ASTM D721-15
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Oil Content of Petroleum Waxes
Standard Test Method for Oil Content of Petroleum Waxes
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The oil content of a wax may have significant effects on several of its properties, such as strength, hardness, flexibility, scuff resistance, coefficient of friction, coefficient of expansion, melting point, and oil straining. The importance of these effects may be dependent upon the ultimate use of the wax.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of oil in petroleum waxes having a congealing point of 30 °C (86 °F) or higher as determined in accordance with Test Method D938, and containing not more than 15 % of oil.2
Note 1: With some types of waxes, of oil contents greater than 5 %, there may be an incompatibility with MEK resulting in the formation of two liquid phases. If this occurs, the test method is not applicable to the material under test.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D721 − 15
Designation: 158/69(85)
Standard Test Method for
1
Oil Content of Petroleum Waxes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D721; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* E128 Test Method for Maximum Pore Diameter and Perme-
ability of Rigid Porous Filters for Laboratory Use
1.1 This test method covers the determination of oil in
2.2 Energy Institute Standards:
petroleum waxes having a congealing point of 30 °C (86 °F) or
4
Specification for IP Standard Thermometers
higher as determined in accordance with Test Method D938,
2
and containing not more than 15 % of oil.
3. Summary of Test Method
NOTE 1—With some types of waxes, of oil contents greater than 5 %,
3.1 The sample is dissolved in methyl ethyl ketone, the
there may be an incompatibility with MEK resulting in the formation of
solution cooled to –32 °C (–25 °F) to precipitate the wax, and
two liquid phases. If this occurs, the test method is not applicable to the
material under test.
filtered. The oil content of the filtrate is determined by
evaporating the methyl ethyl ketone and weighing the residue.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
4. Significance and Use
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
and are not considered standard. 4.1 The oil content of a wax may have significant effects on
several of its properties, such as strength, hardness, flexibility,
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
scuffresistance,coefficientoffriction,coefficientofexpansion,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
meltingpoint,andoilstraining.Theimportanceoftheseeffects
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
may be dependent upon the ultimate use of the wax.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Apparatus
2. Referenced Documents 5.1 Filter Stick and Assembly, consisting of a 10 mm diam-
3
etersinteredglassfilterstickof10 µmto15 µmmaximumpore
2.1 ASTM Standards:
diameter as determined by the method in Appendix X1,
D938 Test Method for Congealing Point of Petroleum
provided with an air pressure inlet tube and delivery nozzle. It
Waxes, Including Petrolatum
isprovidedwithaground-glassjointtofita25 mmby170 mm
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
test tube. The dimensions for a suitable filtration assembly are
shown in Fig. 1.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
NOTE 2—A metallic filter stick may be employed if desired. A filter
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of 1
stick made of stainless steel and having a 12.7 mm ( ⁄2 in.) disk of 10 µm
Subcommittee D02.10.0A on Physical/Chemical Properties.
to 15 µm maximum pore diameter, as determined by Test Method E128,
Current edition approved June 1, 2015. Published June 2015. Originally 5
has been found to be satisfactory. The metallic apparatus is inserted into
approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D721 – 06 (2011).
a 25 mm by 150 mm test tube and held in place by means of a cork.
DOI: 10.1520/D0721-15.
In the IP, this test method is under the jurisdiction of the Standardization
Committee. This test method was issued as a joint ASTM-IP tentative in 1964.
4
This test method was prepared jointly by the Technical Association of Pulp and Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London, WIG 7AR,
Paper Industry and ASTM International. U.K.
5
This test method has been adopted for use by government agencies to replace The sole source of supply of a suitable metal filter stick with designated
Method 5431 of Federal Test Method Standard No. 79lb. porosity G known to the committee at this time is the Pall Corporation, 2200
2
This test method is being used by some laboratories for products of higher oil Northern Boulevard East Hills, NY 11548. A list of United Kingdom suppliers can
content. be obtained from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London, W1G 7AR,
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or United Kingdom. If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM information to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive
1
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary pa
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D721 − 06 (Reapproved 2011) D721 − 15
Designation: 158/69(85)
Standard Test Method for
1
Oil Content of Petroleum Waxes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D721; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of oil in petroleum waxes having a congealing point of 30°C (86°F)30 °C (86 °F)
2
or higher as determined in accordance with Test Method D938, and containing not more than 15 % of oil.
