ASTM C1147-01
(Practice)Standard Practice for Determining the Short Term Tensile Weld Strength of Chemical-Resistant Thermoplastics
Standard Practice for Determining the Short Term Tensile Weld Strength of Chemical-Resistant Thermoplastics
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the preparation and evaluation of joints between two pieces of weldable grades of thermoplastic materials, backed and unbacked, (such as those shown in Table 1) up to 2 in. (50 mm) in thickness.
1.2 Since there are numerous new technologies and techniques constantly being developed for plastic welding, there are no profiles and procedures that can be considered as standard for all plastics at various thicknesses. This practice is not intended to define profiles and procedures; however, it is intended to establish methods to evaluate minimum short term weld factors to be achieved by the welder for the respective plastics.
1.3 Weld procedures used for test pieces should reflect procedures to be used in actual fabrication.
1.4 Welding methods to be used could include machine welding, extrusion welding, and hot gas welding.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C 1147 – 01
Standard Practice for
Determining the Short Term Tensile Weld Strength of
1
Chemical-Resistant Thermoplastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1147; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
TABLE 1 Typical Guide for Hot Gas Welding Temperatures
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers the preparation and evaluation of NOTE 1—For other welding techniques, consult material and equipment
supplier for recommendations.
joints between two pieces of weldable grades of thermoplastic
A B
materials, backed and unbacked, (such as those shown in Table °F Recommended Gas Type
1) up to 2 in. (50 mm) in thickness.
HDPE 500–600 Nitrogen or Air
PP 550–600 Nitrogen or Air
1.2 Since there are numerous new technologies and tech-
PVC 500–550 Air
niques constantly being developed for plastic welding, there
CPVC 550–660 Air
are no profiles and procedures that can be considered as
PVDF 650–680 Nitrogen or Air
ECTFE 665–695 Nitrogen
standard for all plastics at various thicknesses. This practice is
ETFE 675–710 Air
not intended to define profiles and procedures; however, it is
FEP 650–725 Air
intended to establish methods to evaluate minimum short term
PFA 675–750 Air
MFA 536–554 Air
weld factors to be achieved by the welder for the respective
A
Measured 1 4 in. inside weld tip, directly in gas stream.
plastics.
/
B
Inert gas may be used in place of air.
1.3 Weld procedures used for test pieces should reflect
procedures to be used in actual fabrication.
4. Summary of Practice
1.4 Welding methods to be used could include machine
welding, extrusion welding, and hot gas welding.
4.1 The sheets are prepared and welded. Tensile test speci-
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
mens containing a section of the weld are prepared and tested.
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
Specimens of unwelded sheet are tested and compared to the
information only.
welded specimens. The short term weld factor determined is
compared to the standard (see Table 2), or to the factor agreed
2. Referenced Documents
upon between the supplier and the user.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Significance and Use
C 904 Terminology Relating to Chemical-Resistant Non-
2
metallic Materials
5.1 The mechanical performance of welded thermoplastic
D 4285 Test Method for Indicating Oil or Water in Com-
structures is largely dependent on the quality of the welding
3
pressed Air
operation. Fabricators should determine that the proper weld-
4
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
ing procedures are being followed and that welders maintain
their proficiency. Results from this practice are indicative of
3. Terminology
skill in proper welding procedures for different thermoplastic
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this prac-
materials and the use of appropriate welding equipment. If the
tice, see Terminology C 904.
welded test specimens have short term weld factors that meet
or exceed the minimums as set forth in this practice, or as
agreed to by supplier and user, it may be concluded that, with
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C03 on Chemical-
thesamedegreeofskillanddiligencebythewelder,acceptable
Resistant Nonmetallic Materialsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
C03.03on Thermoplastic Fabrications. welds should be obtained in fabricated structures.
Current edition approved May 10, 2001. Published July 2001. Originally
published as C 1147 – 90. Last previous edition C 1147 – 95.
6. Apparatus
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.05.
3
6.1 The apparatus for welding shall consist of the following:
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.02.
