ASTM D4364-13
(Practice)Standard Practice for Performing Outdoor Accelerated Weathering Tests of Plastics Using Concentrated Sunlight
Standard Practice for Performing Outdoor Accelerated Weathering Tests of Plastics Using Concentrated Sunlight
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
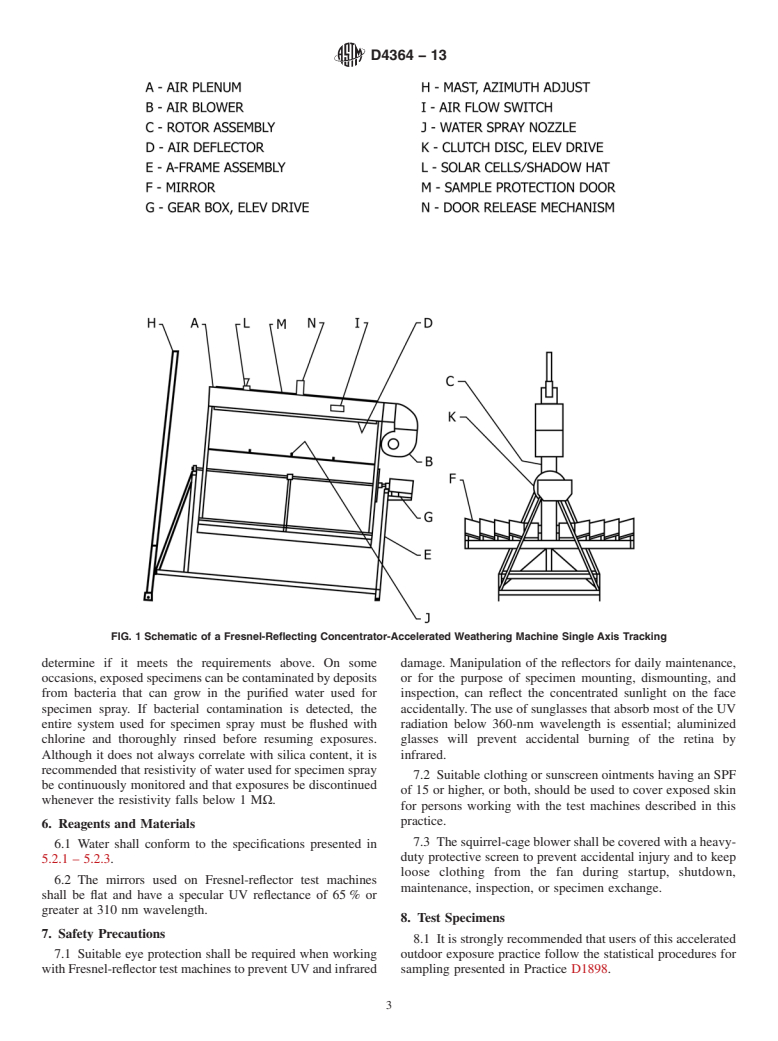
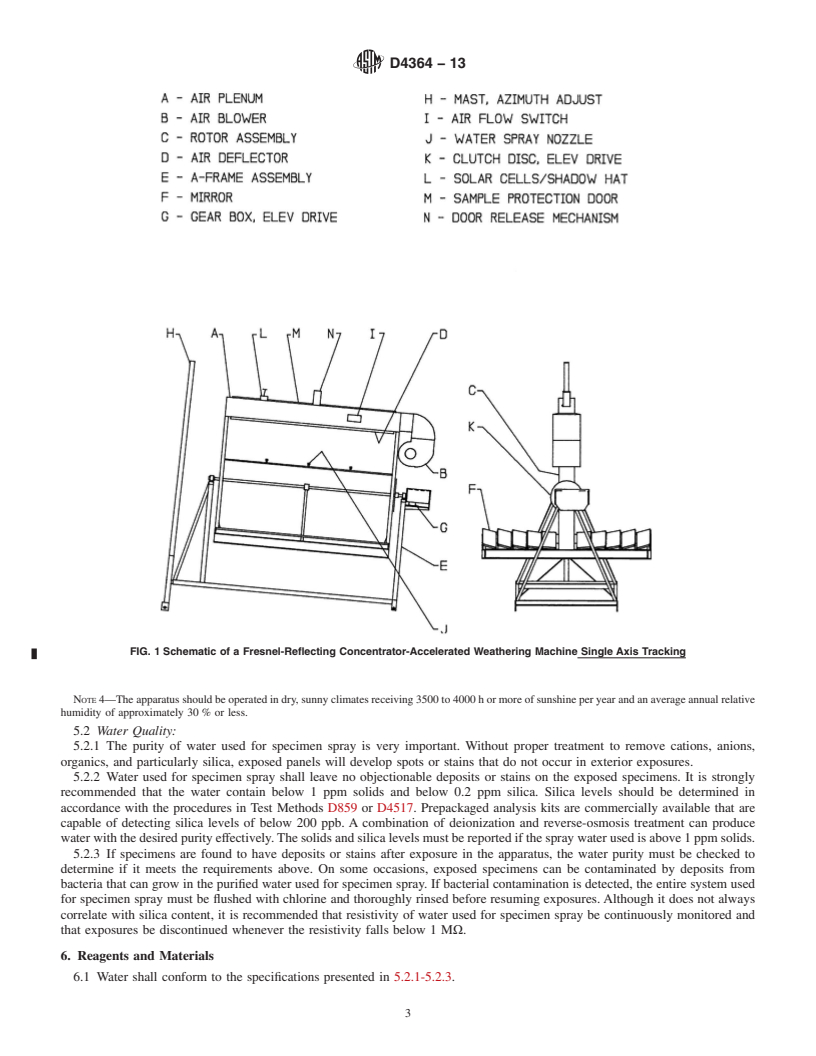
4.1 This practice involves the concentration of sunlight by a system of plane mirrors, arranged to simulate a parabolic trough focused on an air-cooled target board on which the test specimens are mounted. Exposure cycles with and without water spray that are commonly used for this method are described in Table 1. Other exposure cycles not listed in Table 1 can be used, upon consensual agreement between interested parties.
4.1.1 Accelerated outdoor exposure tests performed using this practice in an absence of a programmed moisture cycle are intended to simulate conventional exposure testing on racks facing the equator in desert and arid regions.
4.1.2 Accelerated outdoor exposure tests performed using this practice with a programmed moisture cycle shall possess the feature of spraying high purity water on the specimens in a regular, periodic fashion that is intended to simulate the results of conventional exposure testing on fixed racks facing the equator in subtropical, semi-humid, and temperate regions. Water-spray cycles that are recommended by this practice are given in Table 1.
4.2 The effectiveness of the Fresnel-reflector accelerated outdoor weathering test machines depends primarily on the amount and character of the UV in the direct-beam component of sunlight.Note 2—Use of the apparatus in regions of moderate- to high-diffuse irradiance will reduce the test machine's effectiveness substantially for providing concentrated UV in the target (specimen) area.
4.3 Testing to specific levels (quantities) of solar ultraviolet radiant exposure is recommended. Elapsed time exposure-level determinations shall not be used for testing with this practice. Testing to specific levels of UV irradiation, whether to total UV or within selected wavebands, is an effective method for improving agreement between wintertime and summertime testing on the Fresnel-reflector weathering-test machines. Other seasonal factors such as temperature and time of wetness can affect ...
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the use of Fresnel-reflecting concentrators that use the sun as a source of ultraviolet (UV) and longer wavelength radiation. Such devices are used in the outdoor accelerated exposure testing of plastics.
