged
625 Annealed
3. Classification
686 As formed
Titanium As formed
3.1 The designation of the alloys of this specification shall
5.2.3 Stress Relieving—Whenrequired,stressrelievingshall
be consistent with the nonferrous designations in Table 1.
bespecifiedbythepurchaserfornickelalloys400and405and
4. Ordering Information
all copper alloys.
5.2.4 Threads—Unlessotherwisespecified,thethreadsshall
4.1 Ordersformaterialunderthisspecificationshallinclude
be rolled or cut at the option of the manufacturer.
the following information:
4.1.1 Quantity (number of screws);
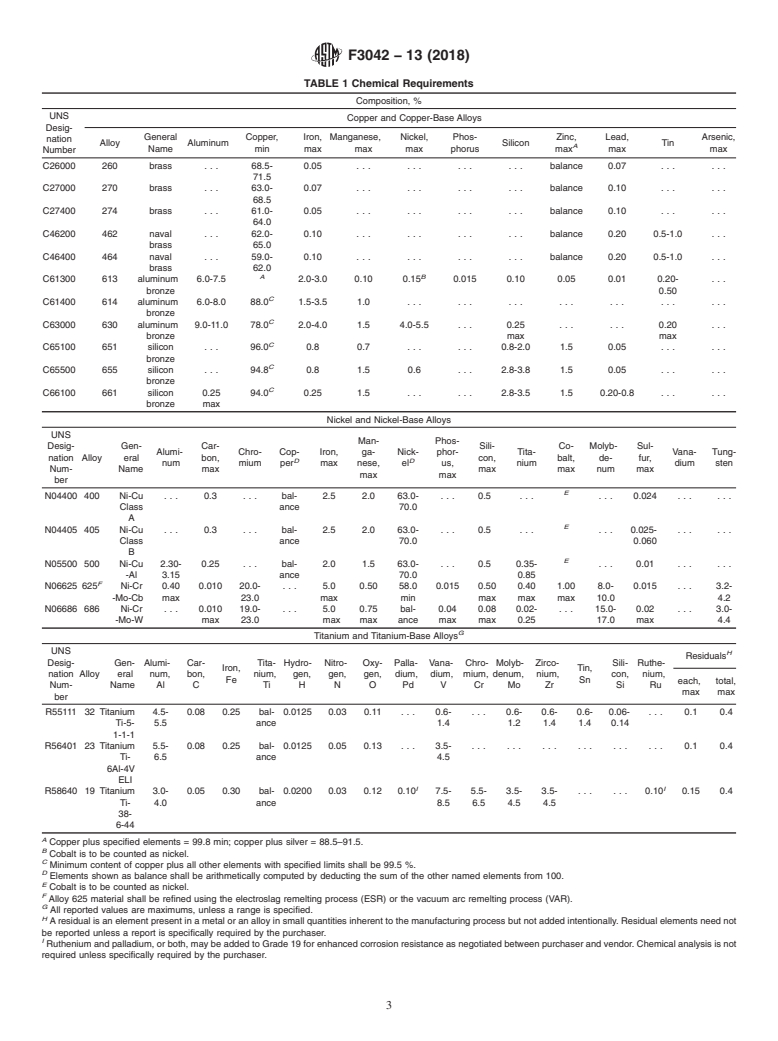
6. Chemical Composition
4.1.2 Name of the screw (hex socket set screw, slotted
6.1 The analysis of the screw material shall conform to the
headless set screw, or square head set screw);
chemical composition specified in Table 1.
4.1.3 Dimensions, including nominal thread designation,
thread pitch and fit, nominal screw length (inches), and point
6.2 Manufacturer’s Analysis—When test reports are re-
configuration. A standard part number in accordance with a
quired on the inquiry or purchase order (see 4.1.8), the
nationally recognized organization or society may be used for
manufacturer shall make individual analyses of randomly
this definition;
selected finished fasteners from the product to be shipped and
4.1.4 Alloy number;
report the results to the purchaser, except as provided in 6.3.2.
4.1.5 Stress relieving, if required;
Alternatively, if heat and lot identities have been maintained,
4.1.6 If titanium is not to be coated;
the analysis of the raw material from which the fasteners have
4.1.7 Black oxide coating, if required (not recommended);
been manufactured may be reported instead of product analy-
4.1.8 Shipment lot testing, as required;
sis.
