ASTM A1009-18
(Specification)Standard Specification for Soft Magnetic MnZn Ferrite Core Materials for Transformer and Inductor Applications
Standard Specification for Soft Magnetic MnZn Ferrite Core Materials for Transformer and Inductor Applications
ABSTRACT
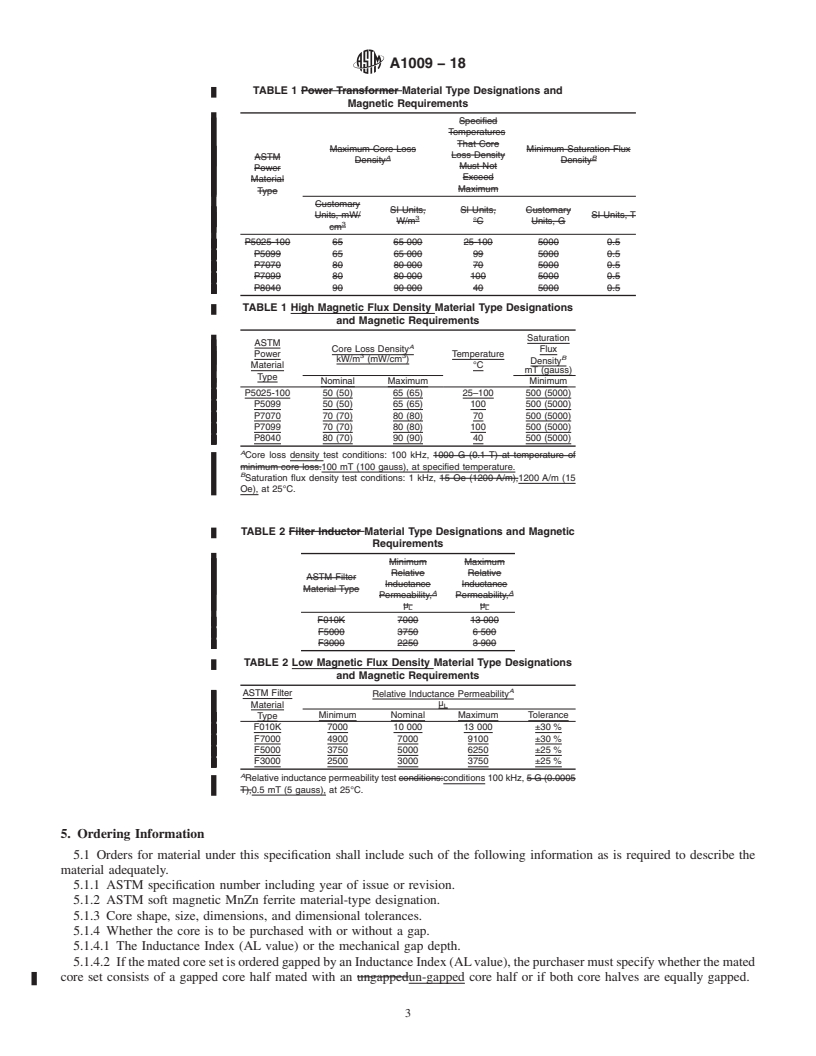
This specification deals with soft magnetic manganese zinc ferrite core materials for high frequency power transformer and filter inductor applications. Standard types of both power transformer and filter inductor material are defined. For power transformer use, there are five types defined by their maximum core loss density and minimum saturation flux density. For filter inductor materials, three types are defined based on their inductance permeability. Apart from magnetic property requirements, dimensional tolerances and workmanship requirements are defined in this specification.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements to which the specified grades of soft magnetic manganese zinc (MnZn) ferrite materials shall conform. Cores made from these materials are used primarily in transformers and inductors.
1.2 Frequency—MnZn ferrite cores are primarily used for frequencies in the range of 10 kHz to 1 MHz. Many inductors have a DC component as well.
1.3 Magnetic Flux Density—Applications consist of two main categories, high and low magnetic flux density.
1.3.1 High Magnetic Flux Density—Transformers used for power conversion. Inductors or chokes used in high current applications.
1.3.2 Low Magnetic Flux Density—Transformers, inductors, chokes used for signal conditioning.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to customary (cgs-emu and inch-pound) units, which are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:A1009 −18
Standard Specification for
Soft Magnetic MnZn Ferrite Core Materials for Transformer
1
and Inductor Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A1009; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This specification covers the requirements to which the 2.1 ASTM Standards:
specified grades of soft magnetic manganese zinc (MnZn) A340 Terminology of Symbols and Definitions Relating to
ferrite materials shall conform. Cores made from these mate- Magnetic Testing
rials are used primarily in transformers and inductors. A1013 Test Method for High-Frequency (10 kHz-1 MHz)
Core Loss of Soft Magnetic Core Components at Con-
1.2 Frequency—MnZn ferrite cores are primarily used for
trolled Temperatures Using the Voltmeter-Ammeter-
frequencies in the range of 10 kHz to 1 MHz. Many inductors
Wattmeter Method
have a DC component as well.
