ASTM D4957-18
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Apparent Viscosity of Asphalt Emulsion Residues and Non-Newtonian Asphalts by Vacuum Capillary Viscometer
Standard Test Method for Apparent Viscosity of Asphalt Emulsion Residues and Non-Newtonian Asphalts by Vacuum Capillary Viscometer
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is useful for characterizing the flow behavior of asphalt emulsion residues and non-Newtonian asphalts. However, since non-Newtonian viscosity values depend on the level of shearing stress, its duration, and the shear history of the material, a non-Newtonian viscosity is not a unique material property. Instead, it is a parameter which is characteristic of the fluid-viscometer system under the conditions of the measurement procedure. Therefore, comparisons of non-Newtonian material behavior should only be made using apparent viscosities determined in similar viscometers under similar conditions of shearing stress and stress history. Procedures of sample preparation are especially important for repeatability or reproducibility of test results.
Note 3: The quality of the results produced by this standard are dependent on the competence of the personnel performing the procedure and the capacity, calibration, and maintenance of the equipment used. Agencies that meet the criteria of Specification D3666 are generally considered capable of competent and objective testing, sampling, inspection, etc. Users of this standard are cautioned that compliance with Specification D3666 alone does not completely ensure reliable results. Reliable results depend on many factors; following the suggestions of Specification D3666 or some similar acceptable guideline provides a means of evaluating and controlling some of those factors.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes procedures primarily designed to determine the apparent viscosities of residues obtained by distilling asphalt emulsions according to Test Method D6997. It is also recommended for use on non-Newtonian asphalts at any temperature within the capability of the apparatus. This test method is useful in characterizing rheological properties of non-Newtonian asphalts as a function of shear rate under the conditions of the test method. This test is run in straight open-end tube viscometers, normally at 60 °C, but is suitable for use at other temperatures. It is applicable over the range from 5 to 50 000 Pa·s.
Note 1: The precision for this test method is based on determinations made at 60 °C.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard, except in reference to viscometer constant or calibration factor (K).
1.3 Warning— Mercury has been designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and many state agencies as a hazardous material that can cause central nervous system, kidney, and liver damage. Mercury or its vapor may be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury-containing products. See the applicable product Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for details and the EPA’s website (www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm) for additional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury, mercury-containing products, or both, in your state may be prohibited by state law.
1.4 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4957 − 18
Standard Test Method for
Apparent Viscosity of Asphalt Emulsion Residues and Non-
1
Newtonian Asphalts by Vacuum Capillary Viscometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4957; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.1 This test method describes procedures primarily de-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
signed to determine the apparent viscosities of residues ob-
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
tainedbydistillingasphaltemulsionsaccordingtoTestMethod
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
D6997. It is also recommended for use on non-Newtonian
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
asphalts at any temperature within the capability of the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
apparatus. This test method is useful in characterizing rheo-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
logical properties of non-Newtonian asphalts as a function of
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
shear rate under the conditions of the test method. This test is
run in straight open-end tube viscometers, normally at 60°C,
2. Referenced Documents
but is suitable for use at other temperatures. It is applicable
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
over the range from 5 to 50 000 Pa·s.
D2171Test Method for Viscosity of Asphalts by Vacuum
NOTE 1—The precision for this test method is based on determinations
Capillary Viscometer
made at 60°C.
D3666Specification for Minimum Requirements for Agen-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
cies Testing and Inspecting Road and Paving Materials
standard,exceptinreferencetoviscometerconstantorcalibra-
D6997Test Method for Distillation of Emulsified Asphalt
tion factor (K).
