ASTM A1101-16
(Specification)Standard Specification for Sintered and Fully Dense Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) Permanent Magnets
Standard Specification for Sintered and Fully Dense Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) Permanent Magnets
ABSTRACT
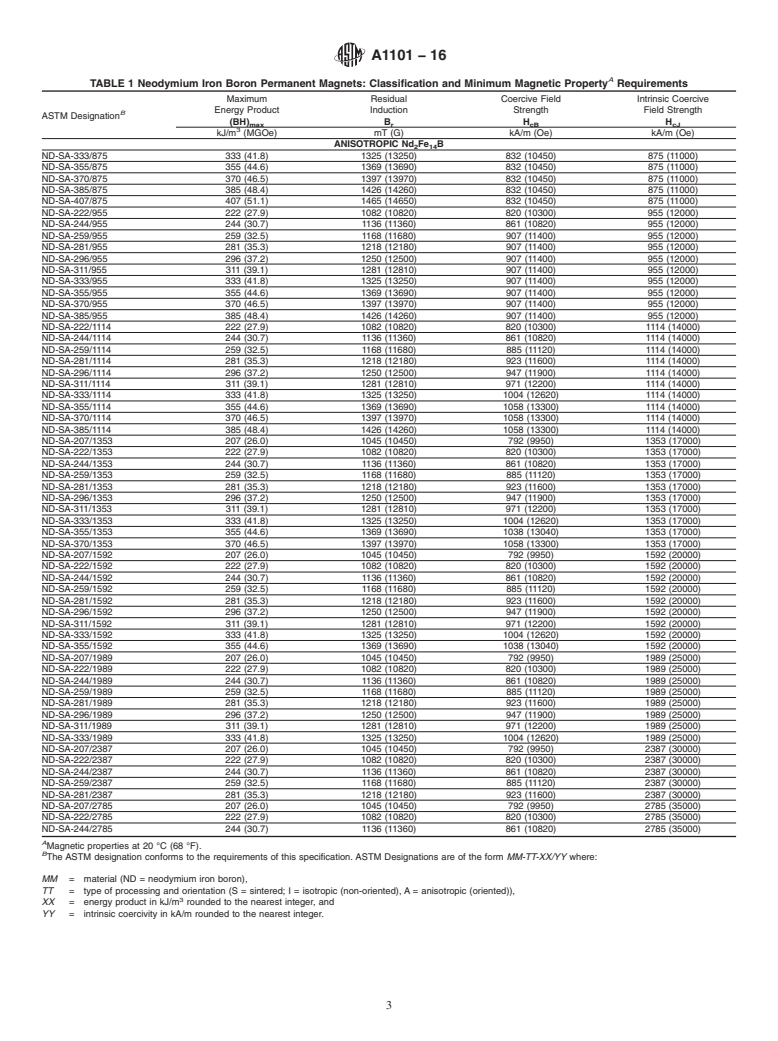
This specification covers technically important, commercially available, magnetically hard sintered and fully dense neodymium iron boron (Nd2Fe14B, NdFeB, or ‘Neo’ permanent magnets. These materials are available in a wide range of compositions with a commensurately large range of magnetic properties. Neodymium iron boron magnets have approximate magnetic properties of residual magnetic induction from 1.08 T (10 800 G) up to 1.5 T (15 000 G) and intrinsic coercive field strength of 875 kA/m (11 000 Oe) to above 2785 kA/m (35 000 Oe). Special grades and isotropic (un-aligned) magnets can have properties outside these ranges.
This specification provides guidance for the chemical composition of neodymium iron boron magnets as well as their physical and mechanical properties, magnetic properties (maximum energy product, residual induction, coercive field strength, intrinsic coercive field strength), workmanship, finish, and appearance. It also includes requirements for sampling, certification, and packaging and package marking.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers technically important, commercially available, magnetically hard sintered and fully dense neodymium iron boron (Nd2Fe14B, NdFeB, or “Neo”) permanent magnets. These materials are available in a wide range of compositions with a commensurately large range of magnetic properties. The numbers in the Nd2Fe14B name indicate the approximate atomic ratio of the key elements.
