ASTM F841-84(1998)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Thrusters, Tunnel, Permanently Installed in Marine Vessels
Standard Specification for Thrusters, Tunnel, Permanently Installed in Marine Vessels
SCOPE
1.1 This specification supplies general characteristics and interface details of propeller type, fixed-tunnel thruster units permanently installed in marine vessels or structures.
1.2 Values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system must be used independent of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification. Note 1-This specification supplies only general design, interface, and purchase information and does not include requirements for use, thruster controls, or associated equipment. The purchaser of the thruster equipment specified herein is cautioned that he must properly correlate the operating requirements with the thruster specified.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: F 841 – 84 (Reapproved 1998)
Standard Specification for
Thrusters, Tunnel, Permanently Installed in Marine Vessels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 841; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope ISO Recommendation ISO/DIS484/11 (Draft)
1.1 This specification supplies general characteristics and
3. Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard
interface details of propeller type, fixed-tunnel thruster units
3.1 thruster—a device constructed such as to provide a
permanently installed in marine vessels or structures.
force or thrust of controlled variable magnitude and direction
1.2 Values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric)
to a marine vessel or structure, usually, but not limited to, a
units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values
propeller mounted within a tunnel located below water level.
stated in each system must be used independent of the other.
3.2 fixedpitch—(FP)apropellerinwhichthebladesarepart
Combiningvaluesfromthetwosystemsmayresultinnoncon-
of, or are rigidly attached to, the hub such that the propeller
formance with the specification.
pitch is constant for a given radius.
NOTE 1—Thisspecificationsuppliesonlygeneraldesign,interface,and
3.3 controllable pitch—(CP)apropellerinwhichtheblades
purchase information and does not include requirements for use, thruster
are attached to a mechanism within the hub by means of bolts
controls,orassociatedequipment.Thepurchaserofthethrusterequipment
or fasteners, so that controlled movement of the mechanism
specified herein is cautioned that he must properly correlate the operating
causes the blades to change pitch in unison.
requirements with the thruster specified.
3.4 tunnel—a part of thruster assembly of circular cross
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
sectionwhichhousesstructuresupportingapropelleranddrive
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
mechanism.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.5 peak power—highest horsepower developed by the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
prime mover, or as limited by the thruster manufacturer.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.6 continuous duty—operation of the thruster continuously
at any power range, up to manufacturer’s rating, for extended
2. Referenced Documents
periods, but not to overlap into recommended maintenance
2.1 ASTM Standards:
intervals.
A 296 Specification for Corrosion-Resistant Iron-
3.7 intermittent duty—operation of the thruster at peak
ChromiumandIron-ChromiumNickelandNickel-BAlloy
power or RPM levels, or both, for periods not exceeding 1 h
Casting
followedbyperiodsof1hatthecontinuousratingorless,with
F25 Test Method for Sizing and Counting Airborne Par-
total running time not exceeding8hin24h.
ticulate Contamination in Clean Rooms and Other Dust-
3.8 landing bars—permanent attachments, usually in the
Controlled Areas Designed for Electronic and Similar
form of plates welded to the tunnel during manufacture,
Applications
intended to provide joining facilities for deck plates or bulk-
2.2 American Bureau of Shipping:
heads, or both, at installation. Landing bars are neither in-
ABS Rules for Building and Classing Steel Vessels
tended to be part of the support structure for the thruster, nor
2.3 ISO Document:
provide support or transmit forces from the vessel structure to
the thruster.
3.9 prime mover—the motor(s) or engine(s) providing the
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F-25 on Ships
and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on power to drive the thruster.
Machinery.
3.10 grid bars—bars installed at the tunnel entrances in the
Current edition approved April 12, 1984. Published June 1984.
form of a mesh to prevent large objects from passing through
Discontinued—See Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.02.
thethrustertunnel.Theareaoccupiedbythegridbarsshallnot
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 10.05.
Available from American Bureau of Shipping, 65 Broadway, New York, NY
exceed 6% of the tunnel cross-sectional area.
10006.
Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 841
4. Classification 5. Ordering Information
4.1 Thrusters manufactured in accordance with this specifi-
5.1 Requestsforquotationandpurchaseordersshallspecify
cation shall be identified as follows:
the following (in absence of specific requirements in ordering
4.1.1 Type I—Fixed pitch.
data, the unit will be provided only as specified herein):
4.1.2 Type II—Controllable pitch.
5.1.1 Description of thruster.
4.2 Each type of thruster may be manufactured to the
5.1.2 ASTM designation and date of issue.
following grade:
5.1.3 Type.
4.2.1 Grade 1—Intermittent duty for docking and naviga-
5.1.4 Grade.
tion.
