ASTM D2852-95(2008)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Styrene-Rubber (SR) Plastic Drain Pipe and Fittings
Standard Specification for Styrene-Rubber (SR) Plastic Drain Pipe and Fittings
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the material, dimensional, and mechanical requirements, and the corresponding test methods for plain-end or bell-end styrene-rubber (SR) plastic drain pipes and fittings in 2 to 6 in. sizes that are suitable for nonpressure underground drainage of sewage and certain other liquid wastes, in applications outside the building limits, where dimensional stability, resistance to aging, and strong eight joints are required. The SR plastics shall contain styrene plastics combined with rubber (polybutadiene or butadiene-styrene type, or both) and compounding materials such as antioxidants and lubricants, and may contain acrylonitrile. When evaluated using the test procedures prescribed herein, the finished pipes and fittings shall conform to the following requirements: workmanship; dimensions such as socket and pipe diameters, wall thickness, laying length, socket depth, and dimensional stability; and mechanical properties such as impact strength, stiffness and deflection temperature, tensile strength and elongation at rupture, modulus of elasticity in tension, Izod impact strength, flattening resistance, solvent cement, and joint tightness.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods for materials, dimensions, workmanship, impact resistance, load-deflection properties, dimensional stability, and joint tightness of plain-end or bell-end styrene-rubber (SR) plastic drain pipe and fittings in sizes 2 through 6 in.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 8, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2852 −95(Reapproved 2008)
Standard Specification for
Styrene-Rubber (SR) Plastic Drain Pipe and Fittings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2852; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
D2444Test Method for Determination of the Impact Resis-
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods
tance of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a
for materials, dimensions, workmanship, impact resistance,
Tup (Falling Weight)
load-deflection properties, dimensional stability, and joint
D3122 Specification for Solvent Cements for Styrene-
tightness of plain-end or bell-end styrene-rubber (SR) plastic
Rubber (SR) Plastic Pipe and Fittings
drain pipe and fittings in sizes 2 through 6 in.
F412Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
2.2 Federal Standard:
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
Fed. Std. No. 123Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
information only.
2.3 Military Standard:
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
MIL-STD-129Marking for Shipment and Storage
test methods portion, Section 8, of this specification: This
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
3. Terminology
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita- nology F412, and abbreviations are in accordance with Termi-
tions prior to use.
nologyD1600,unlessotherwisespecified.Theabbreviationfor
styrene-rubber plastics is SR.
2. Referenced Documents
4. Significance and Use
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D256Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum
4.1 The requirements for this specification are intended to
Impact Resistance of Plastics
provide pipe and fittings suitable for nonpressure underground
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
drainage of sewage and certain other liquid wastes, in appli-
D638Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
cationsoutsidethebuildinglimits,wheredimensionalstability,
D648Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
resistance to aging, and strong eight joints are required. The
Under Flexural Load in the Edgewise Position
plasticdrainpipeandfittingsdescribedinthisspecificationare
D1600TerminologyforAbbreviatedTermsRelatingtoPlas-
intended for use in the following applications:
tics
4.1.1 House connections to septic tanks.
D2122Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
4.1.2 Footing drains (foundation drains).
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
4.1.3 Storm drainage.
D2321PracticeforUndergroundInstallationofThermoplas-
4.2 ThepipeshouldbeinstalledinaccordancewithPractice
tic Pipe for Sewers and Other Gravity-Flow Applications
D2321.
D2412Test Method for Determination of External Loading
5. Materials and Manufacture
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
5.1 Materials—The pipe and fittings shall be made of
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.65 on Land
styrene-rubber (SR) plastics meeting the following require-
Drainage.
ments:
Current edition approved March 1, 2008. Published May 2008. Originally
approved in 1969. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D2852–95(2002).
DOI: 10.1520/D2852-95R08.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
the ASTM website. www.dodssp.daps.mil.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D2852−95 (2008)
5.1.1 The SR plastics compound shall contain at least 50% 6.3 Fitting and Bell-End Dimensions:
styrene plastics, combined with rubbers to a minimum rubber
6.3.1 Socket Diameters—The inside diameters of the sock-
content of 5%, and compounding materials such as antioxi-
ets shall comply with the dimensions in Table 2 when deter-
dants and lubricants, and may contain up to 15% acrylonitrile
mined in accordance with 8.7.1.
combined in the styrene plastics or rubbers, or both. The
6.3.2 Wall Thickness:
rubbers shall be of the polybutadiene or butadiene-styrene
6.3.2.1 For belled pipe and fittings fabricated from pipe
type, or both, with a maximum styrene content of 25% or
sections,thethicknessofthebelledsectionshallbe considered
nitrile type. The combined styrene plastics and rubber content
satisfactory if the bell was formed from pipe meeting the
shall be not less than 90%. No fillers may be used.
requirements of Table 1.