1.2 Neodymium iron boron magnets have approximate magnetic properties of residual magnetic induction, Br, from 1.08 T (10 800 G) up to 1.5 T (15 000 G) and intrinsic coercive field strength, HcJ, of 875 kA/m (11 000 Oe) to above 2785 kA/m (35 000 Oe). Special grades and isotropic (un-aligned) magnets can have properties outside these ranges (see Appendix X4). Specific magnetic hysteresis behavior (demagnetization curve) can be characterized using Test Method A977/A977M.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to customary (cgs-emu and inch-pound) units which are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:A1101 −16
Standard Specification for
Sintered and Fully Dense Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB)
1
Permanent Magnets
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A1101; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope A977/A977M Test Method for Magnetic Properties of High-
Coercivity Permanent Magnet Materials Using Hyster-
1.1 This specification covers technically important, com-
esigraphs
mercially available, magnetically hard sintered and fully dense
2.2 Other Standards:
neodymium iron boron (Nd Fe B, NdFeB, or “Neo”) perma-
2 14
MMPA Standard No. 0100-00 Standard Specifications for
nent magnets. These materials are available in a wide range of
3
Permanent Magnet Materials
compositions with a commensurately large range of magnetic
IEC 60404-8-1 Magnetic Materials Part 8: Specifications for
properties. The numbers in the Nd Fe B name indicate the
2 14
Individual Materials Section 1 – Standard Specifications
approximate atomic ratio of the key elements.
4
for Magnetically Hard Materials
1.2 Neodymium iron boron magnets have approximate
magnetic properties of residual magnetic induction, B , from
3. Terminology
r
1.08T(10 800 G) up to 1.5T(15 000 G) and intrinsic coercive
3.1 The terms and symbols used in this specification, unless
field strength, H , of 875 kA/m (11 000 Oe) to above 2785
cJ
otherwise noted, are defined in Terminology A340.
kA/m (35 000 Oe). Special grades and isotropic (un-aligned)
3.2 Terms that are not defined in Terminology A340 but are
magnets can have properties outside these ranges (see Appen-
in common usage and used herein are as follows.
dix X4). Specific magnetic hysteresis behavior (demagnetiza-
3.2.1 Recoil permeability, µ , is the permeability corre-
tion curve) can be characterized using Test Method A977/
(rec)
sponding to the slope of the recoil line. For reference see
A977M.
incremental, relative, and reversible permeabilities as defined
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
in Terminology A340. In practical use, this is the slope of the
standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
normal hysteresis loop in the second quadrant and in proximity
conversions to customary (cgs-emu and inch-pound) units
to the B-axis. The value of recoil permeability is dimension-
whichareprovidedforinformationonlyandarenotconsidered
less. Note that in producers’ product literature recoil perme-
standard.
ability is sometimes represented by the symbol µ , which is
r
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
defined by Terminology A340 as relative permeability.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2.2 Magnetic characteristics change with temperature.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Two key metrics of permanent magnet performance are re-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
sidual induction, B , and intrinsic coercive field strength, H .
r cJ
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
The change in these characteristics over a defined and limited
temperature range can be reversible, that is, nondestructive.
2. Referenced Documents
Thischangeisrepresentedbyvaluescalledreversibletempera-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: ture coefficients. The symbol for reversible temperature coef-
A340 Terminology of Symbols and Definitions Relating to ficient of induction is α(B ) and of (intrinsic) coercivity is
r
Magnetic Testing α(H ). They are expressed in percent change per degree
cJ
Celsius, %/°C, or the numerically equivalent percent per
Kelvin, %/K, and represent the average rate of change of the
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A06 on
Magnetic Properties and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A06.02 on
3
Material Specifications. Available from the Permanent Magnet Division of the SMMA (www.sm-
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2016. Published November 2016. DOI: ma.org). It was previously available from The International Magnetics Association
10.1520/A1101–16 (IMA). The IMA had been the successor to the MMPA and both organizations
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or (MMPA and IMA) no longer exist.
4
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), 3, rue de
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Varembé, 1st Floor,
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.