ASTM E2709-10
(Practice)Standard Practice for Demonstrating Capability to Comply with a Lot Acceptance Procedure
Standard Practice for Demonstrating Capability to Comply with a Lot Acceptance Procedure
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Lot acceptance procedures are used in industry for inspecting quality characteristics of raw materials, in-process product, and finished product. These procedures, together with process controls, comprise a quality control program. For additional information on process control see Practice E2281 dealing with process capability evaluation and Practice E2587 dealing with the use of control charts in statistical process control.
Lot inspection procedures classify quality characteristics as either attributes (measured on discrete scales such as percent defective) or variables (measured on continuous scales such as length, weight, or concentration).
Operating characteristic curves, which plot the relationship of the lot acceptance probability versus the true lot percent defective, are used to evaluate the discriminatory power of a given lot inspection procedure, or acceptance sampling plan, and are discussed in Practice E2234.
This practice considers inspection procedures that may involve multiple-stage sampling, where at each stage one can decide to accept the lot or to continue sampling, and the decision to reject the lot is deferred until the last stage.
At each stage there are one or more acceptance criteria on the test results; for example, limits on each individual test result, or limits on statistics based on the sample of test results, such as the average, standard deviation, or coefficient of variation (relative standard deviation).
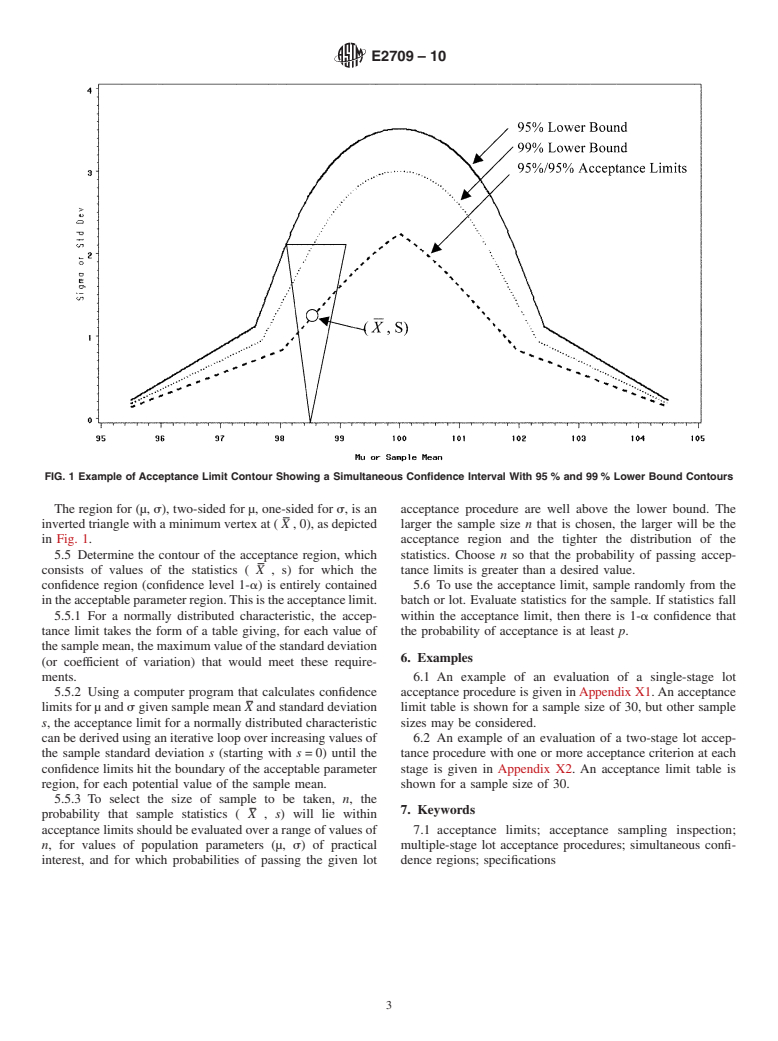
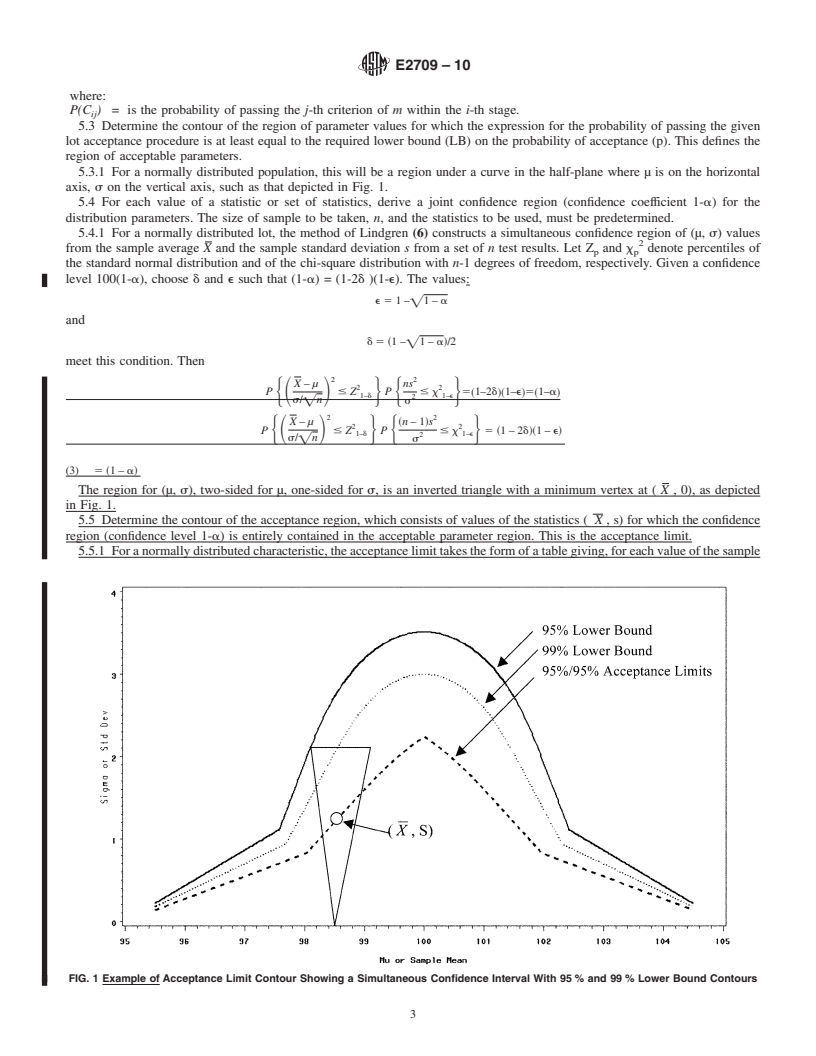
The methodology in this practice defines an acceptance region for a set of test results from the lot such that, at a prescribed confidence level, the probability that a sample from the lot will pass the original lot acceptance procedure is greater than or equal to a prespecified lower bound.
Having test results fall in the acceptance region is not equivalent to passing the original lot acceptance procedure, but provides assurance that a sample would pass the lot acceptance procedure with a specified probability.
Thi...
SCOPE