5.1.2 The SR plastic compound shall meet the following
6.3.2.2 For molded fittings, the wall thickness of the water-
minimumrequirementswhentestedinaccordancewithSection
way and socket or bell shall be no less than the respective
8:
minimum thickness listed for the equivalent pipe wall in Table
Tensile strength at rupture, 3800 psi (26.2 MPa)
2. For reducing fittings or those with smaller inlets, the
Elongation at rupture, %, 15
minimum wall thickness of each inlet shall be no less than the
Modulus of elasticity in tension, 300 000 psi (2068 MPa)
Izod impact strength, notched 0.8 ft·lbf/in. (42.5 J/m) minimum wall thickness for that size pipe.
Deflection temperature at 264 psi (1.82 149 (65)
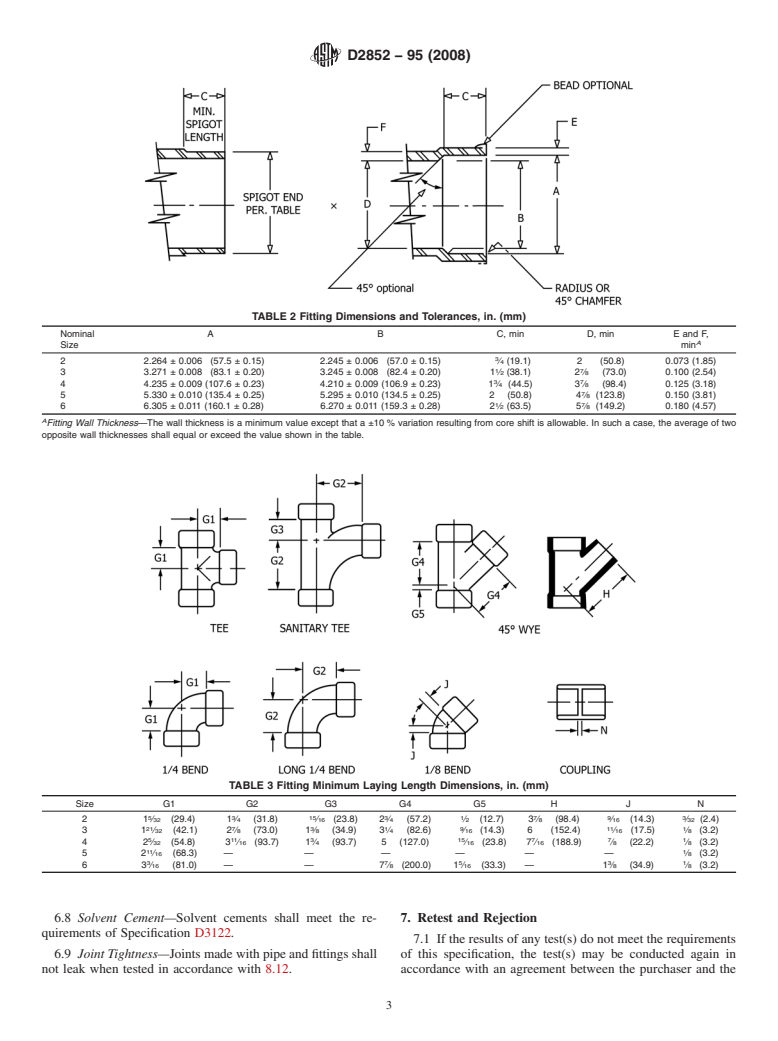
6.3.3 Socket Depth—The socket depth shall be not less than
MPa),° F (°C)
thatshowninTable2whenmeasuredinaccordancewith8.7.3.
5.1.3 Rework Material—Clean rework material, generated
6.3.4 Laying Length—The laying length shall meet the
from the manufacturer’s own pipe or fittings production, may
requirements shown in Table 3. All dimensions are minimum
be used by the same manufacturer, provided that the pipe and
with a negative tolerance of zero.
fittings produced meet all of the requirements of this specifi-
cation.
6.4 Impact Strength—The impact strength of the pipe and
fittings shall not be less than the values given in Table 4 when
6. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
tested in accordance with 8.9.
6.1 Workmanship—The pipe shall be homogeneous
NOTE 1—This test is intended only as a quality control test, not as a
throughout and essentially uniform in color, opacity, density,
simulated service test.
and other properties. The inside and outside surfaces shall be
6.5 Pipe Stiffness—The pipe stiffness at 5% deflection shall
semimatte or glossy in appearance and free of chalking, sticky,
be not less than the values given in Table 5 when tested in
or tacky material.The pipe walls shall be free of cracks, holes,
accordance with 8.10. This requirement does not apply to
blisters, voids, foreign inclusion, or other defects that are
fittings.
visible to the naked eye and that may affect the wall integrity.
