ASTM F899-95
(Specification)Standard Specification for Stainless Steel for Surgical Instruments
Standard Specification for Stainless Steel for Surgical Instruments
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for stainless steel billet, bar, and wire used for the manufacture of surgical instruments. Billet or bar intended for forging into special shapes may also be purchased in accordance with this specification.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 899 – 95
Standard Specification for
Stainless Steel Billet, Bar, and Wire for Surgical
Instruments
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 899; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3. Classification and Type
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for stainless 3.1 Classes—Stainless steel material requirements for sur-
steel billet, bar, and wire used for the manufacture of surgical gical instruments shall conform to one of the following classes,
instruments. Billet or bar intended for forging into special as specified:
shapes may also be purchased in accordance with this specifi- 3.1.1 Class 3—Austenitic Stainless Steel.
cation. 3.1.2 Class 4—Martensitic Stainless Steel.
3.1.3 Class 5—Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.4 Class 6—Ferritic Stainless Steel.
2.1 ASTM Standards: 3.2 Type—Where applicable, the commercially recognized
A 276 Specification for Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel
type of stainless steel is included in Tables 1 and 2.
Bars and Shapes
4. Ordering Information
A 314 Specification for Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel
Billets and Bars for Forging 4.1 Inquiries and orders for material under this specification
A 484/A484M Specification for General Requirements for shall include the following information:
Stainless and Heat-Resisting Bars, Billets, and Forgings 4.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
A 555/A555M Specification for General Requirements for 4.1.2 Classification, optional (see 3.1),
Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Wire and Wire Rods 4.1.3 Type (see 3.2),
A 564 Specification for Hot-Rolled and Cold-Finished Age- 4.1.4 Form (billet, bar, wire),
Hardening Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Bars and 4.1.5 Condition (see 5.1),
Shapes 4.1.6 Finish (see 5.3),
A 582 Specification for Free-Machining Stainless and Heat- 4.1.7 Mechanical properties or hardness (see Section 8), and
Resisting Steel Bars, Hot-Rolled or Cold-Finished 4.1.8 Applicable dimensions including size, thickness,
A 751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for width, and length (exact, random, or multiples) or print
Chemical Analysis of Steel Products number.
2.2 ISO Draft International Standard:
5. Manufacture
ISO/DIS 7153/1 Instruments For Surgery—Metallic
Materials—Part 1: Stainless Steel 5.1 Condition—Billet, bar, and wire shall be furnished to
the instrument manufacturer, as specified, in the hot finished,
2.3 American Society for Quality Control (ASQC) Stan-
dard: cold finished, annealed, solution treated, solution treated and
aged, quench hardened, quench hardened and tempered, or as
C1-1985 Specification of General Requirements for a Qual-
ity Program specified in the instrument manufacturer’s purchase order.
Cautionary Note—Highly hardenable martensitic stainless
billets and bars such as Types 420A, 420B, 420C, 420F, 420F
1 Mod., 440A, 440B, and 440C intended for forging are com-
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-4 on Medical
and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee monly annealed prior to shipment and so specified in order to
F04.33 on Medical and Surgical Instruments.
avoid the possibility of thermal cracking. Other hardenable
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1995. Published November 1995. Originally
martensitic grades such as Types 403, 410, 416, 416 Mod., and
published as F 899 – 84. Last previous edition F 899 – 94.
431, which also may require annealing, depending on their
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
composition and size, are furnished suitable for cold cutting
Available from American National Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New
when so specified on the purchase order.
York, NY 10018.
5 5.2 Conditioning—Billet and bar intended for forging may
Available from American Society for Quality Control, 161 West Wisconsin
be conditioned by chipping, grinding, or other suitable means
Avenue, Milwaukee, WI 53203.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 899
TABLE 1 Composition of Class 3, Austenitic Stainless Steels, %
Carbon, Phosphorus, Silicon, Other
Type Manganese Sulfur Chromium Nickel
max max max Elements
301 0.15 2.00 max 0.045 0.030 max 1.00 16.00–18.00 6.00–8.00 —
302 0.15 2.00 max 0.045 0.030 max 1.00 17.00–19.00 8.00–10.00 N 0.10 max
A
303 0.12 2.00 max 0.060 0.15–0.35 1.00 17.00–19.00 8.00–10.00 Mo 0.70 max
304 0.07 2.00 max 0.045 0.030 max 1.00 17.00–19.00 8.00–11.00 N 0.10 max
316 0.07 2.00 max 0.045 0.030 max 1.00 16.50–18.50 10.50–13.50 Mo 2.00–2.50
N 0.10 max
317 0.08 2.00 max 0.045 0.030 max 1.00 18.00–20.00 11.00–15.00 Mo 3.00–4.00
N 0.10 max
XM-7 0.10 2.00 max 0.045 0.030 max 1.00 17.00–19.00 8.00–10.00 Cu 3.00–4.00
— 0.15 17.00–19.00 0.040 0.040 max 1.00 17.00–19.00 — Mo 0.75–1.25
Cu 0.75–1.25
N 0.40–0.60
A
Optional.
