ASTM D2161-10(2016)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Conversion of Kinematic Viscosity to Saybolt Universal Viscosity or to Saybolt Furol Viscosity
Standard Practice for Conversion of Kinematic Viscosity to Saybolt Universal Viscosity or to Saybolt Furol Viscosity
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 At one time the petroleum industry relied on measuring kinematic viscosity by means of the Saybolt viscometer, and expressing kinematic viscosity in units of Saybolt Universal Seconds (SUS) and Saybolt Furol Seconds (SFS). This practice is now obsolete in the petroleum industry.
4.2 This practice establishes the official equations relating SUS and SFS to the SI kinematic viscosity units, mm2/s.
4.3 This practice allows for the conversion between SUS and SFS units and SI units of kinematic viscosity.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice2 covers the conversion tables and equations for converting kinematic viscosity in mm2/s at any temperature to Saybolt Universal viscosity in Saybolt Universal seconds (SUS) at the same temperature and for converting kinematic viscosity in mm2/s at 122 °F and 210 °F (50 °C and 98.9 °C) to Saybolt Furol viscosity in Saybolt Furol seconds (SFS) at the same temperatures. Kinematic viscosity values are based on water being 1.0034 mm2/s (cSt) at 68 °F (20 °C).
Note 1: A fundamental and preferred method for measuring kinematic viscosity is by use of kinematic viscometers as outlined in Test Method D445. It is recommended that kinematic viscosity be reported in millimetres squared per second, instead of Saybolt Universal Seconds (SUS) or Saybolt Furol Seconds (SFS). This method is being retained for the purpose of calculation of kinematic viscosities from SUS and SFS data that appear in past literature. One millimetre squared per second (mm2/s) equals one centistoke (cSt), which is another unit commonly found in older literature.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for reference information purposes only. The SI unit of kinematic viscosity is mm2/s.
1.2.1 Exception—Fahrenheit temperature units are used in this practice because they are accepted by industry for the type of legacy conversions described in this practice.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2161 − 10 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Practice for
Conversion of Kinematic Viscosity to Saybolt Universal
1
Viscosity or to Saybolt Furol Viscosity
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2161; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2 3
1.1 This practice covers the conversion tables and equa- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
2
tions for converting kinematic viscosity in mm /s at any D445Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
temperature to Saybolt Universal viscosity in Saybolt Univer- and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of DynamicViscos-
sal seconds (SUS) at the same temperature and for converting ity)
2
kinematic viscosity in mm /s at 122°F and 210°F (50°C and D2270Practice for Calculating Viscosity Index from Kine-
98.9°C) to Saybolt Furol viscosity in Saybolt Furol seconds matic Viscosity at 40°C and 100°C
4
(SFS)atthesametemperatures.Kinematicviscosityvaluesare 2.2 ASTM Adjunct:
2
based on water being 1.0034mm /s (cSt) at 68°F (20°C). ADJD2161Viscosity Extrapolation Tables to Zero Degrees
Fahrenheit (SSU)
NOTE1—Afundamentalandpreferredmethodformeasuringkinematic
viscosity is by use of kinematic viscometers as outlined in Test Method
3. Summary of Practice
D445. It is recommended that kinematic viscosity be reported in millime-
tres squared per second, instead of Saybolt Universal Seconds (SUS) or 3.1 The Saybolt Universal viscosity equivalent to a given
Saybolt Furol Seconds (SFS). This method is being retained for the
kinematic viscosity varies with the temperature at which the
purpose of calculation of kinematic viscosities from SUS and SFS data
determination is made. The basic conversion values are those
2
that appear in past literature. One millimetre squared per second (mm /s)
given in Table 1 for 100°F. The Saybolt Universal viscosity
equals one centistoke (cSt), which is another unit commonly found in
equivalent to a given kinematic viscosity at any temperature
older literature.
may be calculated as described in 4.3. Equivalent values at
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
210°F are given in Table 1 for convenience.
standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for
reference information purposes only. The SI unit of kinematic 3.2 The Saybolt Furol viscosity equivalents are tabulated in
2
viscosity is mm /s. Table 3 for temperatures of 122°F and 210°F only.
1.2.1 Exception—Fahrenheit temperature units are used in
3.3 ExamplesforusingthetablesaregiveninAppendixX1.
this practice because they are accepted by industry for the type
4. Significance and Use
of legacy conversions described in this practice.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 4.1 At one time the petroleum industry relied on measuring
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the kinematic viscosity by means of the Saybolt viscometer, and
expressing kinematic viscosity in units of Saybolt Universal
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- Seconds(SUS)andSayboltFurolSeconds(SFS).Thispractice
is now obsolete in the petroleum industry.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.2 This practice establishes the official equations relating
2
SUS and SFS to the SI kinematic viscosity units, mm /s.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum
Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
3
mittee D02.07 on Flow Properties. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
CurrenteditionapprovedJuly1,2016.PublishedJuly2016.Originallyapproved contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
in 1963, replacing former D446 and D666. Last previous edition approved in 2010 Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
ɛ1
as D2161 – 10 . DOI: 10.1520/D2161-10R16. the ASTM website.
2 4
This practice, together with Practice D2270, replaces Compilation of ASTM Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
Viscosity Tables for Kinematic Viscosity Conversions. ADJD2161. Original adjunct produced in 1998.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2161 − 10 (2016)
4.3 This practice all
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D2161 − 10 D2161 − 10 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Practice for
Conversion of Kinematic Viscosity to Saybolt Universal
1
Viscosity or to Saybolt Furol Viscosity
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2161; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1
ε NOTE—The format of continuing Table 1 was corrected editorially in September 2015.
