ASTM C1289-01
(Specification)Standard Specification for Faced Rigid Cellular Polyisocyanurate Thermal Insulation Board
Standard Specification for Faced Rigid Cellular Polyisocyanurate Thermal Insulation Board
SCOPE
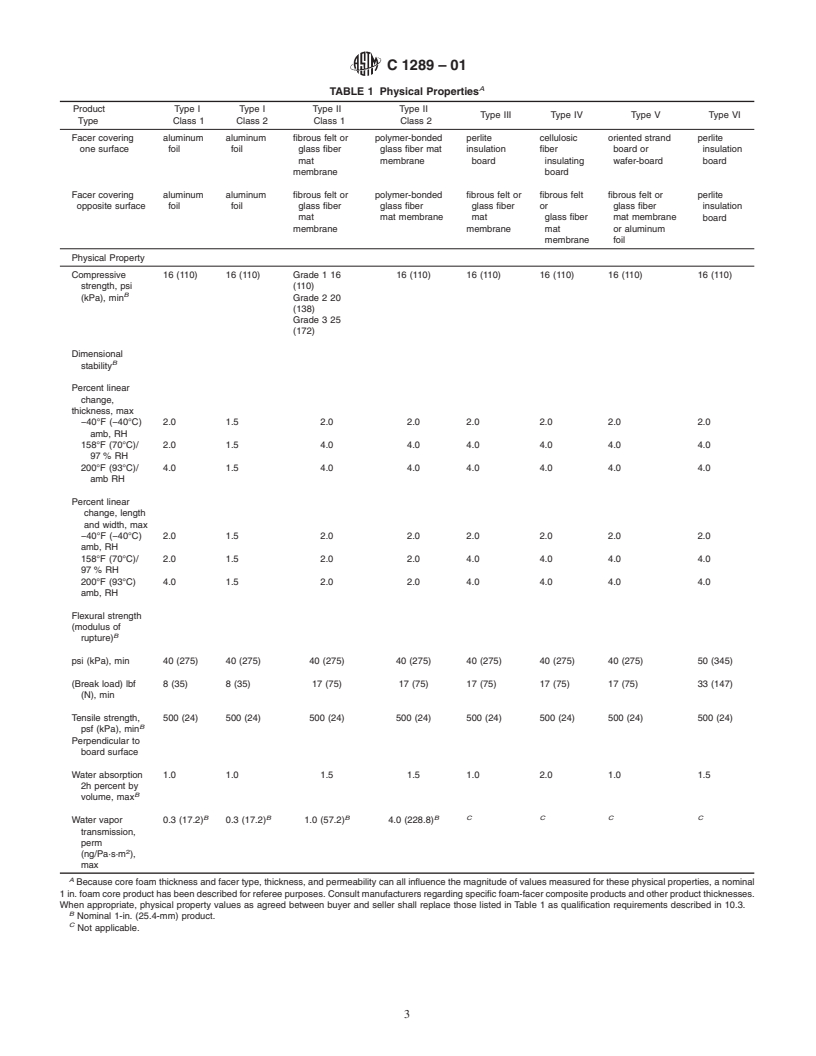
1.1 This specification covers the general requirements for faced thermal insulation boards composed of rigid cellular polyisocyanurate surfaced with other materials. The insulation boards are intended for use at temperatures between -40 and 200oF (40 and 93oC). This specification does not cover cryogenic applications. Consult the manufacturer for specific recommendations and properties in cryogenic conditions. For specific applications, the actual temperature limits shall be agreed upon by the manufacturer and the purchaser.
1.2 This standard is intended to apply to rigid cellular polyurethane-modified polyisocyanurate thermal insulation board products that are commercially acceptable as non-structural panels useful in building construction. The term polyisocyanurate encompasses the term polyurethane. For engineering and design purposes, users should follow specific product information provided by board manufacturers regarding physical properties, system design considerations and installation recommendations.
