ASTM D4796-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Bond Strength of Thermoplastic Traffic Marking Materials
Standard Test Method for Bond Strength of Thermoplastic Traffic Marking Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The function of this test method is to provide numerical instrumental results indicating the cohesive and/or adhesive bond strength of thermoplastic traffic marking to a specified cement brick substrate.
The use of this test method allows the user and manufacturer to control the quality of the product and make inferences about the performance of the thermoplastic traffic marking product. Results from these tests also provide information helpful in researching and developing thermoplastic traffic marking materials.
The method has been revised to be more consistent to methodology in other ASTM bond methods for coatings in Test Methods D4541, D5179, and D7234.
Strict adherence to the procedures outlined is necessary for precision of the test method. Under no conditions should the bond strength be accepted unless there is conformance to the method.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides an instrumental means for the determination of thermoplastic traffic marking material bond strengths using cement bricks and loading fixtures.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4796 − 10
Standard Test Method for
1
Bond Strength of Thermoplastic Traffic Marking Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4796; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.1 This test method provides an instrumental means for the
determination of thermoplastic traffic marking material bond
3. Terminology
strengths using cement bricks and loading fixtures.
3.1 The terms and definitions in Terminology D16 apply to
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
this method.
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only. 3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 cement brick, n—a brick formed by mixing cement
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
and fine sand together and allowing to harden with 210.9 to
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
2
351.5 kg/cm (3000 to 5000 psi) compression strength.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
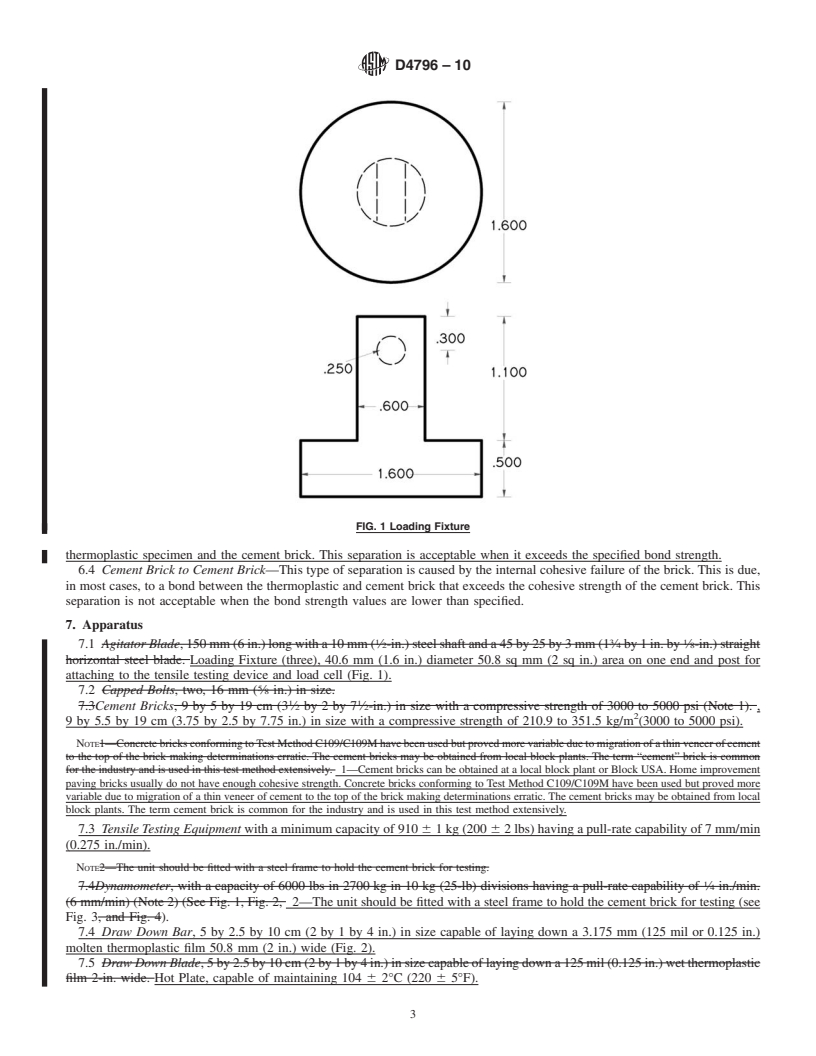
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 3.2.2 loading fixture, n—(alsoreferredtoasdollies,studs,or
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
jigs) metal fixture round and flat on one end for bonding to test
sample and shaped on the other end for attaching to tensile
2. Referenced Documents
testing device (Fig. 1).