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01. 6.1.1 Welding Device, suitable for joining thermoplastics.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C 1147
TABLE 2 Minimum Short Term Weld Factors
Thermoplastic Hot Gas Extrusion Hot Plate
HDPE 0.8 0.8 0.9
PP 0.8 0.8 0.9
A
PVC 0.8 0.9
A
CPVC 0.6 0.8
PVDF 0.8 0.8 0.9
ECTFE 0.9 0.9 0.9
ETFE 0.9 0.9 0.9
FEP 0.9 0.9 0.9
A
TFE (PFA Filler) 0.9 0.9
PFA 0.9 0.9 0.9
A
Not applicable.
6.1.2 Air Supply, when needed, conforming to Test Method
D 4285.
6.1.3 Temperature Measuring Device, capable of measuring
FIG. 1 Test Pieces
the welding temperature to within 61 % for the specific plastic
as set forth in Table 1.
6.1.4 Clamps, suitable for holding the specimen while
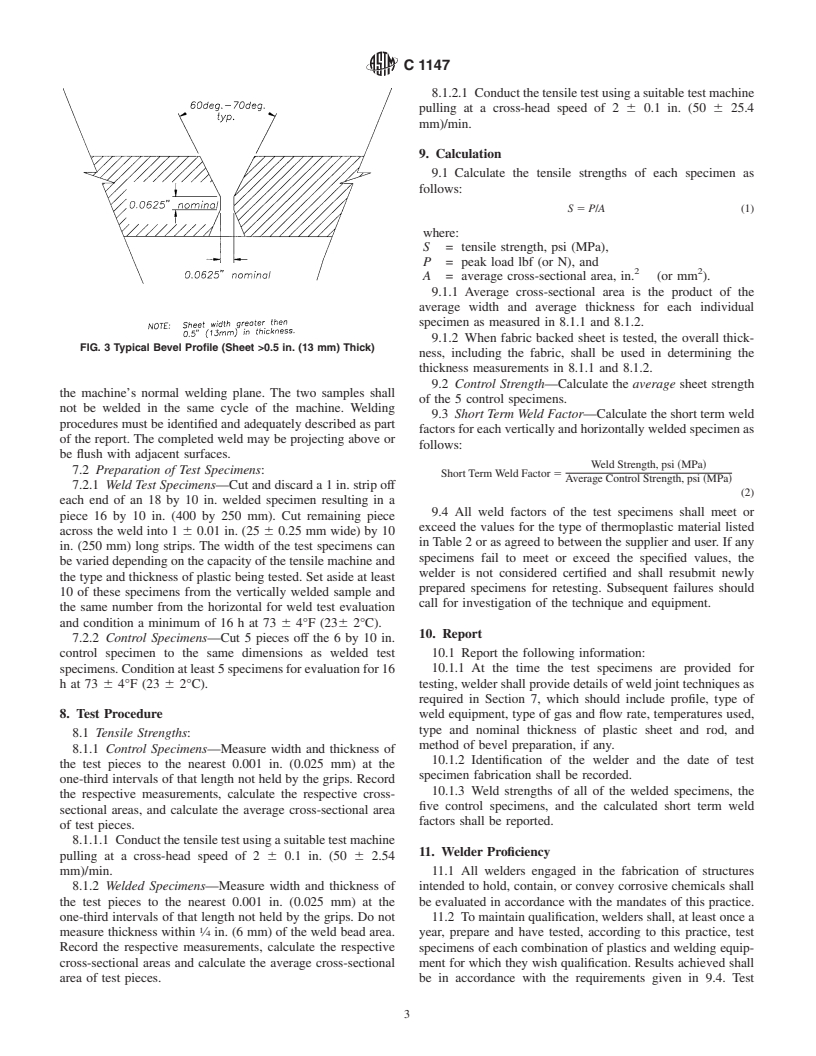
7.1.2 Edge Preparation—Bevel one 18 in. (450 mm) edge
welding.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.