ASTM C1890-19
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for K-slump of Freshly Mixed Concrete
Standard Test Method for K-slump of Freshly Mixed Concrete
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method permits a rapid assessment of the consistency of freshly mixed concrete.
5.2 This test method can be used to provide information on the change in consistency with time of a freshly mixed concrete mixture. It is especially valuable for assessing the consistency of flowing or self-consolidating concrete mixtures.
5.3 This test method can be used to assess batch-to-batch variations in consistency of freshly mixed concrete.
5.4 There is no general reliable relationship between the K-slump value and slump measured in accordance with Test Method C143/C143M or slump flow measured in accordance with Test Method C1611/C1611M. However, this test method is useful as a quality control tool. For example, the user can make trial batches in the laboratory and determine the range in K-slump corresponding to an acceptable range in slump or slump flow. That range in K-slump can be used to check the consistency of field batches.
5.5 This test method is not suitable as the basis for acceptance or rejection of concrete.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers determination the K-slump of freshly mixed concrete, both in the laboratory and in the field.
1.2 The values stated SI units are the standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 The text of this standard refers to notes and footnotes that provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure.2)
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C1890 − 19
Standard Test Method for
1
K-slump of Freshly Mixed Concrete
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1890; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope C172/C172MPractice for Sampling Freshly Mixed Con-
crete
1.1 This test method covers determination the K-slump of
C192/C192MPracticeforMakingandCuringConcreteTest
freshly mixed concrete, both in the laboratory and in the field.
Specimens in the Laboratory
1.2 The values stated SI units are the standard. No other
C1611/C1611MTest Method for Slump Flow of Self-
units of measurement are included in this standard.
Consolidating Concrete
1.3 The text of this standard refers to notes and footnotes
3. Terminology
that provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes
(excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered
3.1 Definitions:
as requirements of the standard. 3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
to Terminology C125.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2.1 K-slump, n—the height of the mortar fraction of fresh
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
concrete that penetrates into a specified perforated tube in-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
sertedintoasampleoffreshconcretefor60seconds,expressed
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
as number from 0 to 11.
(Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic
3.2.1.1 Discussion—The K-slump is related to the ability of
and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon
2
the fresh concrete to flow. The greater the value of K-slump,
prolonged exposure. )
the greater the ability of the concrete to flow.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
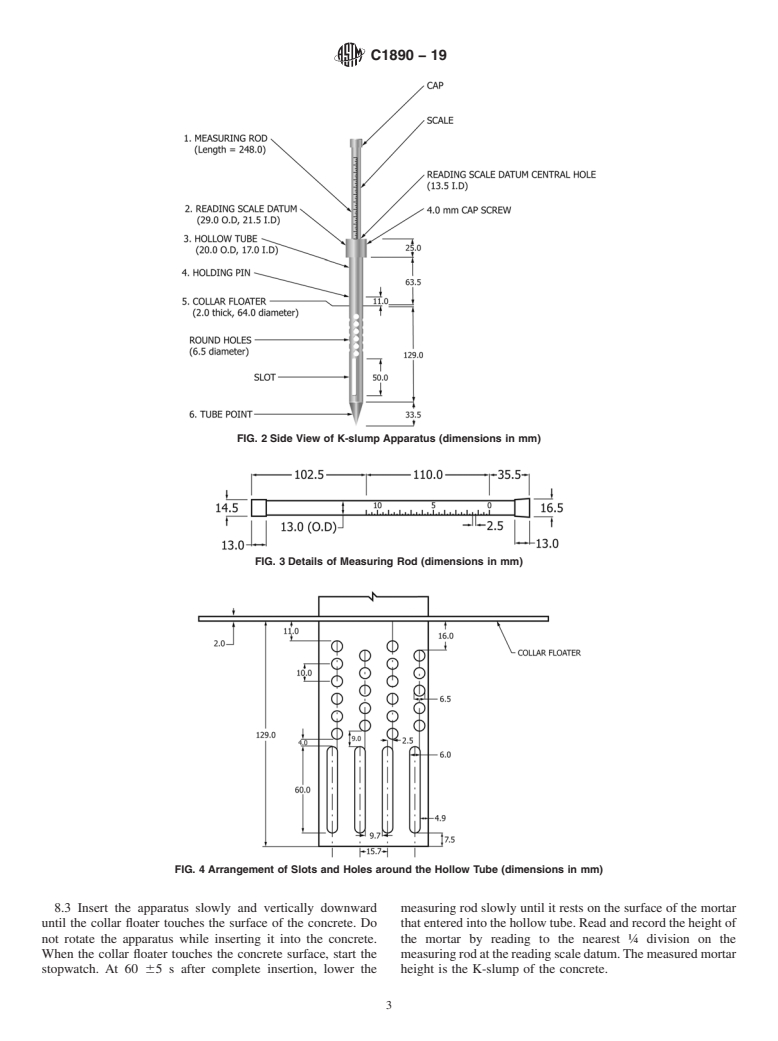
4. Summary of Test Method
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.1 The K-slump apparatus comprises a hollow tube with
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
prescribed perforations and a floating rod with a graduated
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
scale. The tube is inserted into a sample of freshly mixed
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
concrete to a prescribed depth. The mortar fraction of the
2. Referenced Documents concreteisallowedtoflowintotheperforatedtubeforaperiod
3 of60s.Thefloatingrodisthenloweredontothesurfaceofthe
2.1 ASTM Standards:
mortar that has penetrated into the tube. The height of the
C31/C31MPractice for Making and Curing Concrete Test
mortar in the tube is read from the scale marked from 0 to 11
Specimens in the Field
ontheportionofthefloatingrodprotrudingfromthetopofthe
C125Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Ag-
tube.
gregates
C143/C143MTest Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement
5. Significance and Use
Concrete
5.1 This test method permits a rapid assessment of the
consistency of freshly mixed concrete.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on
5.2 This test method can be used to provide information on
Concrete and ConcreteAggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
thechangeinconsistencywithtimeofafreshlymixedconcrete
C09.60 on Testing Fresh Concrete.
mixture. It is especially valuable for assessing the consistency
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2019. Published December 2019. DOI:
10.1520/C1890-19. of flowing or self-consolidating concrete mixtures.
2
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing,
5.3 This test method can be used to assess batch-to-batch
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 04.02.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or variations in consistency of freshly mixed concrete.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.4 There is no general reliable relationship between the
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. K-slump value and slump measured in accordance with Test
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1890 − 19
Method C143/C143M or slump flow measured in accordance 6.1.4 Theholdingpinis4mmindiame
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.