1.1 This practice provides a general methodology for evaluating single-stage or multiple-stage lot acceptance procedures which involve a quality characteristic measured on a numerical scale. This methodology computes, at a prescribed confidence level, a lower bound on the probability of passing a lot acceptance procedure, using estimates of the parameters of the distribution of test results from the lot.
1.2 For a prescribed lower probability bound, the methodology can also generate an acceptance limit table, which defines a set of test method outcomes (for example, sample averages and standard deviations) that would pass the multiple-stage procedure at a prescribed confidence level.
1.3 This approach may be used for demonstrating compliance with in-process, validation, or lot-release specifications.
1.4 The system of units for this practice is not specified.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: E2709 – 10
Standard Practice for
Demonstrating Capability to Comply with a Lot Acceptance
1
Procedure
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2709; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E2587 Practice for Use of Control Charts in Statistical
Process Control
1.1 This practice provides a general methodology for evalu-
ating single-stage or multiple-stage lot acceptance procedures
3. Terminology
whichinvolveaqualitycharacteristicmeasuredonanumerical
3.1 Definitions—See Terminology E456 for a more exten-
scale. This methodology computes, at a prescribed confidence
sive listing of terms in ASTM Committee E11 standards.
level, a lower bound on the probability of passing a lot
3.1.1 characteristic, n—a property of items in a sample or
acceptance procedure, using estimates of the parameters of the
population which, when measured, counted or otherwise ob-
distribution of test results from the lot.
served, helps to distinguish between the items. E2282
1.2 For a prescribed lower probability bound, the method-
3.1.2 mean, n—of a population, µ, average or expected
ology can also generate an acceptance limit table, which
value of a characteristic in a population, of a sample X , sum of
defines a set of test method outcomes (for example, sample
the observed values in a sample divided by the sample size.
averagesandstandarddeviations)thatwouldpassthemultiple-
E2586
stage procedure at a prescribed confidence level.
