ASTM D2162-21
(Practice)Standard Practice for Basic Calibration of Master Viscometers and Viscosity Oil Standards
Standard Practice for Basic Calibration of Master Viscometers and Viscosity Oil Standards
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
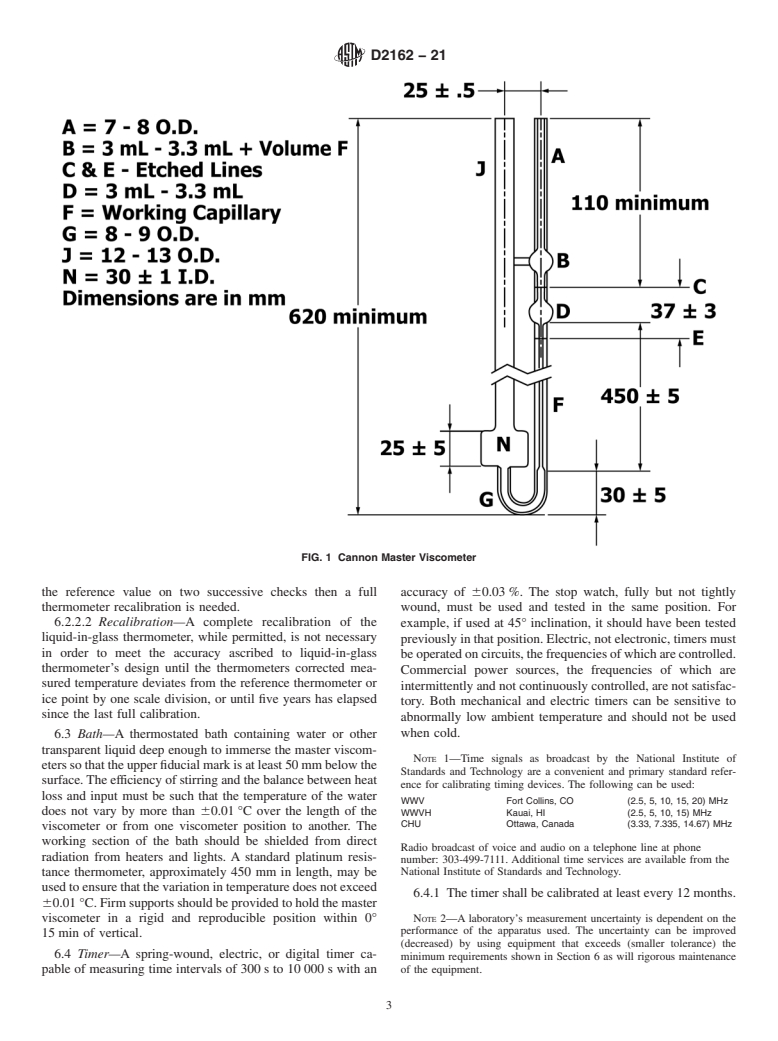
5.1 Because there are surface tension or kinematic viscosity differences, or both, between the primary standard (7.4) and kinematic viscosity standards (7.5), special procedures using master viscometers are required to “step-up” from the kinematic viscosity of the primary standard to the kinematic viscosities of oil standards.
5.2 Using master viscometers calibrated according to this practice, an operator can calibrate kinematic viscometers in accordance with Specifications D446.
5.3 Using viscosity oil standards established in this practice, an operator can calibrate kinematic viscometers in accordance with Specifications D446.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the calibration of master viscometers and viscosity oil standards, both of which may be used to calibrate routine viscometers as described in Test Method D445 and Specifications D446 over the temperature range from 15 °C to 100 °C.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.2.1 The SI-based units for calibration constants and kinematic viscosities are mm2/s2 and mm 2/s, respectively.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see Section 7.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D2162 − 21
Standard Practice for
Basic Calibration of Master Viscometers and Viscosity Oil
1
Standards
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2162; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D1250Guide for the Use of the Joint API and ASTM
Adjunct for Temperature and Pressure Volume Correction
1.1 This practice covers the calibration of master viscom-
FactorsforGeneralizedCrudeOils,RefinedProducts,and
eters and viscosity oil standards, both of which may be used to
Lubricating Oils: API MPMS Chapter 11.1
calibrate routine viscometers as described in Test Method
D1480Test Method for Density and Relative Density (Spe-
D445andSpecificationsD446overthetemperaturerangefrom
cific Gravity) of Viscous Materials by Bingham Pycnom-
15°C to 100°C.