4.1.9 Source inspection, if required;
6.3 Product Analysis:
4.1.10 Certificate of compliance or test report, if required;
6.3.1 Product analyses may be made by the purchaser from
4.1.11 Additionalrequirements,ifany,tobespecifiedonthe
finished products representing each lot. The chemical compo-
purchase order (see Supplementary Requirements); and
sition thus determined shall conform to the requirements in
4.1.12 ASTM International specification and year of issue.
Table 1.
6.3.2 In the event of disagreement, a referee chemical
analysis of samples from each lot shall be made in accordance
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http:// with 11.1 and 11.1.1.
www.asme.org.
AvailablefromSAEInternational(SAE),400CommonwealthDr.,Warrendale, 7. Mechanical Properties
PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
7.1 The hardness limits from Table 2 shall be met as
Available from DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Ave.,
Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil. determined using Test Methods E18.
F3042 − 13 (2018)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
UNS
Copper and Copper-Base Alloys
Desig-
General Copper, Iron, Manganese, Nickel, Phos- Zinc, Lead, Arsenic,
nation
Alloy Aluminum Silicon Tin
A
Name min max max max phorus max max max
Number
C26000 260 brass . . . 68.5- 0.05 . . . . . . . . . . . . balance 0.07 . . . . . .
71.5
C27000 270 brass . . . 63.0- 0.07 . . . . . . . . . . . . balance 0.10 . . . . . .
68.5
C27400 274 brass . . . 61.0- 0.05 . . . . . . . . . . . . balance 0.10 . . . . . .
64.0
C46200 462 naval . . . 62.0- 0.10 . . . . . . . . . . . . balance 0.20 0.5-1.0 . . .
brass 65.0
C46400 464 naval . . . 59.0- 0.10 . . . . . . . . . . . . balance 0.20 0.5-1.0 . . .
brass 62.0
A B
C61300 613 aluminum 6.0-7.5 2.0-3.0 0.10 0.15 0.015 0.10 0.05 0.01 0.20- .
bronze 0.50
C
C61400 614 aluminum 6.0-8.0 88.0 1.5-3.5 1.0 . . . . . . .
bronze
C
C63000 630 aluminum 9.0-11.0 78.0 2.0-4.0 1.5 4.0-5.5 . . . 0.25 . . 0.20 .
bronze max max
C
C65100 651 silicon . 96.0 0.8 0.7 . . . . . . 0.8-2.0 1.5 0.05 . . . . . .
bronze
C
C65500 655 silicon . 94.8 0.8 1.5 0.6 . . . 2.8-3.8 1.5 0.05 . . . . . .
bronze
C
C66100 661 silicon 0.25 94.0 0.25 1.5 . . . . . . 2.8-3.5 1.5 0.20-0.8 . . . . . .
bronze max
Nickel and Nickel-Base Alloys
UNS
Man- Phos-
Desig- Gen- Car- Sili- Co- Molyb- Sul-
Alumi- Chro- Cop- Iron, ga- Nick- phor- Tita- Vana- Tung-
nation Alloy eral bon, con, balt, de- fur,
D D
num mium per max nese, el us, nium dium sten
Num- Name max max max num max
max max
ber
E
N04400 400 Ni-Cu . 0.3 . bal- 2.5 2.0 63.0- . 0.5 . . 0.024 . .
Class ance 70.0
A
E
N04405 405 Ni-Cu . 0.3 . bal- 2.5 2.0 63.0- . 0.5 . . . . 0.025- . .
Class ance 70.0 0.060
B
E
N05500 500 Ni-Cu 2.30- 0.25 . . . bal- 2.0 1.5 63.0- . . . 0.5 0.35- . 0.01 . .