TABLE 2 Composition of Class 6, Ferritic Stainless Steels, %
Carbon, Manganese, Phosphorus, Silicon, Other
Type Sulfur Chromium
max max max Max Elements
430 F 0.08 1.50 0.060 0.15–0.35 1.00 16.00–18.00 Mo 0.60 max
Ni 1.00 max
XM-34 0.08 2.50 0.040 0.28–0.41 1.00 17.50–19.50 Mo 1.50–2.50
to remove injurious surface defects. in the materials used for the manufacture of surgical instru-
5.3 Finish—Types of finish available for bar and wire ments.
products are cold drawn, pickled, ground, ground and polished, 7.3 The chemical composition requirements for Types 301,
or as specified in the instrument manufacturer’s purchase order. 303, 304, 316, 410, 420A, 420B, 420C, and 430F will meet the
composition requirements in ISO/DIS 7153/1.
6. General Requirements for Delivery
7.4 Methods and practices relating to chemical analysis
6.1 In addition to the requirements of this specification, all
required by this specification shall be in accordance with Test
requirements of the current editions of Specification A 484/
Methods, Practices, and Definitions A 751.
A 484M and A555/A 555M shall apply as applicable.
8. Mechanical Requirements
6.2 This ASTM specification compliments the ISO appli-
8.1 Material shall conform to the mechanical property
cable document covering stainless steel for surgical instru-
requirements cited in the appropriate ASTM standards (see 2.1)
ments and, by reference, includes all of the stainless grades in
or shall meet the mechanical property requirements specified in
ISO/DIS 7153/1.
the instrument manufacturer’s purchase order.
7. Chemical Requirements
8.2 When desired, Brinell hardness number (HB), Rockwell
7.1 The heat analysis shall conform to the requirements as hardness, B scale (HRB) or Rockwell hardness, C scale (HRC),
to chemical composition specified in Tables 1-2. limits may be specified. Hardness guidelines for selected Class
7.2 Restricted carbon and sulfur limits for certain Class 4 4 martensitic stainless steels in the annealed condition are
martensitic stainless steels are specified to ensure consistency listed in Table 5.
TABLE 3 Composition of Class 4, Martensitic Stainless Steels, %
Mn P Sulfur Silicon Other
Type Carbon Chromium
Max Max S Max Elements
410 0.09–0.15 1.00 0.040 0.030 max 1.00 11.50–13.50 Ni 1.00 max
410X 0.16–0.21 1.00 0.040 0.030 max 1.00 11.50–13.50 Ni 1.00 max
416 0.09–0.15 1.25 0.060 0.15–0.27 1.00 12.00–14.00 —
416 Mod 0.09–0.15 1.25 0.060 0.28–0.41 1.00 12.00–14.00 —
420A 0.16–0.25 1.00 0.040 0.030 max 1.00 12.00–14.00 Ni 1.00 max
420B 0.26–0.35 1.00 0.040 0.030 max 1.00 12.00–14.00 Ni 1.00 max
420X 0.36–0.41 1.00 0.040 0.030 max 1.00 12.00–14.50 Ni 1.00 max
420C 0.42–0.50 1.00 0.040 0.030 max 1.00 12.50–14.50 Ni 1.00 max
A
420F 0.30–0.40 1.25 0.060 0.20–0.34 1.00 12.50–14.00 Cu 0.60 max
A
Ni 0.50 max
420F Mod 0.20–0.26 2.00 0.040 0.15–0.27 1.00 12.50–14.00 Mo 1.10–1.50
Ni 0.75–1.50
431 0.20 max 1.00 0.040 0.030 max 1.00 15.00–17.00 Ni 1.25–2.50
440A 0.60–0.75 1.00 0.040 0.030 max 1.00 16.00–18.00 Mo 0.75 max
440B 0.75–0.95 1.00 0.040 0.030 max 1.00 16.00–18.00 Mo 0.75 max
440C 0.95–1.20 1.00 0.040 0.030 max 1.00 16.00–18.00 Mo 0.75 max
A
440F 0.95–1.20 1.25 0.060 0.15–0.27 1.00 16.00–18.00 Cu 0.60 max
A
Ni 0.50 max
A
Optional.
