ASTM F924-90(2022)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Resistance to Puncture of Cushioned Resilient Floor Coverings
Standard Test Method for Resistance to Puncture of Cushioned Resilient Floor Coverings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Much of the cushioned resilient flooring in use today is in household kitchens. Kitchen flooring is frequently subjected to the hazard of dropped tableware and cutting knives, that can puncture the wear layer of cushioned resilient flooring. Food and soil that become embedded in these punctures often can not be removed by ordinary maintenance, resulting in unsightly marks. Moisture, grease, or oils that penetrate to the cushion layer can be wicked into the foam and cause permanent discoloration. Ultimately, the service life of the material is shortened.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory procedure for determining the resistance of cushioned resilient floor coverings to punctures from dropped pointed objects such as dinner forks.
1.2 This test method employs a 35-g cylindrical dart with a flat, small-diameter tip that is dropped onto a specimen of flooring. The dart represents the weight of a typical fork and the tip produces a similar puncture to those which result from dropped forks.
1.3 Flooring with thick wear layers may not puncture under even the most severe drop. Although data can be obtained by increasing the drop height or the weight of the dart, values of this magnitude have no practical application.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precaution statement see 8.2.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F924 − 90 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Test Method for
Resistance to Puncture of Cushioned Resilient Floor
Coverings
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF924;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory procedure for
E171 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Flexible Barrier
determining the resistance of cushioned resilient floor cover-
Packaging
ings to punctures from dropped pointed objects such as dinner
F141 Terminology Relating to Resilient Floor Coverings
forks.
F410 Test Method for Wear Layer Thickness of Resilient
1.2 This test method employs a 35-g cylindrical dart with a
Floor Coverings by Optical Measurement
flat, small-diameter tip that is dropped onto a specimen of
flooring. The dart represents the weight of a typical fork and
3. Terminology
the tip produces a similar puncture to those which result from
3.1 Definitions:
dropped forks.
3.1.1 For definitions of other terms used in this test method,
1.3 Flooring with thick wear layers may not puncture under
refer to Terminology F141.
even the most severe drop. Although data can be obtained by
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
increasing the drop height or the weight of the dart, values of
3.2.1 puncture, n—a break in the wear layer of the speci-
this magnitude have no practical application.
men.An indentation at the point of impact shall be considered
a puncture only if the wear layer is broken completely through
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
at some point.
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only 3.2.2 wicking, n—the presence of ink below the wear layer
and are not considered standard. of the specimen in areas adjacent to a puncture. This can be
seen next to the actual cut, and appears either as spots on the
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
pattern layer or as a general discoloration.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Significance and Use
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4.1 Much of the cushioned resilient flooring in use today is
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
in household kitchens. Kitchen flooring is frequently subjected
For specific precaution statement see 8.2.
to the hazard of dropped tableware and cutting knives, that can
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
puncture the wear layer of cushioned resilient flooring. Food
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
and soil that become embedded in these punctures often can
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
notberemovedbyordinarymaintenance,resultinginunsightly
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
marks. Moisture, grease, or oils that penetrate to the cushion
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
layer can be wicked into the foam and cause permanent
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
discoloration. Ultimately, the service life of the material is
shortened.
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeF06onResilient
Floor Coverings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F06.20 on Test
Methods. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2022. Published October 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as F924 – 90 (2015). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/F0924-90R22. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F924 − 90 (2022)
5. Apparatus shall be a flat cap with a ⁄4 in. diameter opening in the center.
This hole should have smooth, rounded sides.
5.1 Dart Drop Assembly (Fig. 1), consisting of a ⁄2 in.
plywood platform tilted 20° from horizontal, and a vertical
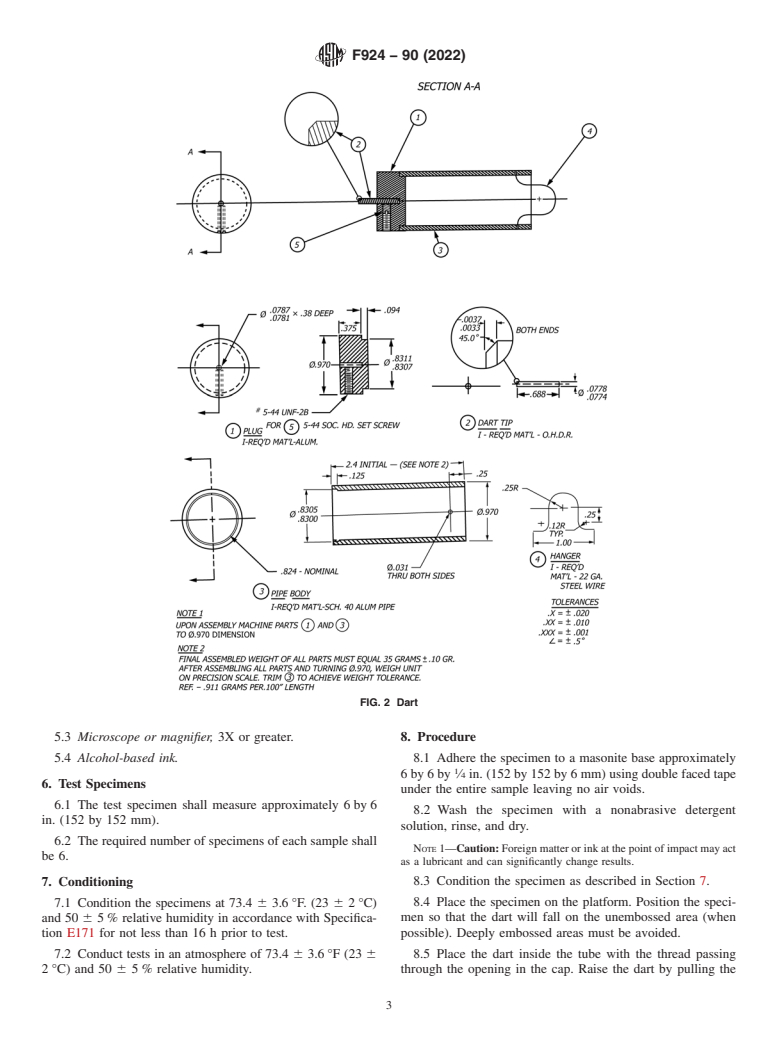
5.2 Dart (Fig. 2), consisting of a 0.970 6 0.003 in. (246 6
slotted tube at least 40 in. (1016 mm) long with an inside
0.76 mm) outside diameter hollow cylindrical aluminum body
diameter of 1.05 6 0.05 in. (26.7 6 2 mm). The mouth of the
with a 0.078 6 0.0005 in. (2.0 6 0.013 mm) diameter tip at
tube shall be approximately 2 in. (50.8 mm) above the center
one end and a steel wire loop at the other end, weighing a total
of the platform. The tube shall be marked in 1 in. or less
of 35 6 0.10 g. A length of size “A” silk thread at least 60 in.
graduations showing the height above the surface of a mo
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.