ASTM D2427-06(2015)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of C2 through C5 Hydrocarbons in Gasolines by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of C<inf>2</inf> through C<inf>5</inf> Hydrocarbons in Gasolines by Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 In hydrocarbon type analyses of gasolines, highly volatile fuels can need to be stabilized by depentanization (Test Method D2001) prior to analysis. A knowledge of the composition of light hydrocarbons in the overhead from the depentanization process is useful in converting analyses of the depentanized fraction to a total sample basis.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the two (C2) through five(C5-) carbon paraffins and mono-olefins in gasolines. The concentrations by volume or mass (weight) of the following components are generally reported:
1.1.1 Ethylene plus ethane
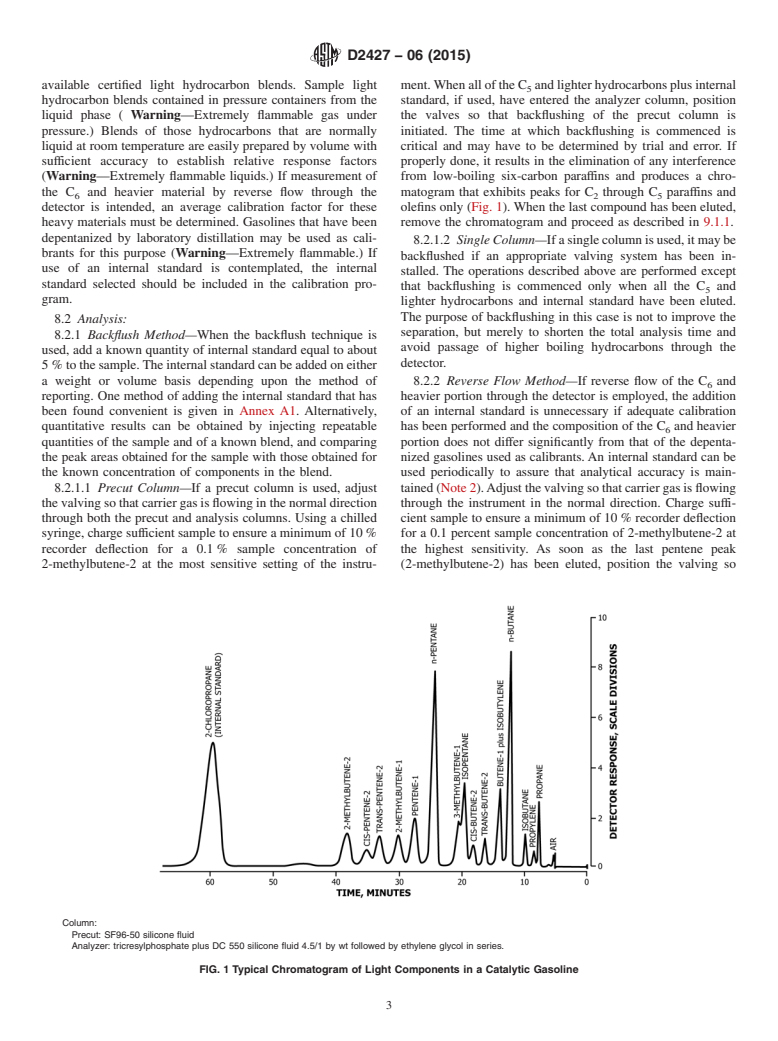
1.1.2 Propane
1.1.3 Propylene
1.1.4 Isobutane
1.1.5 n-Butane
1.1.6 Butene-1 plus isobutylene
1.1.7 trans-Butene-2
1.1.8 cis-Butene-2
1.1.9 Isopentane
1.1.10 3-Methylbutene-1
1.1.11 n-Pentane
1.1.12 Pentene-1
1.1.13 2-Methylbutene-1
1.1.14 trans-Pentene-2
1.1.15 cis-Pentene-2
1.1.16 2-Methylbutene-2
1.2 This test method does not cover the determination of cyclic olefins, diolefins, or acetylenes. These are usually minor components in finished gasolines.
1.3 Samples to be analyzed should not contain significant amounts of material boiling lower than ethylene.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4.1 Exception—Alternative units, in common usage, are also provided to improve the clarity and aid the user of this test method.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2427 − 06 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of C through C Hydrocarbons in Gasolines
2 5
1
by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2427; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the two
(C ) through five(C -) carbon paraffins and mono-olefins in
2 5 2. Referenced Documents
gasolines. The concentrations by volume or mass (weight) of
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
the following components are generally reported:
D2001 Test Method for Depentanization of Gasoline and
1.1.1 Ethylene plus ethane
Naphthas
1.1.2 Propane
1.1.3 Propylene
3. Summary of Test Method
1.1.4 Isobutane
3.1 The sample is injected into a gas-liquid partition col-
1.1.5 n-Butane
umn. The components are separated as they pass through the
1.1.6 Butene-1 plus isobutylene
column with an inert carrier gas and their presence in the
1.1.7 trans-Butene-2
effluent is detected and recorded as a chromatogram. Materials
1.1.8 cis-Butene-2
containing components having more than five carbon atoms
1.1.9 Isopentane
can either be backflushed from the system without
1.1.10 3-Methylbutene-1
measurement, or recorded as a broad peak by reversing the
1.1.11 n-Pentane
direction of the carrier gas through the column at such time as
1.1.12 Pentene-1
to regroup the higher-boiling portion (C and heavier) of the
6
1.1.13 2-Methylbutene-1
sample. If backflushing is used, the concentration of C
2
1.1.14 trans-Pentene-2
through C hydrocarbons may be related to the whole sample
5
1.1.15 cis-Pentene-2
by adding a known quantity of low-boiling internal standard to
1.1.16 2-Methylbutene-2
the sample prior to analysis.Alternatively, a known amount of
1.2 This test method does not cover the determination of
sample can be charged and compared to a standard sample run
cyclic olefins, diolefins, or acetylenes. These are usually minor
under the same conditions. Sample composition is determined
components in finished gasolines.