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: 3.2.3 thermoplastic, n—traffic marking (same as 3.2.4).
C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of
3.2.4 thermoplastic traffıc marking, n—a highly filled
Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube
100 % total solids highway marking system that when heated
Specimens)
toamoltenstatecanbeextrudedorsprayedontoaroadsurface
D16 TerminologyforPaint,RelatedCoatings,Materials,and
and when cooled forms a solid durable delineator or road
Applications
marking thermoplastic usually melted to 218°C (425°F).
D4541 Test Method for Pull-Off Strength of Coatings Using
Portable Adhesion Testers
4. Summary of Test Method
D5179 Test Method for Measuring Adhesion of Organic
4.1 The thermoplastic specimen is prepared for this test by
Coatings to Plastic Substrates by Direct Tensile Testing
first melting a sample to its application temperature under
D7234 Test Method for Pull-OffAdhesion Strength of Coat-
continuous agitation. The specimen is then applied to the
ings on Concrete Using Portable Pull-Off Adhesion Tes-
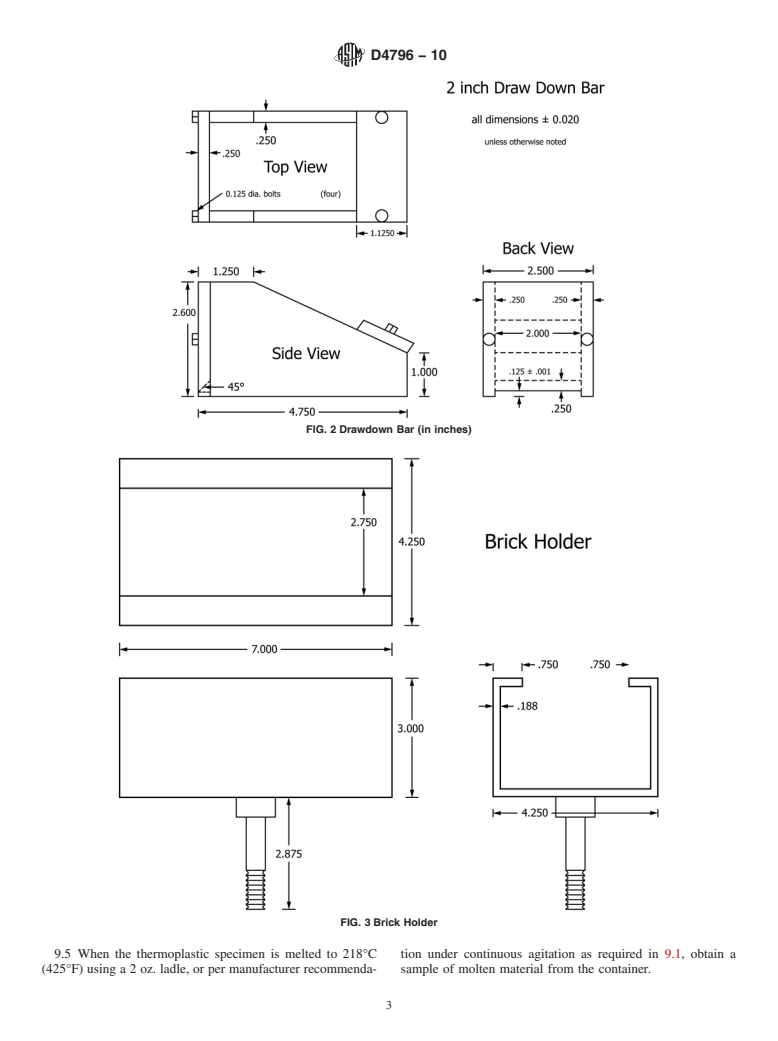
specified cement brick using a hot drawdown bar (Fig. 2),
ters
heated to 104 6 2°C (220 6 5°F), at 3.175 mm (125 mils)
D7307 PracticeforSamplingofThermoplasticTrafficMark-
thickness. While the thermoplastic is still soft, three cuts are
ing Materials
made with a 40.6 mm (1.6 in.) diameter die, heated to 104 6
D7308 Practice for Sample Preparation of Thermoplastic
2°C (220 6 5°F), in order to separate the test area from the rest
Traffic Marking Materials
of the drawdown. The die may be heated while submerged in
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
glycerin to prevent thermoplastic from sticking to the die. The
ASTM Test Methods
test areas are allowed to cool slightly and then three 40.6 mm
(1.6 in.) diameter heated loading fixtures are laid on the test
areas. The samples are then allowed to cure overnight before
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
determining the bond strength on a tensile testing device.