eter
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
D1590Test Method for Surface Tension of Water
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
D8278Specification for Digital Contact Thermometers for
standard.
Test Methods Measuring Flow Properties of Fuels and
1.2.1 The SI-based units for calibration constants and kine-
Lubricants
2 2 2
matic viscosities are mm /s and mm /s, respectively.
E1Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
E563Practice for Preparation and Use of an Ice-Point Bath
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the as a Reference Temperature
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
E644Test Methods for Testing Industrial Resistance Ther-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- mometers
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
E1137SpecificationforIndustrialPlatinumResistanceTher-
For specific warning statements, see Section 7. mometers
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
E1750Guide for Use of Water Triple Point Cells
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- E2593Guide for Accuracy Verification of Industrial Plati-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
num Resistance Thermometers
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
E2877Guide for Digital Contact Thermometers
3
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
2.2 ISO Standard:
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ISO 3666Viscosity of Water
2. Referenced Documents
3. Terminology
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1 Definitions:
D445Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
3.1.1 digital contact thermometer (DCT) , n—an electronic
andOpaqueLiquids(andCalculationofDynamicViscos-
device consisting of a digital display and associated tempera-
ity)
ture sensing probe.
D446Specifications and Operating Instructions for Glass
3.1.1.1 Discussion—This device consists of a temperature
Capillary Kinematic Viscometers
sensor connected to a measuring instrument; this instrument
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
measures the temperature-dependent quantity of the sensor,
computes the temperature from the measured quantity, and
provides a digital output. This digital output goes to a digital
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum
displayand/orrecordingdevicethatmaybeinternalorexternal
Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
to the device.
mittee D02.07 on Flow Properties.
Current edition approved April 1, 2021. Published April 2021. Originally
3.1.1.2 Discussion—The devices are often referred to as a
approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D2162–17. DOI:
“digitalthermometers,”howeverthetermincludesdevicesthat
10.1520/D2162-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2162 − 21
sense temperature by means other than being in physical 5.2 Using master viscometers calibrated according to this
contact with the media
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2162 − 17 D2162 − 21
Standard Practice for