F 899
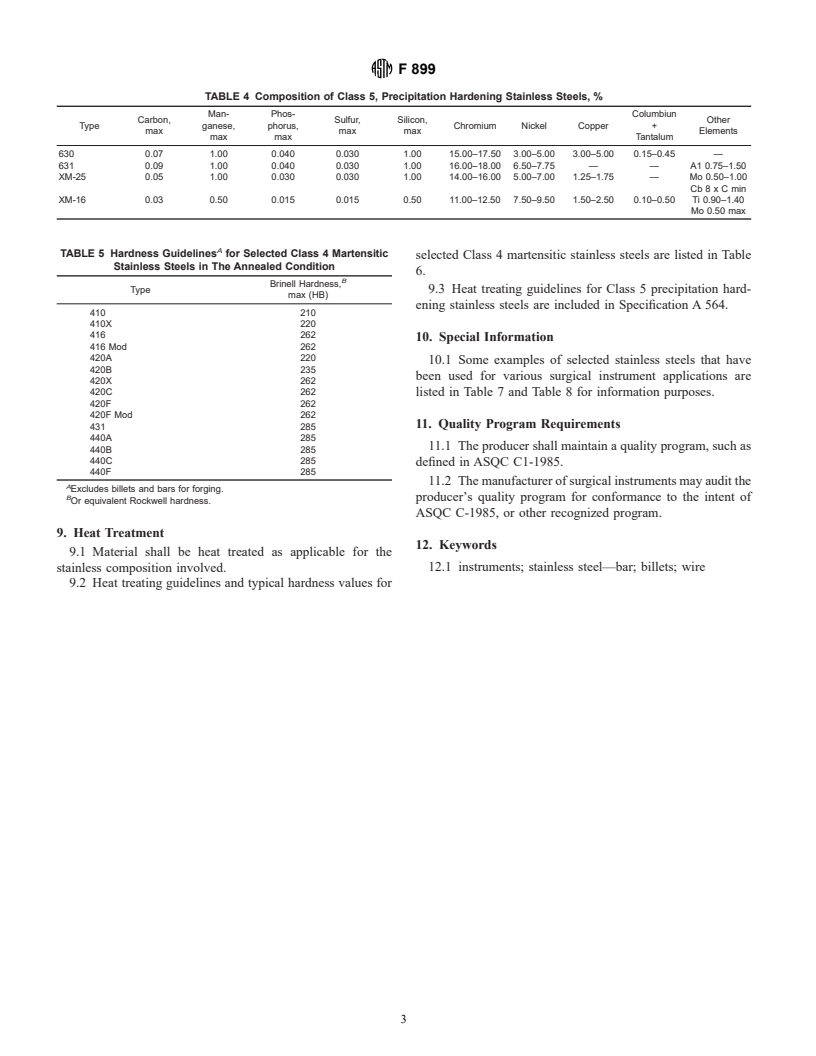
TABLE 4 Composition of Class 5, Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steels, %
Man- Phos- Columbiun
Carbon, Sulfur, Silicon, Other
Type ganese, phorus, Chromium Nickel Copper +
max max max Elements
max max Tantalum
630 0.07 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 15.00–17.50 3.00–5.00 3.00–5.00 0.15–0.45 —
631 0.09 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 16.00–18.00 6.50–7.75 — — A1 0.75–1.50
XM-25 0.05 1.00 0.030 0.030 1.00 14.00–16.00 5.00–7.00 1.25–1.75 — Mo 0.50–1.00
Cb8xCmin
XM-16 0.03 0.50 0.015 0.015 0.50 11.00–12.50 7.50–9.50 1.50–2.50 0.10–0.50 Ti 0.90–1.40
Mo 0.50
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.