ASTM D3170/D3170M-14
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Chipping Resistance of Coatings
Standard Test Method for Chipping Resistance of Coatings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Owners consider chipping of coatings, particularly on the leading faces and edges of automobile surfaces, unacceptable. In formulating a coating or coating system to meet service requirements, the resistance to chipping damage by flying objects such as gravel is one of the properties of importance since it can vary considerably as other properties are adjusted. Since resistance to chipping decreases at lower temperatures partly as the result of decreased flexibility, the test may be more directly related to service conditions by performing it at a low temperature. This test method is designed to produce a controlled amount of impact by the media on the coated panel in order to enhance reproducibility.
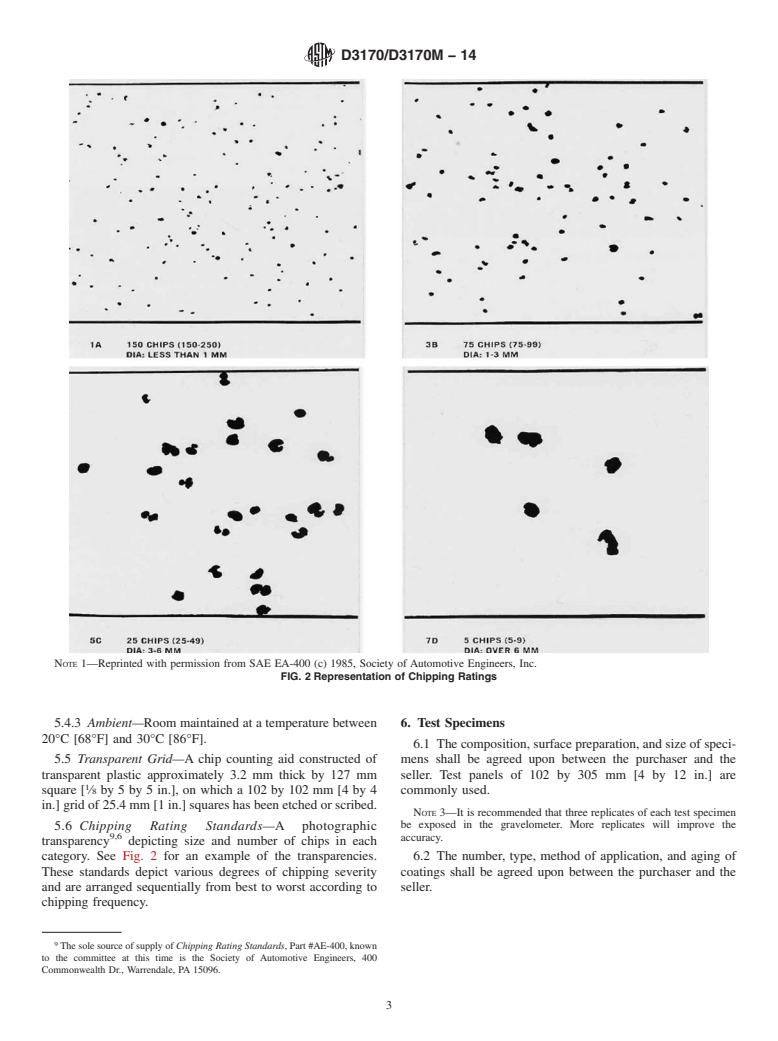
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resistance of coatings to chipping damage by stones or other flying objects.
Note 1: This test method is similar to SAE J-400.
1.2 All dimensions are nominal unless otherwise specified.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3170/D3170M − 14
Standard Test Method for
1
Chipping Resistance of Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3170/D3170M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope D1186 Test Methods for Nondestructive Measurement of
Dry Film Thickness of Nonmagnetic Coatings Applied to
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resis-
3
a Ferrous Base (Withdrawn 2006)
tance of coatings to chipping damage by stones or other flying
D1400 TestMethodforNondestructiveMeasurementofDry
objects.
Film Thickness of Nonconductive Coatings Applied to a
3
NOTE 1—This test method is similar to SAE J-400.
Nonferrous Metal Base (Withdrawn 2006)
1.2 All dimensions are nominal unless otherwise specified. D1733 Method for Preparation of Aluminum Alloy Panels
for Testing Paint, Varnish, Lacquer, and Related Products
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
3
(Withdrawn 1979)
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
D2201 Practice for Preparation of Zinc-Coated and Zinc-
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
Alloy-Coated Steel Panels for Testing Paint and Related
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
Coating Products
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
2.2 Other Documents:
with the standard.
