ASTM D1442-06
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Maturity of Cotton Fibers (Sodium Hydroxide Swelling and Polarized Light Procedures)
Standard Test Method for Maturity of Cotton Fibers (Sodium Hydroxide Swelling and Polarized Light Procedures)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the percentage of mature fibers in a sample of loose, chemically untreated cotton fibers, whether taken before processing or unravelled from a textile product.
1.2 This test method gives two optional procedures for determining maturity, as follows:
1.2.1 Procedure 1Sodium Hydroxide Swelling.
1.2.2 Procedure 2Polarized Light. For other test methods for the determination of maturity of cotton fibers refer to Test Methods D 1464 and D 2480.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measure are included in this standard.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1442–06
Standard Test Method for
Maturity of Cotton Fibers (Sodium Hydroxide Swelling and
1
Polarized Light Procedures)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1442; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
3
1. Scope of Cotton Fibers by the Causticaire Method
D7139 Terminology for Cotton Fibers
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the per-
centage of mature fibers in a sample of loose, chemically
3. Terminology
untreated cotton fibers, whether taken before processing or
3.1 For all terminology relating to D13.11, Cotton Fibers,
unravelled from a textile product.
refer to Terminology D7139.
1.2 This test method gives two optional procedures for
3.1.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard:
determining maturity, as follows:
cotton fiber maturity, immature fibers, in testing with sodium
1.2.1 Procedure 1—Sodium Hydroxide Swelling.
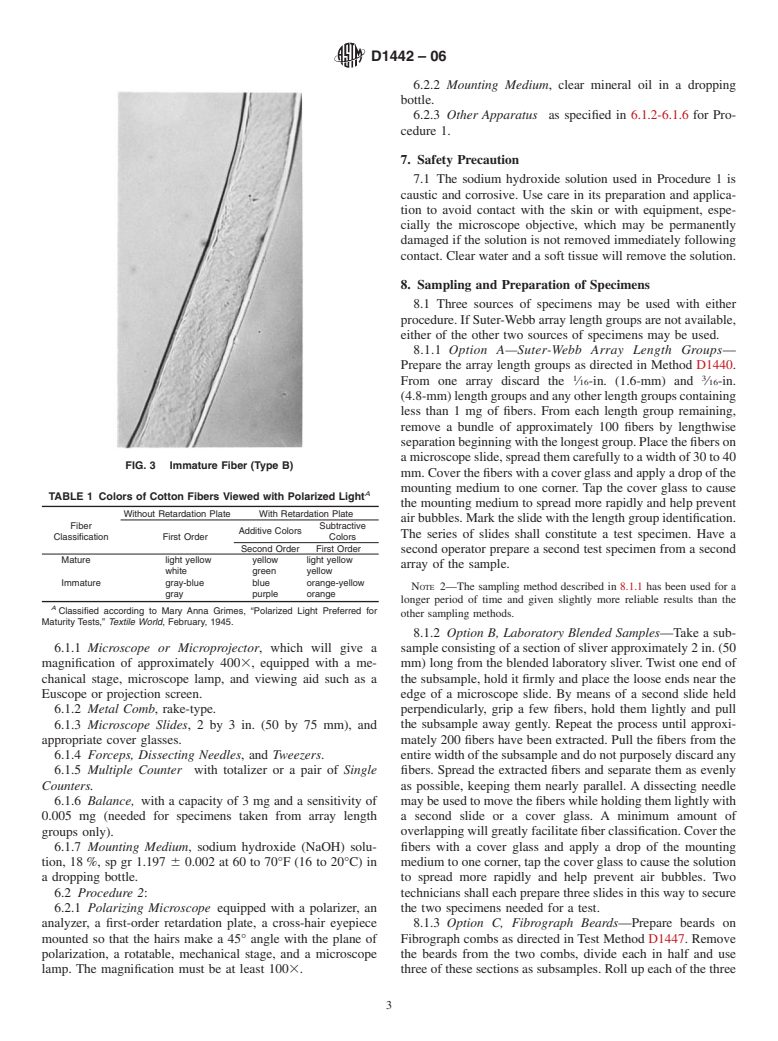
hydroxide solutions (See Fig. 1 and Fig. 2), immature fibers,
1.2.2 Procedure 2—Polarized Light.
observed under polarized light, lumen, mature fibers, in testing
NOTE 1—For other test methods for the determination of maturity of
with sodium hydroxide solutions (see Fig. 3), mature fibers,
cotton fibers refer to Test Methods D1464 and D2480.
observed under polarized light (see Table 1), micronaire
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
reading, test specimen, in cotton maturity test.
standard. No other units of measure are included in this
3.2 For all other terminology related to textiles, refer to
standard.
Terminology D123.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4. Summary of Test Method
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 4.1 Fibers are laid parallel on a microscope slide, covered
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
with a cover glass, treated with a mounting medium, and the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. magnified images are then classified as mature or immature
fibers.
2. Referenced Documents
4.2 The method offers two procedures for classifying the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
fibers as mature or immature:
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
4.2.1 Procedure 1, Sodium Hydroxide Swelling, which uses
D1440 Test Method for Length and Length Distribution of
an 18 % solution of sodium hydroxide as the mounting
Cotton Fibers (Array Method)
medium and a laboratory microscope for viewing the fibers at
D1447 Test Method for Length and Length Uniformity of
a magnification of 4003.
Cotton Fibers by Photoelectric Measurement
4.2.2 Procedure 2, Polarized Light, which uses clear min-
D1464 Test Method for Differential Dyeing Behavior of
eral oil as the mounting medium and requires a polarizing
Cotton
microscope giving a magnification of 1003. Fibers are classi-
D1776 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
fied according to their second-order interference colors, using
D2480 Test Method for Maturity Index and Linear Density
a first-order (or full wave) retardation plate (Table 1).
5. Significance and Use
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 onTextiles
5.1 Information regarding the percentage of immature fibers
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.11 on Cotton Fibers.
is desirable because immature fibers: (1) break easily during
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2006.PublishedJuly2006.Originallyapproved
processing; (2) have a tendency to form neps; (3) have a
in 1952. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D1442 – 00. DOI: 10.1520/
tendency to become entangled around particles of trash and
D1442-06.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
the ASTM website. on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1442–06
FIG. 1 Mature Fiber
FIG. 2 Immature Fiber (Type A)
ide Swelling procedure may be preferred for routine testing of
leaf, thus making cleaning more difficult and increasing the
large numbers of samples. Technicians are more easily trained
amount of fiber removed with foreign matter; ( 4) adversely
for the latter method. Arbitrary classification as to maturity
affect yarn and fabric appearance; and ( 5) may appear
must be made with bot
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.