ASTM C756-87(2006)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Cleanability of Surface Finishes
Standard Test Method for Cleanability of Surface Finishes
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method was developed to guide the user in selecting a finish coating or material that is resistant to soiling in a particular application.
The numerical values derived by this test method enables the user to rank finish coatings and materials in regard to soil retention or ease of soil removal.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the numerical evaluation of the ease or difficulty of cleaning soiled surface finishes. This test method is applicable to all surface finishes not affected by water.
1.2 Values given in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. Inch-pound units are provided for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:C756–87 (Reapproved 2006)
Standard Test Method for
1
Cleanability of Surface Finishes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C756; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope reference surface, while indexes less than 1.0 indicate that the
test surface is more easily cleanable than the standard of
1.1 This test method covers the numerical evaluation of the
comparison.
ease or difficulty of cleaning soiled surface finishes. This test
3.2 The soiling agent used consists of polyethylene glycol,
method is applicable to all surface finishes not affected by
a black dye, and a fluorescent tracer, each of which is readily
water.
water soluble.
1.2 Values given in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. Inch-pound units are provided for information only.
4. Significance and Use
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 This test method was developed to guide the user in
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
selecting a finish coating or material that is resistant to soiling
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
in a particular application.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.2 The numerical values derived by this test method
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
enables the user to rank finish coatings and materials in regard
2. Referenced Documents to soil retention or ease of soil removal.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Apparatus
C282 Test Method for Acid Resistance of Porcelain Enam-
5.1 Motor-Driven Lapping Plate, 203-mm (8-in.) diameter,
els(Citric Acid Spot Test)
3
speed 163 r/min.
C614 TestMethodforAlkaliResistanceofPorcelainEnam-
5.2 Automatic Polishing Unit, 11-s cycle, adjustable to
els
4
7
48-mm (1 ⁄8-in.) stroke.
3. Summary of Test Method 5.3 Hypodermic Syringe, glass, 2-mL capacity, without
needle.
3.1 The test method consists of applying an exact amount of
5.4 Repeating Pipet, 0.025 mL (25 µl) capacity.
a fluorescent water-soluble soiling agent to a specimen surface
5.5 Repeating Pipet, 10-mL capacity.
and then cleaning the surface with a reproducible machine-
5.6 Desiccator approximately 254 mm (10 in.) diameter.
wiping technique. The soil remaining on the specimen after
1
5.7 Cleaning Head, brass, 57 mm (2 ⁄4 in.), with worm-
wipingisextractedwithawatersolventandthefluorescenceof
driven hose clamp for attachment of cleaning tissues (Fig. 1).
the solution measured. A standard reference surface is treated
5.8 Soiling Head, brass, 25 mm (1 in.) diameter, with
inasimilarmanner.Thecleanabilityindexofthesurfaceunder
25-mm (1-in.) diameter facing of polytetrafluoroethylene at-
testisexpressedastheratioofthefluorescenceofthesolutions
tached with a water-proof household cement (Fig. 1).
extracted from the test surface and from the standard reference
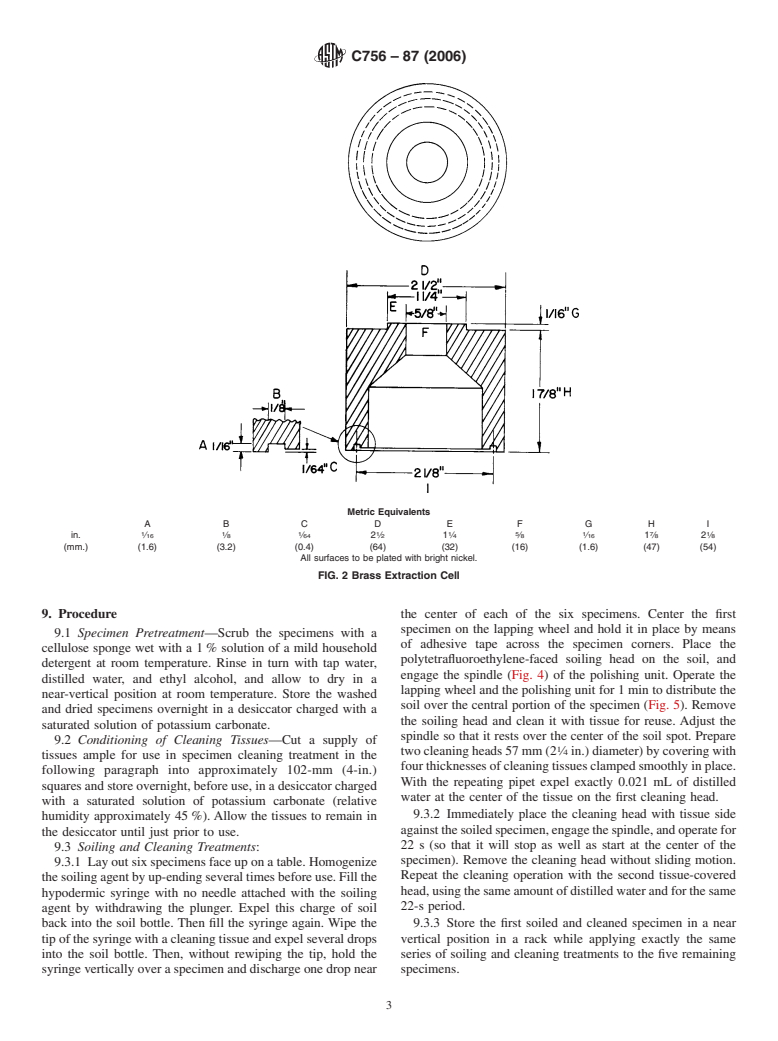
5.9 Extraction Cell, fitted with a fluorosilicone O-ring, size
surface. Cleanability indexes greater than 1.0 indicate that the
5
1 1
3.2 by 57 mm ( ⁄8 by 2 ⁄4 in.) (Fig. 2).
test surface is more difficult to clean than the standard
3
Suitable lapping plates are available from Buehler Ltd., 2120 Greenwood St.,
Evanston, IL60204, Struers, Inc., 20102 Progress Drive, Cleveland, OH, 44136; or
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB08onMetallic other Metallurgical Supply Sources.
4
and Inorganic Coatings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B08.12 on An Olsen “S.M.” Automatic Polisher has been found suitable and is available
Materials for Porcelain Enamel and Ceramic-Metal Systems. under the code name OLPOL from Struers, Inc., 20102 Progress Drive, Cleveland,
Current edition approved April 1, 2006. Published May 2006. Originally OH 44136.
5
approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as C756 – 87 (1999). O-rings must be fluorosilicone polymer; consult Precision Associates, 742 N.
DOI: 10.1520/C0756-87R06. Washington Ave., Minneapolis, MN 55401; Parker Seal Co., 10567 W. Jefferson
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Blvd., Culver City, CA 90230; & B. W. Rogers (Parker Dis.) 1000 Brookpark Rd.,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Cleveland, OH 44109. Also see other sources in Thomas Register under SEALS:
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on “O” RINGS.Asuitable device for clamping the cell to a specimen is shown in Fig.
the ASTM website. 3 and Fig. 5.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.