3.1.3 multiple-stage lot acceptance procedure, n—a proce-
1.3 This approach may be used for demonstrating compli-
dure for accepting a lot that involves more than one stage of
ance with in-process, validation, or lot-release specifications.
sampling and testing a given quality characteristic and one or
1.4 The system of units for this practice is not specified.
more acceptance criteria per stage.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.4 standard deviation, n—of a population, s, the square
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
root of the average or expected value of the squared deviation
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
of a variable from its mean – of a sample, s, the square root of
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
the sum of the squared deviations of the observed values in the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
sample divided by the sample size minus 1. E2586
2. Referenced Documents 3.1.5 test method, n—a definitive procedure that produces a
2 test result. E2282
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
3.2.1 acceptable parameter region, n—the set of values of
E2234 Practice for Sampling a Stream of Product by
parameters characterizing the distribution of test results for
Attributes Indexed by AQL
which the probability of passing the lot acceptance procedure
E2281 Practice for Process and Measurement Capability
is greater than a prescribed lower bound.
Indices
3.2.2 acceptance region, n—the set of values of parameter
E2282 Guide for Defining the Test Result of a Test Method
estimates that will attain a prescribed lower bound on the
E2586 Practice for Calculating and Using Basic Statistics
probability of passing a lot acceptance procedure at a pre-
scribed level of confidence.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee E11 on Quality and
3.2.3 acceptance limit, n—the boundary of the acceptance
Statistics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E11.20 on Test Method
region, for example, the maximum sample standard deviation
Evaluation and Quality Control.
test results for a given sample mean.
Current edition approved May 1, 2010. Published October 2010. Originally
approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as E2709 – 09. DOI:
4. Significance and Use
10.1520/E2709-10.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4.1 Lot acceptance procedures are used in industry for
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
inspecting quality characteristics of raw materials, in-process
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. product, and finished product. These procedures, together with
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2709 – 10
process controls, comprise a quality con
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately,ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:E2709–09 Designation: E2709 – 10
Standard Practice for
Demonstrating Capability to Comply with a Lot Acceptance
1
Procedure
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2709; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 Thispracticeprovidesageneralmethodologyforevaluatingsingle-stageormultiple-stagelotacceptanceprocedureswhich
involve a quality characteristic measured on a numerical scale. This methodology computes, at a prescribed confidence level, a
lower bound on the probability of passing a lot acceptance procedure, using estimates of the parameters of the distribution of test
results from the lot.
1.2 For a prescribed lower probability bound, the methodology can also generate an acceptance limit table, which defines a set
of test method outcomes (for example, sample averages and standard deviations) that would pass the multiple-stage procedure at
a prescribed confidence level.
1.3 This approach may be used for demonstrating compliance with in-process, validation, or lot-release specifications.
1.4 The system of units for this practice is not specified.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E2234 Practice for Sampling a Stream of Product by Attributes Indexed by AQL
E2281 Practice for Process and Measurement Capability Indices
E2282 Guide for Defining the Test Result of a Test Method
E2586 Practice for Calculating and Using Basic Statistics
E2587 Practice for Use of Control Charts in Statistical Process Control
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—See Terminology E456 for a more extensive listing of terms in ASTM Committee E11 standards.
3.1.1 characteristic, n—a property of items in a sample or population which, when measured, counted or otherwise observed,
helps to distinguish between the items. E2282
3.1.2 mean, n—of a population, µ, average or expected value of a characteristic in a population, of a sample X , sum of the
observed values in a sample divided by the sample size. E2586
3.1.3 multiple-stage lot acceptance procedure, n—aprocedureforacceptingalotthatinvolvesmorethanonestageofsampling
and testing a given quality characteristic and one or more acceptance criteria per stage.
3.1.4 standard deviation, n—of a population, s, the square root of the average or expected value of the squared deviation of
avariablefromitsmean– of a sample, s,thesquarerootofthesumofthesquareddeviationsoftheobservedvaluesinthesample
divided by the sample size minus 1. E2586
3.1.4
3.1.5 test method, n—a definitive procedure that produces a test result. E2282
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 acceptable parameter region, n—the set of values of parameters characterizing the distribution of test results for which
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee E11 on Quality and Statistics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E11.30 on Statistical Quality
Control.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2009. Published September 2009. DOI: 10.1520/E2709-09.
Current edition approved May 1, 2010. Published October 2010. Originally approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as E2709–09. DOI:
10.1520/E2709-10.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2709 – 10
the probability of passing the lot acceptance procedure is greater than a prescribed lower bound.
3.2.2 acceptance region, n—thesetofvaluesofparameterestimatesthatwillattainaprescribedlowerboundontheprobability
of passing a lot acceptance procedure at a prescribed level of confidence.
3.2.3 acceptance limit, n—the boundary of the acceptance region, for example, the maximum sample standard deviation test
results for a given
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.