Holes deliberately placed in perforated pipe are acceptable.
NOTE 2—The 5% deflection criterion, which was arbitrarily selected
for testing convenience, should not be considered as a limitation with
The surfaces shall be free of excessive bloom. Bloom or
respect to in-use deflection. The engineer is responsible for establishing
chalking may develop in pipe exposed to direct rays of the sun
the acceptable deflection limit.
(ultraviolet radiant energy) for extended periods and conse-
NOTE 3—The strength and load-carrying capabilities of plastic drain
quently these requirements do not apply to pipe after extended
and sewer pipe are measured and reported as Pipe Stiffness, which is
exposure to direct rays of the sun.
determined in accordance with Test Method D2412. The term “crush
strength”isnotapplicabletoplasticpipingbecause(a)thevaluesobtained
6.2 Pipe Dimensions:
can be significantly different, depending on the bedding, loading, or
6.2.1 Pipe Diameters—The outside and inside diameters of
testing technique used; and (b) the term derives from rigid pipe and refers
the pipe shall be within the tolerances given in Table 1 when
to its ultimate strength at rupture.
tested in accordance with 8.6.1.
6.6 Flattening—The pipe shall show no evidence of
6.2.2 Wall Thickness—Pipe wall thickness shall meet the
splitting, cracking, or breaking at 20% deflection when tested
requirements of Table 1 when measured in accordance with
in accordance with 8.8.
8.6.2.
6.2.3 Laying Length—The laying length shall be 10 ft with 6.7 Dimensional Stability—The average decrease in inside
atoleranceof−0+ ⁄2in.,unlessotherwisespecified.Thelaying diameterofpipeandfittingsshallnotexceed10%whentested
length shall be determined in accordance with 8.6.3. in accordance with 8.11.
TABLE 1 Dimensions and Tolerances for SR Plastic Drain Pipe, in. (mm)
Permissible Deviations of
the Diameter from Mea- Minimum Average Minimum Wall
Nominal Size Average Outside Diameter
sured Average (Out-of- Inside Diameter Thickness
roundness)
2 2.250 ± 0.006 (57.2 ± 0.15) ±0.030 (±0.76) 2.000 (50.8) 0.073 (1.85)
3 3.250 ± 0.008 (82.6 ± 0.20) ±0.040 (±1.02) 2.875 (73.0) 0.100 (2.54)
4 4.215 ± 0.009 (104.8 ± 0.23) ±0.050 (±1.27) 3.875 (98.4) 0.125 (3.18)
5 5.300 ± 0.010 (134.6 ± 0.25) ±0.060 (±1.52) 4.875 (123.8) 0.150 (3.81)
6 6.275 ± 0.011 (159.4 ± 0.28) ±0.070 (±1.78) 5.875 (149.2) 0.180 (4.57)
D2852−95 (2008)
TABLE 2 Fitting Dimensions and Tolerances, in. (mm)
Nominal A B C, min D, min E and F,
A
Size min
2 2.264 ± 0.006 (57.5 ± 0.15) 2.245 ± 0.006 (57.0 ± 0.15) ⁄4 (19.1) 2 (50.8) 0.073 (1.85)
1 7
3 3.271 ± 0.008 (83.1 ± 0.20) 3.245 ± 0.008 (82.4 ± 0.20) 1 ⁄2 (38.1) 2 ⁄8 (73.0) 0.100 (2.54)
3 7
4 4.235 ± 0.009 (107.6 ± 0.23) 4.210 ± 0.009 (106.9 ± 0.23) 1 ⁄4 (44.5) 3 ⁄8 (98.4) 0.125 (3.18)
5 5.330 ± 0.010 (135.4 ± 0.25) 5.295 ± 0.010 (134.5 ± 0.25) 2 (50.8) 4 ⁄8 (123.8) 0.150 (3.81)
1 7
6 6.305 ± 0.011 (160.1 ± 0.28) 6.270 ± 0.011 (159.3 ± 0.28) 2 ⁄2 (63.5) 5 ⁄8 (149.2) 0.180 (4.57)
A
Fitting Wall Thickness—The wall thickness is a minimum value except that a ±10 % variation resulting from core shift is allowable. In such a case, the average of two
opposite wall thicknesses shall equal or exceed the value shown in the table.