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.44 on Traffic Coatings.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2010. Published March 2011. Originally
5. Significance and Use
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D4796 – 88 (2004).
DOI: 10.1520/D4796-10.
5.1 The function of this test method is to provide numerical
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
instrumental results indicating the cohesive and/or adhesive
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
bond strength of thermoplastic traffic marking to a specified
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. cement brick substrate.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4796 − 10
thermoplastic specimen and the cement brick. This separation
is acceptable when it exceeds the specified bond strength.
6.4 Cement Brick to Cement Brick
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D4796–88(Reapproved2004) Designation:D4796–10
Standard Test Method for
1
Bond Strength of Thermoplastic Traffic Marking Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4796; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method provides an instrumental means for the determination of thermoplastic traffic marking material bond
strengths using cement bricks and steel cubes. loading fixtures.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube Specimens)
D16 Terminology for Paint, Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications
C881/C881MSpecification for Epoxy-Resin-Base Bonding Systems for Concrete D4541 Test Method for Pull-Off Strength of
Coatings Using Portable Adhesion Testers
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics 5179 Test Method for MeasuringAdhesion of Organic Coatings to Plastic Substrates by
Direct Tensile Testing
E284Terminology of Appearance D7234 Test Method for Pull-Off Adhesion Strength of Coatings on Concrete Using Portable
Pull-Off Adhesion Testers
F412Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems D7307 Practice for Sampling of Thermoplastic Traffic Marking Materials
D7308 Practice for Sample Preparation of Thermoplastic Traffic Marking Materials
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Terminology D883, E284, and F412 unless otherwise indicated.
3.1 The terms and definitions in Terminology D16 apply to this method.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 cement brick, n—a brick formed by mixing cement and fine sand together and allowing to harden. —a brick formed by
2
mixing cement and fine sand together and allowing to harden with 210.9 to 351.5 kg/cm (3000 to 5000 psi) compression strength.
3.2.2 loading fixture, n—(also referred to as dollies, studs, or jigs) metal fixture round and flat on one end for bonding to test
sample and shaped on the other end for attaching to tensile testing device (Fig. 1).
3.2.3 thermoplastic, n—traffic marking (same as 3.2.33.2.4).
3.2.33.2.4 thermoplastic traffıc marking, n—a highly filled 100 % total solids highway marking system that when heated to a
molten state can be extruded or sprayed onto a road surface and when cooled forms a solid durable delineator or road marking
thermoplastic usually melted to 218°C (425°F).
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1The thermoplastic specimen is prepared for this test by first melting a sample to its application temperature under continuous
agitation. The specimen is then applied to the specified cement brick by a hot drawdown blade. Two steel cubes are then
immediately placed onto the hot thermoplastic line and the excess thermoplastic trimmed away from around the two steel cubes.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.44 on Traffic Coatings.
Current edition approved JuneDec. 1, 2004.2010. Published June 2004.March 2011. Originally approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 19982004 as
D4796–88(1998).D4796 – 88 (2004). DOI: 10.1520/D4796-88R04.10.1520/D4796-10.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4796–10
After the trimming is complete, the steel cubes are removed. A heat
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.