1.2 This practice provides a procedure for performing outdoor accelerated exposure testing of plastics using a Fresnel-reflector outdoor accelerated weathering test machine. The apparatus is described herein and in Practice G90 more completely.
1.3 This practice is applicable to a range of plastic materials including, but not limited to, plastic films, sheets, laminates, and extruded and molded products in a variety of shapes and sizes, as specified in 8.2 and 8.3.
1.4 This practice describes test conditions that attempt to simulate plastics exposures in desert and subtropical climates. Specimen preparation, property testing procedures, and the evaluation of results are covered in existing test methods or specifications for specific materials.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 7. Note 1—This standard is equivalent to ISO 877-3: 2009.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D4364 −13
Standard Practice for
Performing Outdoor Accelerated Weathering Tests of
1
Plastics Using Concentrated Sunlight
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4364; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This practice covers the use of Fresnel-reflecting con-
D859 Test Method for Silica in Water
centrators that use the sun as a source of ultraviolet (UV) and
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
longer wavelength radiation. Such devices are used in the
D1435 Practice for Outdoor Weathering of Plastics
outdoor accelerated exposure testing of plastics.
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
1.2 This practice provides a procedure for performing out-
tics
3
door accelerated exposure testing of plastics using a Fresnel-
D1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics (Withdrawn 1998)
reflector outdoor accelerated weathering test machine. The
D4141 Practice for Conducting Black Box and Solar Con-
apparatus is described herein and in Practice G90 more centrating Exposures of Coatings
completely. D4517 Test Method for Low-Level Total Silica in High-
Purity Water by Flameless Atomic Absorption Spectros-
1.3 This practice is applicable to a range of plastic materials
copy
including, but not limited to, plastic films, sheets, laminates,
E772 Terminology of Solar Energy Conversion
and extruded and molded products in a variety of shapes and
E824 Test Method for Transfer of Calibration From Refer-
sizes, as specified in 8.2 and 8.3.
ence to Field Radiometers
G7 Practice for Atmospheric Environmental Exposure Test-
1.4 This practice describes test conditions that attempt to
ing of Nonmetallic Materials
simulate plastics exposures in desert and subtropical climates.