-Al 3.15 ance 70.0 0.85
F
N06625 625 Ni-Cr 0.40 0.010 20.0- . 5.0 0.50 58.0 0.015 0.50 0.40 1.00 8.0- 0.015 . . . 3.2-
-Mo-Cb max 23.0 max min max max max 10.0 4.2
N06686 686 Ni-Cr . . . 0.010 19.0- . 5.0 0.75 bal- 0.04 0.08 0.02- . . . 15.0- 0.02 . . . 3.0-
-Mo-W max 23.0 max max ance max max 0.25 17.0 max 4.4
G
Titanium and Titanium-Base Alloys
UNS
H
Residuals
Desig- Gen- Alumi- Car- Tita- Hydro- Nitro- Oxy- Palla- Vana- Chro- Molyb- Zirco- Sili- Ruthe-
Iron, Tin,
nation Alloy eral num, bon, nium, gen, gen, gen, dium, dium, mium, denum, nium, con, nium,
Fe Sn
each, total,
Num- Name Al C Ti H N O Pd V Cr Mo Zr Si Ru
max max
ber
R55111 32 Titanium 4.5- 0.08 0.25 bal- 0.0125 0.03 0.11 . . . 0.6- . . . 0.6- 0.6- 0.6- 0.06- . 0.1 0.4
Ti-5- 5.5 ance 1.4 1.2 1.4 1.4 0.14
1-1-1
R56401 23 Titanium 5.5- 0.08 0.25 bal- 0.0125 0.05 0.13 . . . 3.5- . . . . . . 0.1 0.4
Ti- 6.5 ance 4.5
6Al-4V
ELI
I I
R58640 19 Titanium 3.0- 0.05 0.30 bal- 0.0200 0.03 0.12 0.10 7.5- 5.5- 3.5- 3.5- . . 0.10 0.15 0.4
Ti- 4.0 ance 8.5 6.5 4.5 4.5
38-
6-44
A
Copper plus specified elements = 99.8 min; copper plus silver = 88.5–91.5.
B
Cobalt is to be counted as nickel.
C
Minimum content of copper plus all other elements with specified limits shall be 99.5 %.
D
Elements shown as balance shall be arithmetically computed by deducting the sum of the other named elements from 100.
E
Cobalt is to be counted as nickel.
F
Alloy 625 material shall be refined using the electroslag remelting process (ESR) or the vacuum arc remelting process (VAR).
G
All reported values are maximums, unless a range is specified.
H
A residual is an element present in a metal or an alloy in small quantities inherent to the manufacturing process but not added intentionally. Residual elements need not
be reported unless a report is specifically required by the purchaser.
I
Ruthenium and palladium, or both, may be added to Grade 19 for enhanced corrosion resistance as negotiated between purchaser and vendor. Chemical analysis is not
required unless specifically required by the purchaser.
F3042 − 13 (2018)
TABLE 2 Hardness
UNS
Nominal
Designation Alloy General Name Hardness
Thread Dia, in.
Numbers
C26000 260 Brass All 69 - 91HRB
C27000 270 Brass All 69 - 91HRB
C27400 274 Brass All 69 - 91HRB
C46200 462 Naval brass All 65 - 90 HRB
C46400 464 Naval brass All 55 - 75 HRB
C61300 613 Aluminum bronze All 70 - 95 HRB
C61400 614 Aluminum bronze All 70 - 95 HRB
C63000 630 Aluminum bronze All 85 - 100 HRB
C65100 651 Silicon bronze Thru 0.750 75 - 95 HRB
0.875 - 2.000 70 - 95 HRB
C65500 655 Silicon bronze All 60 - 80 HRB
C66100 661 Silicon bronze All 75 - 95 HRB
N04400 400 Nickel copper A Thru 0.750 75 HRB - 25 HRC
0.875 - 2.000 60 HRB - 25 HRC
N04405 405 Nickel copper B All 60 HRB - 20 HRC
N05500 500 Ni-Cu-Al All 24 - 37 HRC
N06625 625 Ni-Cr-Mo-Cb All 85 HRB - 35 HRC
N06686 686, Grade 1 Ni-Cr-Mo-W All 21 - 45 HRC
R55111 32 Titanium Ti-5-1-1-1 All 24 - 38 HRC
R56401 23 Titanium Ti-6Al-4V ELI All 25 - 36 HRC
R58640 19 Titanium Ti-38-6-44 All 24 - 38 HRC
8. Dimensions intersectarenotpermissible.Forperipheraldiscontinuities,the
maximum depth may be 0.06 D.
8.1 Unlessotherwisespecifiedbythepurchaser,theproduct
shall conform to the requirements of ASME B18.3 for hex
10. Sampling and Number of Tests
socket set screws or ASME B18.6.2 for slotted headless set
10.1 Guide F1470 shall be used to determine the necessary
screws or square head set screws. Threads shall be in accor-
s
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.