1.3 Magnetic Flux Density—Applications consist of two 3. Terminology
main categories, high and low magnetic flux density.
3.1 The terms and symbols used in this specification are
1.3.1 High Magnetic Flux Density—Transformers used for
defined in Terminology A340.
power conversion. Inductors or chokes used in high current
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
applications.
3.2.1 air core inductance (L )—theA value, assuming an
air L
1.3.2 Low Magnetic Flux Density—Transformers,inductors,
effective permeability of one. A is proportional to the factors
L
chokes used for signal conditioning.
of shape and size of the core. The air core inductance is
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as 2
expressed as nanohenries per turn squared (nH/N ).
standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
L 5 µ A ⁄L (1)
air o e e
conversions to customary (cgs-emu and inch-pound) units,
whichareprovidedforinformationonlyandarenotconsidered
where:
standard. 2
A = effective cross-sectional area of core in mm ,
e
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
L = effective magnetic path length of core in mm, and
e
µ = the magnetic constant as 0.4 π nH/mm.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
o
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2.2 effective initial permeability (µ )—the initial perme-
c
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
ability of the material as defined in A340, adjusted for known
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
processing variables that are not accounted for in the L term
air
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
such as mating surface finish and heat treatment. Can vary with
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
size, shape, and material.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.2.3 inductance index (A value)—the inductance normal-
L
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
ized for the number of turns. Is proportional to the factors of
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
effective initial permeability of the material core, shape, and
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
size. It allows quick determination of expected inductance
when used with the number of turns on the winding of the
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A06 on
Magnetic Propertiesand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A06.02 on
2
Material Specifications. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2018. Published November 2018. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as A1009 – 05 (2010). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/A1009-18. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A1009−18
TABLE 2 Low Magnetic Flux Density Material Type Designations
intended application. The inductance index is expressed as
2 and Magnetic Requirements
nanohenries per turn squared (nH/N ):
A
ASTM Filter
Relative Inductance Permeability
A 5 L µ (2)
L air e µ
Material L
And therefore the expected inductance (L) is:
Type Minimum Nominal Maximum Tolerance
F010K 7000 10 000 13 000
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A1009 − 05 (Reapproved 2010) A1009 − 18
Standard Specification for
Soft Magnetic MnZn Ferrite Core Materials for High
Frequency (10 kHz-1 MHz) Power Transformer and Filter
1
Inductor Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A1009; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers the requirements to which the specified grades of soft magnetic manganese zinc (MnZn) ferrite
materials shall conform. Cores made from these materials are used primarily in power transformers and filter inductors.
1.2 Frequency—MnZn ferrite cores are primarily used for frequencies in the range of 10 kHz to 1 MHz. Many inductors have
a DC component as well.
1.3 Magnetic Flux Density—Applications consist of two main categories, high and low magnetic flux density.
1.3.1 High Magnetic Flux Density—Transformers used for power conversion. Inductors or chokes used in high current
applications.
1.3.2 Low Magnetic Flux Density—Transformers, inductors, chokes used for signal conditioning.
1.4 The values stated in customary (cgs-emu and inch-pounds) SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in
parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI customary (cgs-emu and inch-pound) units, which are provided for information
only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A340 Terminology of Symbols and Definitions Relating to Magnetic Testing
A1013 Test Method for High-Frequency (10 kHz-1 MHz) Core Loss of Soft Magnetic Core Components at Controlled
Temperatures Using the Voltmeter-Ammeter-Wattmeter Method
3. Terminology
3.1 The terms and symbols used in this specification are defined in Terminology A340.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
2
3.2.1 Inductance Index (AL value)—the self inductance per winding turn squared (L/N ) expressed in units of nanohenries per
2
turns squared (nH/N ).
where:
–9
n = nano = 10 ,
nH = inductance in nanohenries, and
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A06 on Magnetic Propertiesand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A06.02 on Material
Specifications.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2010Oct. 1, 2018. Published December 2010November 2018. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20052010
as A1009 – 05.A1009 – 05 (2010). DOI: 10.1520/A1009-05R10.10.1520/A1009-18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A1009 − 18
2 2 2
N = number of turns on winding (example: 0.005 H with a 100 turn coil = 0.005 ⁄(100) H/N = 500 nH/N ).
3.2.2 Mated Core Set—Two or more core segments assembled with the magnetic flux path perpendicular to the mating surface.
3.2.3 Air core inductance, L , is the inductance of a core with the same magnetic path length and cross-sectional core area but
air
with the relative permeability of air.
3.2.3.1 Customary Units
2 29
L 5 4ΠAN 10 /l , H
air 1
where:
N = number of turns on winding;
2
A = cross-sectional area of core specimen, cm ; and
l = effective magnetic path length, cm.
1
3.2.3.2 SI Units
2 27
L 5 4ΠAN 10 /l , H
air 1
where:
N = number of turns on winding;
2
A = cross-sectional area of core specimen, m ; and
l = effective magnetic path length, m.
1
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 air core inductance (L )—the A value, ass
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.