G24 Practice for Conducting Exposures to Daylight Filtered
Specimen preparation, property testing procedures, and the
Through Glass
evaluation of results are covered in existing test methods or
G90 Practice for Performing Accelerated Outdoor Weather-
specifications for specific materials.
ing of Nonmetallic Materials Using Concentrated Natural
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Sunlight
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
G113 Terminology Relating to Natural andArtificial Weath-
standard.
ering Tests of Nonmetallic Materials
4
2.2 ISO Standard:
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
ISO 877-3: 2009 Plastics—Methods of exposure to solar
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
radiation—Part 3: Intensified weathering using concen-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
trated solar radiation
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
3. Terminology
tionary statements are given in Section 7.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of technical terms pertain-
NOTE 1—This standard is equivalent to ISO 877-3: 2009.
ing to plastics used in this practice, see Terminologies D883,
D1600, E772, and G113 (for weathering terminology).
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
1
ThispracticeisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD20onPlasticsand the ASTM website.
3
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.50 on Durability of Plastics. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
Current edition approved July 15, 2013. Published August 2013. Originally www.astm.org.
4
approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D4364 – 05. DOI: Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
10.1520/D4364-13. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4364−13
photodegradable plastics are not recommended for testing with this
4. Significance and Use
practice for this reason.
4.1 This practice involves the concentration of sunlight by a
4.5 Since the natural environment varies with respect to
system of plane mirrors, arranged to simulate a parabolic
time, geography, and topography, it can be expected that the
trough focused on an air-cooled target board on which the test
effects of natural exposure will vary
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4364 − 05 D4364 − 13
Standard Practice for
Performing Outdoor Accelerated Weathering Tests of
1
Plastics Using Concentrated Sunlight
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4364; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This practice covers the use of Fresnel-reflecting concentrators that use the sun as a source of ultraviolet (UV) and longer
wavelength radiation. Such devices are used in the outdoor accelerated exposure testing of plastics.
1.2 This practice provides a procedure for performing outdoor accelerated exposure testing of plastics using a Fresnel-reflector
outdoor accelerated weathering test machine. The apparatus is described herein and in Practice G90 more completely.
1.3 This practice is applicable to a range of plastic materials including, but not limited to, plastic films, sheets, laminates, and
extruded and molded products in a variety of shapes and sizes, as specified in 8.2 and 8.3.
1.4 This practice describes test conditions that attempt to simulate plastics exposures in desert and subtropical climates.
Specimen preparation, property testing procedures, and the evaluation of results are covered in existing test methods or
specifications for specific materials.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 7.
NOTE 1—This standard and ISO 877.2-1991, Method C, are technically equivalent.is equivalent to ISO 877-3: 2009.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D859 Test Method for Silica in Water
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1435 Practice for Outdoor Weathering of Plastics
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
3
D1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics (Withdrawn 1998)
D4141 Practice for Conducting Black Box and Solar Concentrating Exposures of Coatings
D4517 Test Method for Low-Level Total Silica in High-Purity Water by Flameless Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
E772 Terminology of Solar Energy Conversion
E824 Test Method for Transfer of Calibration From Reference to Field Radiometers
G7 Practice for Atmospheric Environmental Exposure Testing of Nonmetallic Materials
G24 Practice for Conducting Exposures to Daylight Filtered Through Glass
G90 Practice for Performing Accelerated Outdoor Weathering of Nonmetallic Materials Using Concentrated Natural Sunlight
G113 Terminology Relating to Natural and Artificial Weathering Tests of Nonmetallic Materials
4
2.2 ISO Standard:
ISO 877.2-1991,877-3: 2009 Method C, Methods of Exposure to Direct Weathering, to Weathering Using Glass-Filtered
Daylight, and to Intensified Weathering Using Fresnel MirrorsPlastics—Methods of exposure to solar radiation—Part 3:
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.50 on Durability of Plastics.
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 2005July 15, 2013. Published October 2005August 2013. Originally approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 20022005
as D4364 – 02.D4364 – 05. DOI: 10.1520/D4364-05.10.1520/D4364-13.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4364 − 13
Intensified weathering using concentrated solar radiation
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of technical terms pertaining to plas
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.