5.1.5 Input Shaft Angle—Refer to Fig. 1.
4.2.2 Grade 2—Continuous duty for stationkeeping or dy-
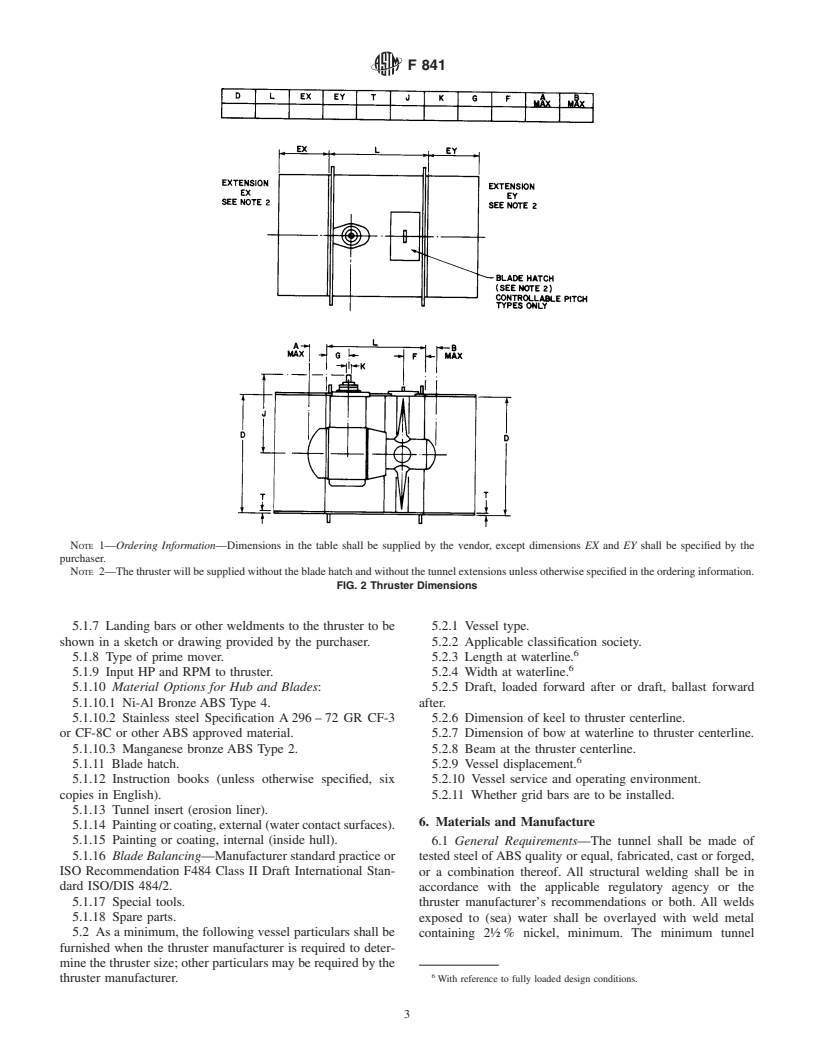
namic positioning. 5.1.6 Tunnel Extensions—Refer to Fig. 2.
NOTE 1—The thruster will be supplied without the blade hatch unless otherwise specified in the ordering data.
FIG. 1 Input Shaft Angle
F 841
NOTE 1—Ordering Information—Dimensions in the table shall be supplied by the vendor, except dimensions EX and EY shall be specified by the
purchaser.
NOTE 2—Thethrusterwillbesuppliedwithoutthebladehatchandwithoutthetunnelextensionsunlessotherwisespecifiedintheorderinginformation.
FIG. 2 Thruster Dimensions
5.1.7 Landing bars or other weldments to the thruster to be 5.2.1 Vessel type.
shown in a sketch or drawing provided by the purchaser. 5.2.2 Applicable classification society.
5.1.8 Type of prime mover. 5.2.3 Length at waterline.
5.1.9 Input HP and RPM to thruster. 5.2.4 Width at waterline.
5.1.10 Material Options for Hub and Blades: 5.2.5 Draft, loaded forward after or draft, ballast forward
5.1.10.1 Ni-Al Bronze ABS Type 4. after.
5.1.10.2 Stainless steel Specification A296–72 GR CF-3 5.2.6 Dimension of keel to thruster centerline.
or CF-8C or other ABS approved material. 5.2.7 Dimension of bow at waterline to thruster centerline.
5.1.10.3 Manganese bronze ABS Type 2. 5.2.8 Beam at the thruster centerline.
5.1.11 Blade hatch. 5.2.9 Vessel displacement.
5.1.12 Instruction books (unless otherwise specified, six 5.2.10 Vessel service and operating environment.
copies in English). 5.2.11 Whether grid bars are to be installed.
5.1.13 Tunnel insert (erosion liner).
6. Materials and Manufacture
5.1.14 Paintingorcoating,external(watercontactsurfaces).
5.1.15 Painting or coating, internal (inside hull). 6.1 General Requirements—The tunnel shall be made of
5.1.16 Blade Balancing—Manufacturerstandardpracticeor
tested steel ofABS quality or equal, fabricated, cast or forged,
ISO Recommendation F484 Class II Draft International Stan- or a combination thereof. All structural welding shall be in
dard ISO/DIS 484/2.
accordance with the applicable regulatory agency or the
5.1.17 Special tools. thruster manufacturer’s recommendations or both. All welds
5.1.18 Spare parts.
exposed to (sea) water shall be overlayed with weld metal
5.2 As a minimum, the following vessel particulars shall be containing 2½% nickel, minimum. The minimum tunnel
furnished when the thruster manufacturer is required to deter-
mine the thruster size; other particulars may be required by the
thruster manufacturer. With reference to fully loaded design conditions.
F 841
material thickness shall meet applicable classification society 6.7.3 The right-angle drive shafting and propeller hub shall
requirements. A replaceable insert may be provided in the be removable, if necessary, for inspection or repair without
tunnel in way of the propeller tips to prevent erosion of the removing the tunnel from the vessel.
tunnel wall (Fig. 3). The minimum width of the insert shallbe
6.7.4 The propeller shall be statistically balanced as speci-
10% of the propeller diameter. If an insert is not used, the
fied in the ordering data.
tunnel
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.