E1Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E77Test Method for Inspection and Verification of Ther-
1.3 Warning—Mercury has been designated by the United
mometers
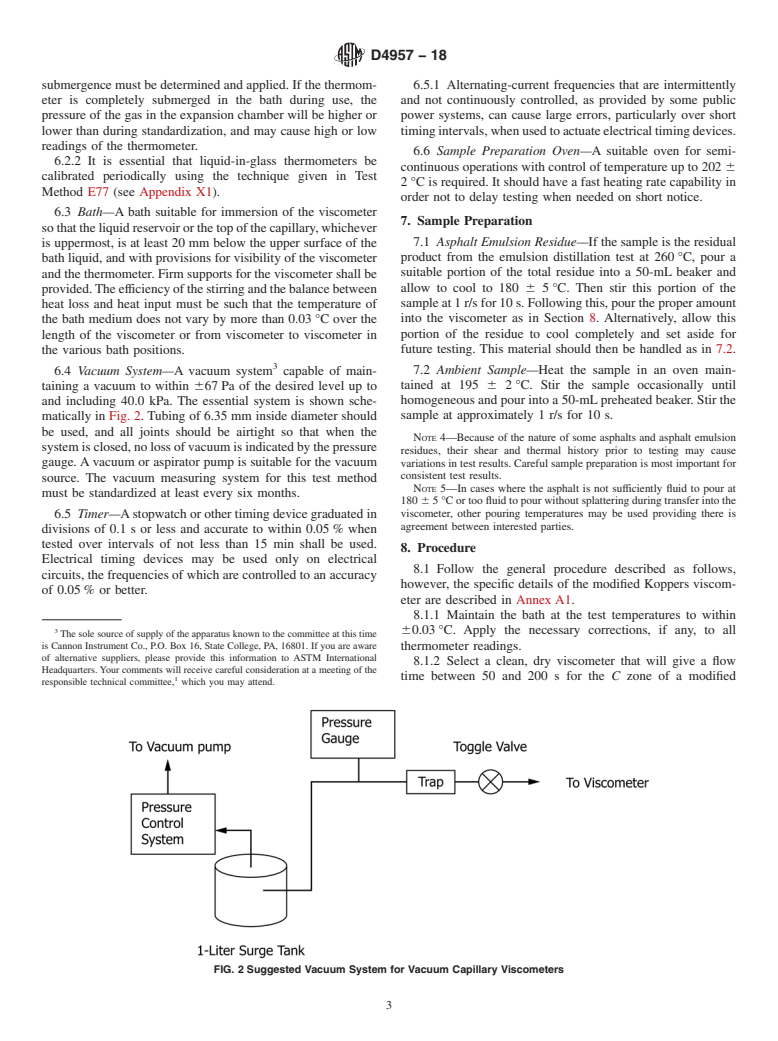
StatesEnvironmentalProtectionAgency(EPA)andmanystate
E644Test Methods for Testing Industrial Resistance Ther-
agenciesasahazardousmaterialthatcancausecentralnervous
mometers
system,kidney,andliverdamage.Mercuryoritsvapormaybe
E1137/E1137MSpecification for Industrial Platinum Resis-
hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should
tance Thermometers
be taken when handling mercury and mercury-containing
E2251Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermom-
products. See the applicable product Material Safety Data
eters with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
Sheets (MSDS) for details and the EPA’s website
(www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm) for additional information.
3. Terminology
Users should be aware that selling mercury, mercury-
3.1 Definitions:
containingproducts,orboth,inyourstatemaybeprohibitedby
3.1.1 apparent viscosity—the determined viscosity obtained
state law.
bythetestmethodunderdescription.Viscosityistheresistance
1.4 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes
to deformation or internal friction of a liquid expressed as the
whichprovideexplanatorymaterial.Thesenotesandfootnotes
ratio of the shear stress to shear rate, whether this ratio is
(excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered
constant or not. The unit of viscosity obtained by dividing the
as requirements of the standard.
2
shearing stress in N/m by the rate of shear in reciprocal
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
seconds is called the pascal second (Pa·s). The English unit of
2
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
viscosity is the poise (P) with dimensions of 0.1N·s/m
2
(dynes/cm /s), and is equivalent to 0.1 Pa·s.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road
and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.44 on
2
Rheological Tests. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Jan. 15, 2018. Published January 2018. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approvedin1989.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2008asD4957–08whichwas Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
withdrawn January 2017 and reinstated in January 2018. DOI: 10.1520/D4957-18. the ASTM website.
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.