4
Test for Chip Resistance of Surface Coatings (J-400)
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1 Standardized road gravel is projected by means of a
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
controlled air blast at the coated specimens. All testing is
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
conducted under controlled temperature conditions, generally
either at ambient (room) temperature or at -29 6 3°C [-20 6
2. Referenced Documents
5°F]. After the gravel impact, tape is applied to remove any
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
loose coating chips and the degree of chipping is determined.
D609 Practice for Preparation of Cold-Rolled Steel Panels
for Testing Paint, Varnish, Conversion Coatings, and
4. Significance and Use
Related Coating Products
4.1 Owners consider chipping of coatings, particularly on
D823 Practices for Producing Films of Uniform Thickness
the leading faces and edges of automobile surfaces, unaccept-
of Paint, Varnish, and Related Products on Test Panels
able.Informulatingacoatingorcoatingsystemtomeetservice
D1005 Test Method for Measurement of Dry-Film Thick-
requirements, the resistance to chipping damage by flying
ness of Organic Coatings Using Micrometers
objects such as gravel is one of the properties of importance
since it can vary considerably as other properties are adjusted.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
Since resistance to chipping decreases at lower temperatures
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
partly as the result of decreased flexibility, the test may be
Subcommittee D01.55 on Factory Applied Coatings on Preformed Products.
more directly related to service conditions by performing it at
Current edition approved June 15, 2014. Published July 2014. Originally
approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D3170 – 12. DOI:
10.1520/D3170_D3170M-14.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.astm.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth
the ASTM website. Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3170/D3170M − 14
FIG. 1 Gravel Projecting Machine
Different specifications may be necessary for other media types.
a low temperature. This test method is designed to produce a
7,6
controlled amount of impact by the media on the coated panel
5.2 Gravel—Water-eroded alluvial road gravel passing
in order to enhance reproducibility. 5
through a 16-mm [ ⁄8-in.] space screen but retained on a
3
9.5-mm [ ⁄8-in.] space screen. Note t
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D3170 − 12 D3170/D3170M − 14
Standard Test Method for
1
Chipping Resistance of Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3170;D3170/D3170M; the number immediately following the designation indicates
the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resistance of coatings to chipping damage by stones or other flying objects.
NOTE 1—This test method is similar to SAE J-400.
1.2 All dimensions are nominal unless otherwise specified.
1.3 The values stated in metric units either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as the standard. The
English units given in parentheses are for information only. All dimensions are nominal unless otherwise specified.values stated
in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values
from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D609 Practice for Preparation of Cold-Rolled Steel Panels for Testing Paint, Varnish, Conversion Coatings, and Related Coating
Products
D823 Practices for Producing Films of Uniform Thickness of Paint, Varnish, and Related Products on Test Panels
D1005 Test Method for Measurement of Dry-Film Thickness of Organic Coatings Using Micrometers
D1186 Test Methods for Nondestructive Measurement of Dry Film Thickness of Nonmagnetic Coatings Applied to a Ferrous
3
Base (Withdrawn 2006)
D1400 Test Method for Nondestructive Measurement of Dry Film Thickness of Nonconductive Coatings Applied to a
3
Nonferrous Metal Base (Withdrawn 2006)
D1733 Method for Preparation of Aluminum Alloy Panels for Testing Paint, Varnish, Lacquer, and Related Products (Withdrawn
3
1979)
D2201 Practice for Preparation of Zinc-Coated and Zinc-Alloy-Coated Steel Panels for Testing Paint and Related Coating
Products
2.2 Other Documents:
4
Test for Chip Resistance of Surface Coatings (J-400)
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 Standardized road gravel is projected by means of a controlled air blast at the coated specimens. All testing is conducted
under controlled temperature conditions, generally either at ambient (room) temperature or at -29 6 3°C (-20[-20 6 5°F).5°F].
After the gravel impact, tape is applied to remove any loose coating chips and the degree of chipping is determined.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.55 on Factory Applied Coatings on Preformed Products.
Current edition approved July 15, 2012June 15, 2014. Published October 2012July 2014. Originally approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 20072012 as
D3170 – 03 (2007). 12. DOI: 10.1520/D3170-12.10.1520/D3170_D3170M-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3170/D3170M − 14
FIG. 1 Gravel Projecting Machine
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Owners consider chipping of coatings, particularly on the leading faces and edges of automobile surfaces, unacceptable. In
formulating a coating or coating system to meet service requirements, the resistance to chipping damage by flying objects such
as gravel is one of the properties of importance since it can vary considerably as other properties are adjusted. Since resistance
to chipping decreases at lower temperatures partl
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.