ASTM E2342-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Durability Testing of Duct Sealants
Standard Test Method for Durability Testing of Duct Sealants
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Residential duct systems are often field designed and assembled. There are many joints, often of dissimilar materials that require both mechanical connection and air sealing. Without this sealing, duct systems would be extremely leaky and hence inefficient. While some duct sealants are rated on their properties at the time of manufacture or during storage, none of these ratings adequately addresses the in-service lifetime. This test method has been developed to address this durability issue.
This standard applies to products which list duct sealing as one of their uses. This includes duct tape (cloth, metal foil or plastic backed), mastics and sprayed/aerosol sealants. It does not apply to caulks or plaster patches that are not intended to be permanent duct sealing methods.
The standard duct leak site is a collar to plenum connection for round duct that is 10 to 20 cm (4 to 8 in.) in diameter. This perpendicular connection was chosen because almost all residential duct systems have this type of connection and in field observations of duct systems, it is often this type of connection that has sealant failure.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes an accelerated aging test for evaluating the durability of duct sealants by exposure to temperatures and static pressures characteristic of residential duct systems.
1.2 This test method is intended to produce a relative measure of the durability of duct sealants. This standard does not measure durability under specific conditions of weather and building operation that might be experienced by an individual building and duct system. Instead it evaluates the sealant method under fixed conditions that do not include the manifold effects of installation practice.
1.3 This test method only addresses sealants not mechanical strength of the connections.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements see Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:E2342–03
Standard Test Method for
Durability Testing of Duct Sealants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2342; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Duct leakage has been identified as a major source of energy loss in residential buildings. Most duct
leakageoccursattheconnectionstoregisters,plenumsorbranchesintheductsystem.Ateachofthese
connections a method of sealing the duct system is required. Typical sealing methods include tapes or
mastics applied around the joints in the system. Field examinations of duct systems have typically
shown that these seals tend to fail over extended periods of time.
The proposed method evaluates the durability of duct sealants by blowing heated air into test
sections, combined with a pressure difference between the test sections and their surroundings. The
temperatures and pressures were chosen to expose the test sections to typical conditions that are found
in residential duct systems. The duct leakage site geometry represents a leakage site commonly found
in duct systems. The test sections are constructed from standard duct fittings.
1. Scope E632 Practice for Developing Accelerated Tests to Aid
Prediction of the Service Life of Building Components and
1.1 This test method describes an accelerated aging test for
Materials
evaluating the durability of duct sealants by exposure to
temperatures and static pressures characteristic of residential
3. Terminology
duct systems.
3.1 Practice E632 defines much of the terminology used in
1.2 This test method is intended to produce a relative
this standard.
measure of the durability of duct sealants. This standard does
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
notmeasuredurabilityunderspecificconditionsofweatherand
3.2.1 air-leakage rate—the volume of air movement per
building operation that might be experienced by an individual
unit time across the duct wall.
building and duct system. Instead it evaluates the sealant
3.2.2 duct sealant—a method and/or material for sealing
method under fixed conditions that do not include the manifold
leaks in forced air thermal distribution duct systems.
effects of installation practice.
1.3 This test method only addresses sealants not mechanical
4. Summary of Test Method
strength of the connections.
4.1 To evaluate sealant durability this test method uses a
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
standardized joint configuration with controlled temperature
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
and pressure differences. These temperatures and pressures are
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
chosen to represent conditions found in residential duct sys-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
tems. The test apparatus applies temperature and pressure
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
conditions, and measures how well the sealant performs over
7.
statements see Section
time.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Significance and Use
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1 Residential duct systems are often field designed and
assembled. There are many joints, often of dissimilar materials
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
that require both mechanical connection and air sealing.
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.41
Without this sealing, duct systems would be extremely leaky
on Air Leakage and Ventilation Performance.
and hence inefficient. While some duct sealants are rated on
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2003. Published February 2004. DOI: 10.1520/
E2342-03. their properties at the time of manufacture or during storage,
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
none of these ratings adequately addresses the in-service
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
lifetime. This test method has been developed to address this
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
durability issue.
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E2342–03
5.2 This standard applies to products which list duct sealing sure difference between the inside and outside of the test
as one of their uses. This includes duct tape (cloth, metal foil section, and a cap to seal the end of the test section. See Fig.
orplasticbacked),masticsandsprayed/aerosolsealants.Itdoes 2. For these test section leakage measurements, the air flow
not apply to caulks or plaster patches that are not intended to measuring device shall have an accuracy of 60.085 m /h (0.05
be permanent duct sealing methods. cfm) or 61 % of the measured flow, whichever is greater.
5.3 The standard duct leak site is a collar to plenum 6.2.2 Durability Test Apparatus—A device for blowing hot
connection for round duct that is 10 to 20 cm (4 to 8 in.) in air through one or more test sections. This device is comprised
diameter. This perpendicular connection was chosen because of the following components.
almost all residential duct systems have this type of connection 6.2.2.1 Air-Moving Equipment—A fan that is capable of
and in field observations of duct systems, it is often this type of moving air through the test sections. The fan must be selected
connection that has sealant failure. to provide the required flow rates and pressure differences. In
addition, the fan must be selected to be capable of operating at
6. Apparatus
the hot conditions existing in the test apparatus.