from the chromatogram by comparing peak areas with those
obtained using known amounts of calibration standards or a
1.3 Samples to be analyzed should not contain significant
synthetic blend.
amounts of material boiling lower than ethylene.
4. Significance and Use
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
4.1 In hydrocarbon type analyses of gasolines, highly vola-
standard.
tile fuels can need to be stabilized by depentanization (Test
1.4.1 Exception—Alternative units, in common usage, are
Method D2001) prior to analysis. A knowledge of the compo-
also provided to improve the clarity and aid the user of this test
sition of light hydrocarbons in the overhead from the depen-
method.
tanization process is useful in converting analyses of the
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the depentanized fraction to a total sample basis.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5. Apparatus
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5.1 Chromatograph—Any chromatograph having a thermo-
stated oven and a detection system of adequate sensitivity may
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
2
Subcommittee D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2015. Published December 2015. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D2427 – 06 (2011). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D2427-06R15. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2427 − 06 (2015)
be used. The detection system must have sufficient sensitivity 6.4 Solid Support, for use in packed column; usually
to produce a recorder deflection of at least 5 mm for 0.1 liquid crushed firebrick or diatomaceous earth. Mesh size should be
appropriate to the system selected from the supplement.
volume percent of pentene-1 in the sample or synthetic blend
being analyzed.
7. Preparation of Apparatus
NOTE 1—If the sensitivity of a given system is inadequate, it c
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2427 − 06 (Reapproved 2011) D2427 − 06 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of C through C Hydrocarbons in Gasolines
2 5
1
by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2427; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the two (C ) through five(C -) carbon paraffins and mono-olefins in gasolines.
2 5
The concentrations by volume or mass (weight) of the following components are generally reported:
1.1.1 Ethylene plus ethane
1.1.2 Propane
1.1.3 Propylene
1.1.4 Isobutane
1.1.5 n-Butane
1.1.6 Butene-1 plus isobutylene
1.1.7 trans-Butene-2
1.1.8 cis-Butene-2
1.1.9 Isopentane
1.1.10 3-Methylbutene-1
1.1.11 n-Pentane
1.1.12 Pentene-1
1.1.13 2-Methylbutene-1
1.1.14 trans-Pentene-2
1.1.15 cis-Pentene-2
1.1.16 2-Methylbutene-2
1.2 This test method does not cover the determination of cyclic olefins, diolefins, or acetylenes. These are usually minor
components in finished gasolines.
1.3 Samples to be analyzed should not contain significant amounts of material boiling lower than ethylene.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4.1 Exception—Alternative units, in common usage, are also provided to improve the clarity and aid the user of this test
method.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2001 Test Method for Depentanization of Gasoline and Naphthas
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 The sample is injected into a gas-liquid partition column. The components are separated as they pass through the column
with an inert carrier gas and their presence in the effluent is detected and recorded as a chromatogram. Materials containing
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods.
Current edition approved May 1, 2011Oct. 1, 2015. Published August 2011December 2015. Originally approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 20062011 as
D2427D2427 – 06 (2011).–06. DOI: 10.1520/D2427-06R11.10.1520/D2427-06R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2427 − 06 (2015)
components having more than five carbon atoms can either be backflushed from the system without measurement, or recorded as
a broad peak by reversing the direction of the carrier gas through the column at such time as to regroup the higher-boiling portion
(C and heavier) of the sample. If backflushing is used, the concentration of C through C hydrocarbons may be related to the
6 2 5
whole sample by adding a known quantity of low-boiling internal standard to the sample prior to analysis. Alternatively, a known
amount of sample can be charged and compared to a standard sample run under the same conditions. Sample composition is
determined from the chromatogram by comparing peak areas with those obtained using known amounts of calibration standards
or a synthetic blend.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 In hydrocarbon type analyses of gasolines, highly volatile fuels can need to be stabilized by depentanization (Test Method
D2001) prior to analysis. A knowledge of the composition of light hydrocarbons in the overhead from the depentanization process
is useful in converting analyses of the depentanized fraction to a total sample basis.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Chromatograph—Any chromatograph having a thermostated oven and a detection system of adequate sensitivity may be
used. The detection system must have sufficient sensitivity to produce a recorder deflection of at least 5 mm 5
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.