1. Scope*Scope
2 2
1.1 This practice covers the conversion tables and equations for converting kinematic viscosity in mm /s at any temperature
to Saybolt Universal viscosity in Saybolt Universal seconds (SUS) at the same temperature and for converting kinematic viscosity
2
in mm /s at 122122 °F and 210°F (50210 °F (50 °C and 98.9°C)98.9 °C) to Saybolt Furol viscosity in Saybolt Furol seconds (SFS)
2
at the same temperatures. Kinematic viscosity values are based on water being 1.0034 mm1.0034 mm /s (cSt) at 68°F (20°C).68 °F
(20 °C).
NOTE 1—A fundamental and preferred method for measuring kinematic viscosity is by use of kinematic viscometers as outlined in Test Method D445.
It is recommended that kinematic viscosity be reported in millimetres squared per second, instead of Saybolt Universal Seconds (SUS) or Saybolt Furol
Seconds (SFS). This method is being retained for the purpose of calculation of kinematic viscosities from SUS and SFS data that appear in past literature.
2
One millimetre squared per second (mm /s) equals one centistoke (cSt), which is another unit commonly found in older literature.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for reference
2
information purposes only. The SI unit of kinematic viscosity is mm /s.
1.2.1 Exception—Fahrenheit temperature units are used in this practice because they are accepted by industry for the type of
legacy conversions described in this practice.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity)
D2270 Practice for Calculating Viscosity Index from Kinematic Viscosity at 40 °C and 100 °C
4
2.2 ASTM Adjunct:
ADJD2161 Viscosity Extrapolation Tables to Zero Degrees Fahrenheit (SSU)
3. Summary of Practice
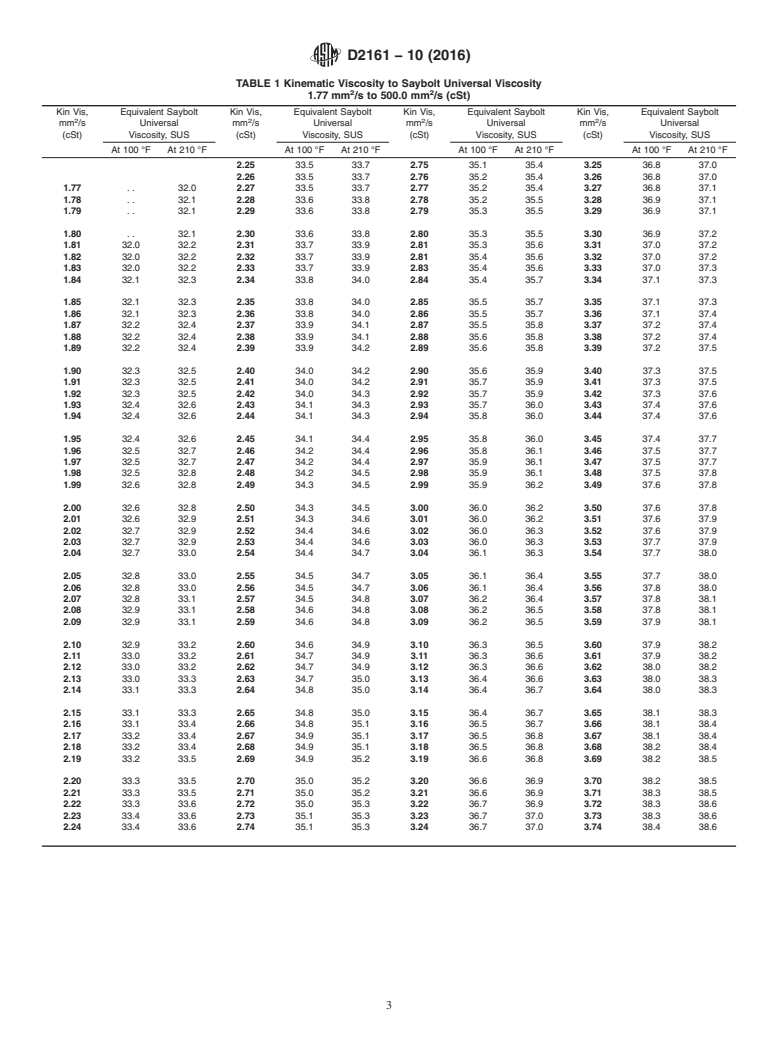
3.1 The Saybolt Universal viscosity equivalent to a given kinematic viscosity varies with the temperature at which the
determination is made. The basic conversion values are those given in Table 1 for 100°F.100 °F. The Saybolt Universal viscosity
equivalent to a given kinematic viscosity at any temperature may be calculated as described in 4.3. Equivalent values at
210°F210 °F are given in Table 1 for convenience.
3.2 The Saybolt Furol viscosity equivalents are tabulated in Table 3 for temperatures of 122°F122 °F and 210°F210 °F only.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.07 on Flow Properties.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2010July 1, 2016. Published November 2010July 2016. Originally approved in 1963, replacing former D446 and D666. Last previous
ε1ɛ1
edition approved in 20052010 as D2161–05 – 10 . DOI: 10.1520/D2161-10E01.10.1520/D2161-10R16.
2
This practice, together with Practice D2270, replaces Compilation of ASTM Viscosity Tables for Kinematic Viscosity Conversions.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No. ADJD2161. Original adjunct produced in 1998.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 -
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.