6.1 The following is a general description of the required 6.2.2.2 Pressure-Measuring Devices—Manometers or pres-
apparatus. Any arrangement of equipment using the same sure indicators to measure pressure difference with an accuracy
principles and capable of performing the test procedure within of 60.2 Pa (0.0008 in. of water) or 61 % of the measured
the allowable tolerances is permitted. pressure, whichever is greater.
6.2 Major Components—There are two major components 6.2.2.3 Temperature-Measuring Devices—Instruments to
required to perform the testing: a test section leakage measure- measure temperature with an accuracy of 61°C (2°F). The test
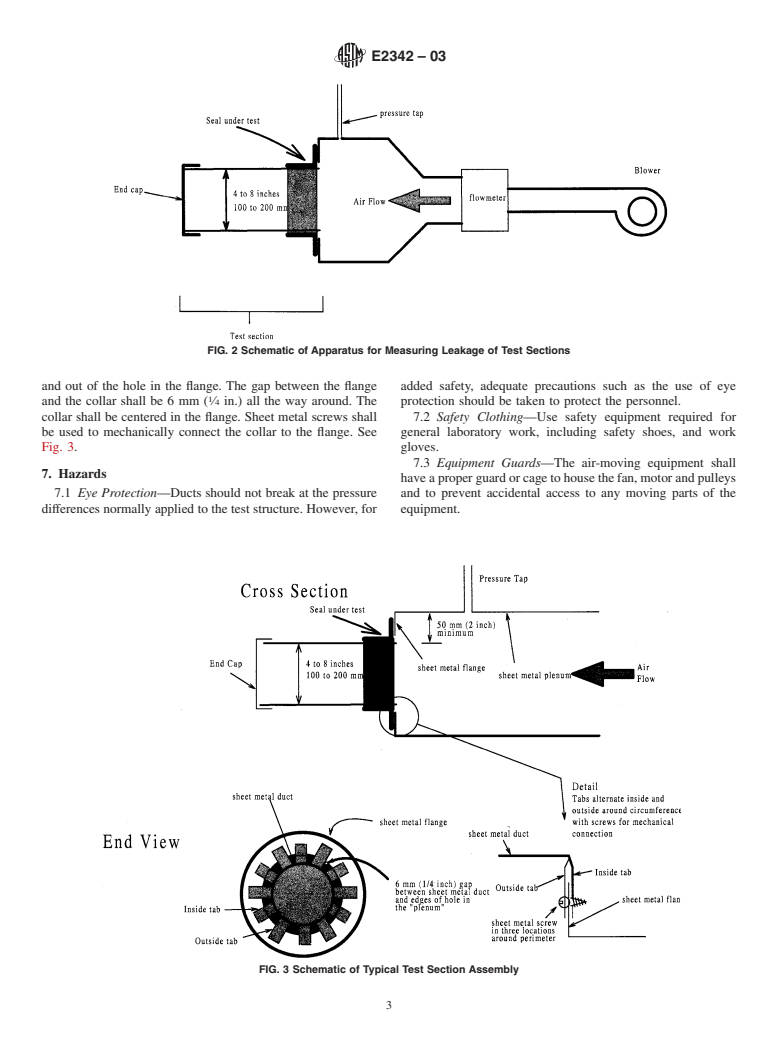
ment device (Fig. 1) and a durability test apparatus (Fig. 2). section surface temperatures shall be measured using surface
6.2.1 Test Section Leakage Measuring Device—A device mounttemperaturesensorswithheattransferpastebetweenthe
for measuring the leakage of individual test sections. This sensor and the test section.
device shall consist of a fan to blow air into the test section, a 6.3 Test Section—Sheet metal duct system components
flowmeasurementdeviceformeasuringtheflowrateinthetest combined to create a plenum to collar connection. The test
section, a pressure measuring device for measuring the pres- section consists of a flange and a collar with fingers to fold in
FIG. 1 Schematic of Durability Apparatus
E2342–03
FIG. 2 Schematic of Apparatus for Measuring Leakage of Test Sections
and out of the hole in the flange. The gap between the flange added safety, adequate precautions such as the use of eye
and the collar shall be 6 mm ( ⁄4 in.) all the way around. The protection should be taken to protect the personnel.
collar shall be centered in the flange. Sheet metal screws shall
7.2 Safety Clothing—Use safety equipment required for
be used to mechanically connect the collar to the flange. See general laboratory work, including safety shoes, and work
Fig. 3.
gloves.
7.3 Equipment Guards—The air-moving equipment shall
7. Hazards
haveaproperguardorcagetohousethefan,motorandpulleys
7.1 Eye Protection—Ducts should not break at the pressure and to prevent accidental access to any moving parts of the
differences normally applied to the test structure. However, for equipment.
FIG. 3 Schematic of Typical Test Section Assembly
E2342–03
7.4 Noise Protection—Make hearing protection available 6 0.08 in. of water), with the air inside the duct at a higher
for personnel who must be close to the noise that may be pressure than outside.
generated by the fan.
8.5.2 The test section surface temperature shall be con-
7.5 Debris and Fumes—Du
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.