NOTE 1—With some types of waxes, of oil contents greater than 5 %, there may be an incompatibility with MEK resulting in the formation of two
liquid phases. If this occurs, the test method is not applicable to the material under test.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D938 Test Method for Congealing Point of Petroleum Waxes, Including Petrolatum
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E128 Test Method for Maximum Pore Diameter and Permeability of Rigid Porous Filters for Laboratory Use
2.2 Energy Institute Standards:
4
Specification for IP Standard Thermometers
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 The sample is dissolved in methyl ethyl ketone, the solution cooled to –32°C (–25°F)–32 °C (–25 °F) to precipitate the wax,
and filtered. The oil content of the filtrate is determined by evaporating the methyl ethyl ketone and weighing the residue.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 The oil content of a wax may have significant effects on several of its properties, such as strength, hardness, flexibility, scuff
resistance, coefficient of friction, coefficient of expansion, melting point, and oil straining. The importance of these effects may be
dependent upon the ultimate use of the wax.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.10.0A on Physical/Chemical Properties.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2011June 1, 2015. Published October 2011June 2015. Originally approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 20062011 as
D721D721 – 06 (2011).-06. DOI: 10.1520/D0721-06R11.10.1520/D0721-15.
In the IP, this test method is under the jurisdiction of the Standardization Committee. This test method was issued as a joint ASTM-IP tentative in 1964.
This test method was prepared jointly by the Technical Association of Pulp and Paper Industry and ASTM International.
This test method has been adopted for use by government agencies to replace Method 5431 of Federal Test Method Standard No. 79lb.
2
This test method is being used by some laboratories for products of higher oil content.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London, WIG 7AR, U.K.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D721 − 15
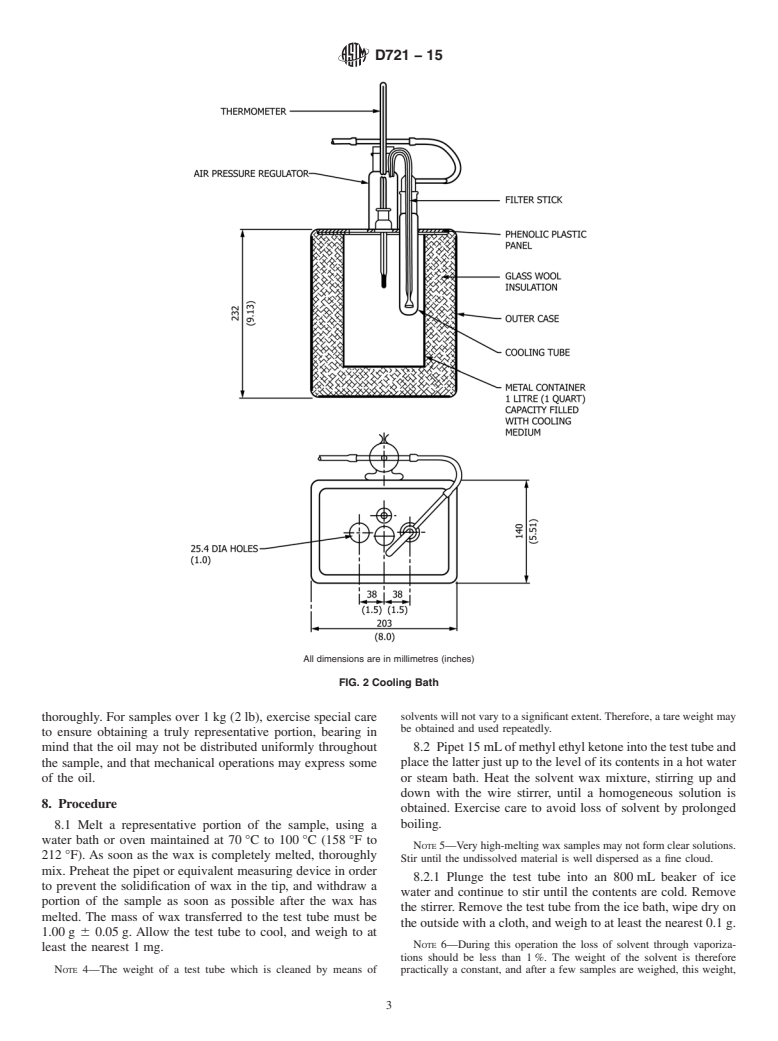
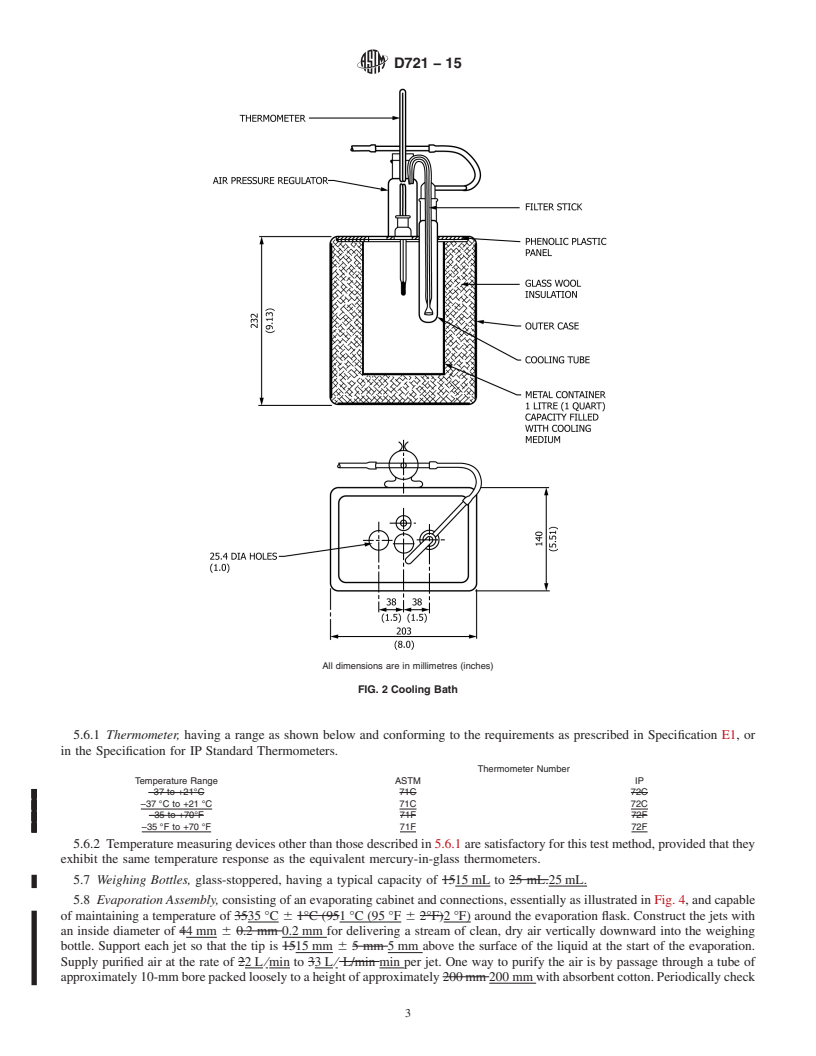
5. Apparatus
5.1 Filter Stick and Assembly, consisting of a 10-mm10 mm diameter sintered glass filter stick of 1010 μm to 15 μm 15 μm
maximum pore diameter as determined by the method in Appendix X1, provided with an air pressure inlet tube and delivery
nozzle. It is provided with a ground-glass joint to fit a 2525 mm by 170-mm170 mm test tube. The dimensions for a suitable
filtration assembly are shown in Fig. 1.
1
NOTE 2—A metallic filter stick may be employed if desired. A filter stick made of stainless steel
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.