Basic Calibration of Master Viscometers and Viscosity Oil
1
Standards
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2162; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
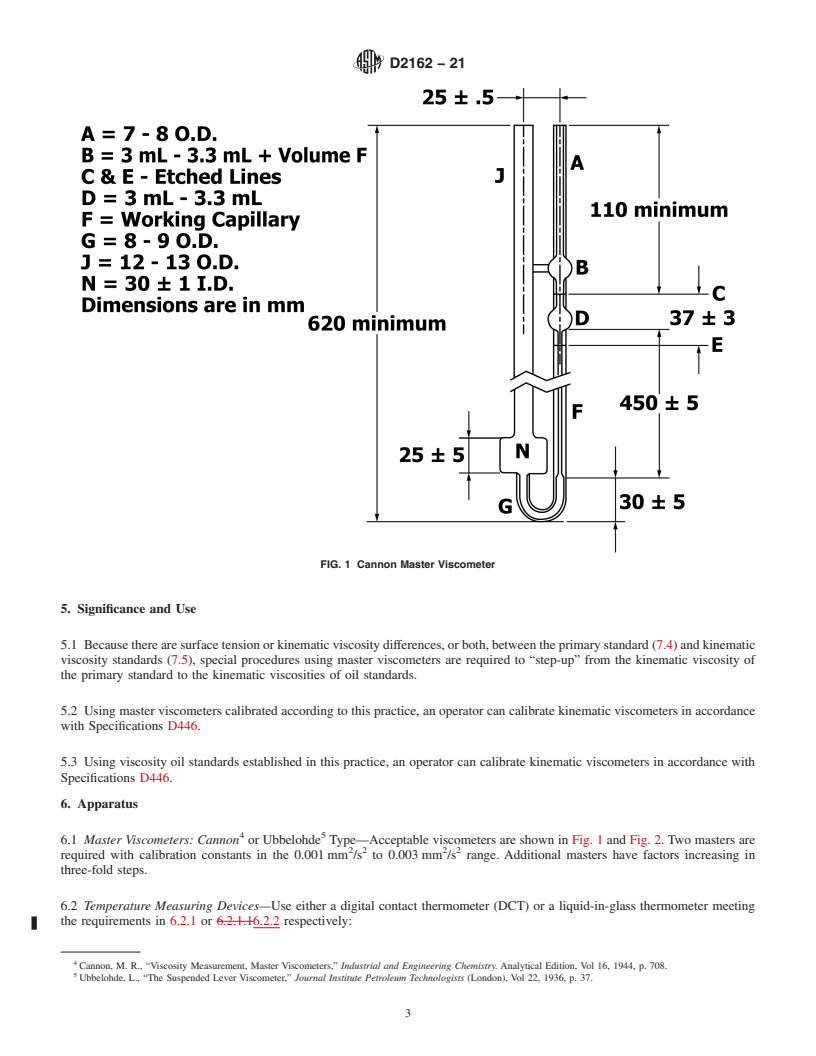
1.1 This practice covers the calibration of master viscometers and viscosity oil standards, both of which may be used to calibrate
routine viscometers as described in Test Method D445 and Specifications D446 over the temperature range from 15 °C to 100 °C.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
2 2 2
1.2.1 The SI-based units for calibration constants and kinematic viscosities are mm /s and mm /s, respectively.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see Section 7.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity)
D446 Specifications and Operating Instructions for Glass Capillary Kinematic Viscometers
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D1250 Guide for the Use of the Joint API and ASTM Adjunct for Temperature and Pressure Volume Correction Factors for
Generalized Crude Oils, Refined Products, and Lubricating Oils: API MPMS Chapter 11.1
D1480 Test Method for Density and Relative Density (Specific Gravity) of Viscous Materials by Bingham Pycnometer
D1590 Test Method for Surface Tension of Water
D8278 Specification for Digital Contact Thermometers for Test Methods Measuring Flow Properties of Fuels and Lubricants
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E563 Practice for Preparation and Use of an Ice-Point Bath as a Reference Temperature
E644 Test Methods for Testing Industrial Resistance Thermometers
E1137 Specification for Industrial Platinum Resistance Thermometers
E1750 Guide for Use of Water Triple Point Cells
E2593 Guide for Accuracy Verification of Industrial Platinum Resistance Thermometers
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.07 on Flow Properties.
Current edition approved May 1, 2017April 1, 2021. Published May 2017April 2021. Originally approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 20142017 as
D2162 – 14.D2162 – 17. DOI: 10.1520/D2162-17.10.1520/D2162-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2162 − 21
E2877 Guide for Digital Contact Thermometers
3
2.2 ISO Standard:
ISO 3666 Viscosity of Water
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 digital contact thermometer (DCT) , n—an electronic device consisting of a digital display and associated temperature
sensing probe.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
This device consists of a temperature sensor connected to a measuring instrument; this instrument measures the temperature-
dependent quantity of the sensor, computes the temperature from the measured quantity, and provides a digital output. This digital
output goes to a digital display and/or recording device that may be internal or external to the device. These devices are sometimes
referred to as “digital thermometers.”
3.1.1.2 Discussion—
The devices are often referred to as a “digital thermometers,” ho
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.