TABLE 3 Fitting Minimum Laying Length Dimensions, in. (mm)
Size G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 H J N
5 3 15 3 1 7 9 3
21 ⁄32 (29.4) 1 ⁄4 (31.8) ⁄16 (23.8) 2 ⁄4 (57.2) ⁄2 (12.7) 3 ⁄8 (98.4) ⁄16 (14.3) ⁄32 (2.4)
21 7 3 1 9 11 1
31 ⁄32 (42.1) 2 ⁄8 (73.0) 1 ⁄8 (34.9) 3 ⁄4 (82.6) ⁄16 (14.3) 6 (152.4) ⁄16 (17.5) ⁄8 (3.2)
5 11 3 15 7 7 1
42 ⁄32 (54.8) 3 ⁄16 (93.7) 1 ⁄4 (93.7) 5 (127.0) ⁄16 (23.8) 7 ⁄16 (188.9) ⁄8 (22.2) ⁄8 (3.2)
11 1
52 ⁄16 (68.3) — — — — — — ⁄8 (3.2)
3 7 5 3 1
63 ⁄16 (81.0) — — 7 ⁄8 (200.0) 1 ⁄16 (33.3) — 1 ⁄8 (34.9) ⁄8 (3.2)
6.8 Solvent Cement—Solvent cements shall meet the re- 7. Retest and Rejection
quirements of Specification D3122.
7.1 If the results of any test(s) do not meet the requirements
6.9 Joint Tightness—Jointsmadewithpipeandfittingsshall of this specification, the test(s) may be conducted again in
not leak when tested in accordance with 8.12. accordance with an agreement between the purchaser and the
D2852−95 (2008)
TABLE 4 Minimum Impact Strength Requirements of Pipe and
tions specified by the manufacturer. The speed of testing shall
Fittings at 73°F (23°C)
be 0.20 to 0.25 in. (5 to 6 mm)/min.
Minimum Impact
Nominal Size, in.
8.6 Pipe Dimensions:
ft·lbf m·kg
8.6.1 Pipe Diameters:
210 1.4
310 1.4 8.6.1.1 Measure the average outside diameter of the pipe in
415 2.1
accordance with Test Method D2122. Use either a tapered-
515 2.1
sleeve gage or a vernier circumferential wrap tape accurate to
615 2.1
60.001 in. (60.02 mm).
8.6.1.2 Measure the average inside diameter of the pipe in
TABLE 5 Minimum Pipe Stiffness for Pipe accordance with Test Method D2122.
Minimum Pipe Stiffness at 5 % 8.6.2 Wall Thickness—Measure the wall thickness in accor-
Deflection
dance with Test Method D2122. Make sufficient readings, a
Nominal Size, in. Original and Water Immersion
minimum of six, to ensure that the minimum thickness has
Specimens
been determined. Use a cylindrical anvil tubing micrometer
psi MPa
accurate to 60.001 in. (60.02 mm).
2 50 0.35
8.6.3 Length—Determine the over-all length of the pipe in
3 42 0.29
4 38 0.26
accordance with Test Method D2122 using a steel tape with at
5 37 0.26
least ⁄16-in. (1-mm) graduations. For belled or coupled pipe,
6 34 0.23
determine the laying length by measuring the bell or coupling
socket depth with a steel rule with at least ⁄16-in. graduations
and subtracting this dimension from the overall length.
seller. There shall be no agreement to lower the minimum
8.7 Fitting and Bell-End Socket Dimensions:
requirement of the specification by such means as omitting
tests that are a part of the specification, substituting or 8.7.1 Socket Diameters—Measure the inside diameters of
modifying a test method, or by changing the specification the sockets at the socket entrance and bottom, using an inside
micrometer accurate to 60.001 in. (60.02 mm) or a telescop-
limits. In retesting, the product requirements of this specifica-
tion shall be met and the test methods designated in the ing pin gage in conjunction with an outside micrometer
specification shall be followed. If, upon retest, failure occurs, accurate to 60.001 in. Determine the average inside diameters
thequantityofproductrepresentedbythetest(s)doesnotmeet attheentranceandthebottomofthesocketbytakingsufficient
the requirements of this specification. readingsateachposition.Calculatetheaverageinsidediameter
at each position by taking the mean of the minimum and
8. Test Methods
maximum values.
8.1 Conditioning—Condition the specimens prior to test at 8.7.2 Wall Thickness—Measure the wall thickness in accor-
73.4 6 3.6°F (23 6 2°C) and 50 6 5% relative humidity for dance with Test Method D2122. Make sufficent readings, a
not less than 40 h in accordance with Procedure A of Practice minimum of six, to ensure that the minimum thickness has
D618, for those tests where conditioning is required and in all been determined. Use a cylindrical anvil tubing micrometer
cases of disagreement. accurate to 60.001 in. (60.02 mm).
8.7.3 Socket Depth—Measure the socket depth using a steel
8.2 Test Conditions—Conduct tes
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.