1.3 The use of thermal insulation materials covered by this specification may be regulated by building codes, or other agencies that address fire performance, or both. The fire performance of the material should be addressed through standard fire test methods established by the appropriate governing documents.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only and may be approximate. For conversion to metric units other than those contained in this standard, refer to IEEE/ASTM SI 10.
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods, Section 11, in this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: C 1289 – 01
Standard Specification for
Faced Rigid Cellular Polyisocyanurate Thermal Insulation
1
Board
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1289; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
1.1 This specification covers the general requirements for
to use.
faced thermal insulation boards composed of rigid cellular
polyisocyanurate surfaced with other materials. The insulation
2. Referenced Documents
boards are intended for use at temperatures between−40 and
2.1 The following documents, of the issue in effect on the
200°F (−40 and 93°C). This specification does not cover
date of material purchase, form a part of this specification to
cryogenic applications. Consult the manufacturer for specific
the extent specified herein:
recommendations and properties in cryogenic conditions. For
2.2 ASTM Standards:
specific applications, the actual temperature limits shall be
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulating Materi-
agreed upon by the manufacturer and the purchaser.
2
als
1.2 This standard is intended to apply to rigid cellular
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measure-
polyurethane-modified polyisocyanurate thermal insulation
ments and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of
board products that are commercially acceptable as non-
2
the Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
structural panels useful in building construction. The term
C203 Test Methods for Breaking Load and Flexural Prop-
polyisocyanurate encompasses the term polyurethane. For
2
erties of Block Type Thermal Insulation
engineering and design purposes, users should follow specific
2
C208 Specification for Cellulosic Fiber Insulating Board
product information provided by board manufacturers regard-
2
C209 Test Methods for Cellulosic Fiber Insulating Board
ing physical properties, system design considerations and
C303 Test Method for Density of Preformed Block-Type
installation recommendations.
2
Thermal Insulation
1.3 The use of thermal insulation materials covered by this
C390 Criteria for Sampling and Acceptance of Preformed
specification may be regulated by building codes, or other
2
Thermal Insulation Lots
agencies that address fire performance, or both. The fire
C518 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measure-
performance of the material should be addressed through
ments and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of
standard fire test methods established by the appropriate
2
the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
governing documents.
C550 Test Method for MeasuringTrueness and Squareness
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
2
of Rigid Block Thermal Insulation
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
2
C728 Specification for Perlite Thermal Insulation Board
information only and may be approximate. For conversion to
C 1045 Practice for Calculating Thermal Transmission
metricunitsotherthanthosecontainedinthisstandard,referto
2
Properties from Steady-State Heat Flux Measurements
IEEE/ASTM SI 10.
C1058 Practice for Selecting Temperatures for Evaluating
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
2
and Reporting Thermal Properties of Thermal Insulation
test methods, Section 11, in this specification. This standard
C1114 TestMethodforSteady-StateThermalTransmission
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
2
Properties by Means of the Thin-Heater Apparatus
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
C1303 Test Method for Estimating the Long-Term Change
in the Thermal Resistance of Unfaced Rigid Closed Cell
Plastic Foams by Slicing and Scaling Under Controlled
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on
2
Laboratory Conditions
Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.22 on
Organic and Nonhomogeneous Inorganic Thermal Insulations.
Current edition approved April 10, 2001. Published June 2001. Originally
2
published as C1289–95. Last previous edition C1289–98. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.06.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1289–01
C1363 Test Method for Thermal Performance of Building inorganic/asphalt-saturated/polymer-bonded/fibrous felt or
2
Assemblies by Means of a Hot Box Apparatus uncoated/asphalt-coated/polymer-bonded/glassfibermatmem-
D226 Specification for Asphalt-Saturated Organic Felt brane facer on the other major surface of the core foam.
3
Used in Roofing and Waterproofing 4.1.5 Type V—Faced with oriented strand board or wafer-
D1621
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.