ASTM D4819-96(2005)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Flexible Cellular Materials Made From Polyolefin Plastics
Standard Specification for Flexible Cellular Materials Made From Polyolefin Plastics
ABSTRACT
This specification applies to flexible closed-cell materials made from polyolefin plastics and blends of polyolefin plastics. Two types of flexible, closed-cell polyolefin foams are covered: type I - closed cell foams made with polyolefin plastics and either chemically or radiation crosslinked, and type II - closed cell foams made with polyolefin plastics that are non-crosslinked. Cellular polyolefin foams furnished under this specification shall be manufactured from any resin or blend of resins that are members of the polyolefin family together with added compounding materials. Unless otherwise specified, the color of cellular polyolefin foams shall be natural.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification applies to flexible closed-cell materials made from polyolefin plastics and blends of polyolefin plastics as defined in Section .
1.2 Extruded or molded shapes too small to permit the cutting of standard test specimens are difficult to classify or test by standard test methods and will usually require special testing procedures or the use of standard test sheets.
1.3 In case of conflict between the provisions of this specification and those of detailed specifications for a particular product, the latter shall take precedence. These detailed specifications for the flexible closed-cell polyolefin plastic foams should state the particular test or tests desired.
1.4 In cases involving referee decisions, SI units shall be used.
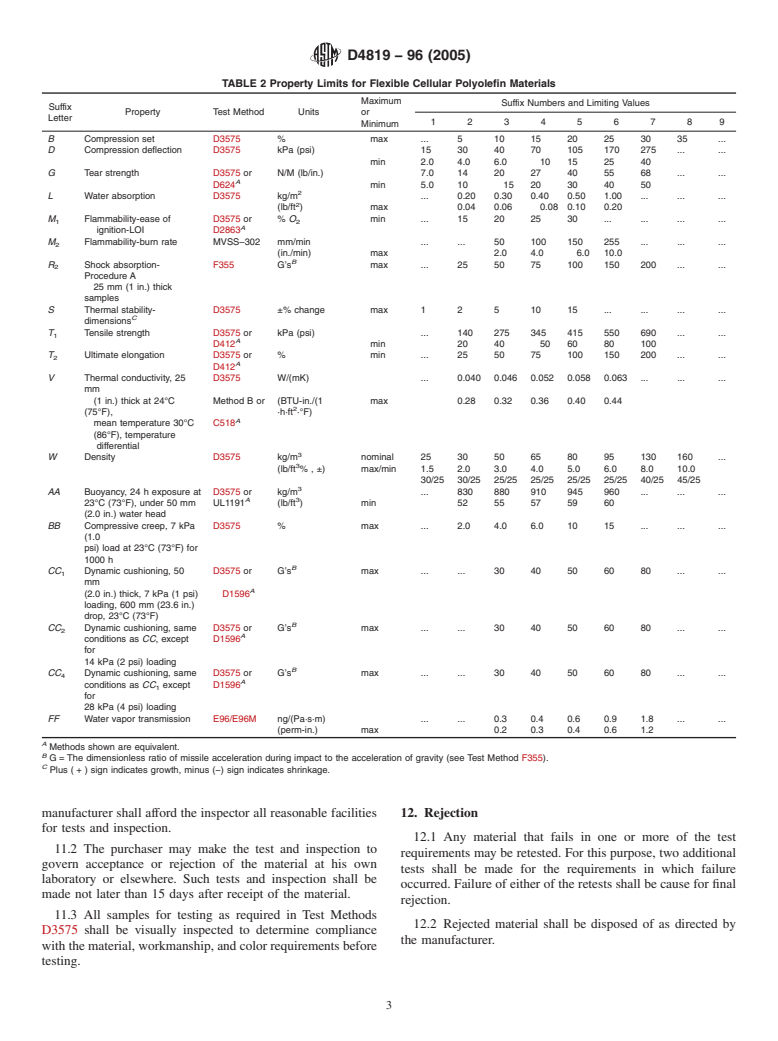
1.5 This specification does not contain test procedures or values for all the suffix letters listed in and . Where the procedure is not described in this specification or special limits are desired, or both, the test procedures and values must be arranged between the purchaser and the supplier.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only. There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D4819 −96(Reapproved 2005)
Standard Specification for
Flexible Cellular Materials Made From Polyolefin Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4819; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D624 Test Method for Tear Strength of Conventional Vul-
canized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers
1.1 This specification applies to flexible closed-cell materi-
D1596 Test Method for Dynamic Shock Cushioning Char-
als made from polyolefin plastics and blends of polyolefin
acteristics of Packaging Material
plastics as defined in Section 3.
D2863 Test Method for Measuring the Minimum Oxygen
1.2 Extruded or molded shapes too small to permit the
Concentration to Support Candle-Like Combustion of
cuttingofstandardtestspecimensaredifficulttoclassifyortest
Plastics (Oxygen Index)
by standard test methods and will usually require special
D3575 Test Methods for Flexible Cellular Materials Made
testing procedures or the use of standard test sheets.
From Olefin Polymers
E96/E96M Test Methods for Water Vapor Transmission of
1.3 In case of conflict between the provisions of this
specification and those of detailed specifications for a particu- Materials
F355 TestMethodforImpactAttenuationofPlayingSurface
lar product, the latter shall take precedence. These detailed
specifications for the flexible closed-cell polyolefin plastic Systems and Materials
foams should state the particular test or tests desired.
2.2 Motor Vehicle Safety Standard:
MVSS-302 Flammability of Vehicle Interior Materials—
1.4 In cases involving referee decisions, SI units shall be
Passenger Cars, Multipurpose Passenger Vehicles, Trucks
used.
and Buses
1.5 This specification does not contain test procedures or
2.3 UL Standard:
values for all the suffix letters listed in Table 1 and Table 2.
UL1191 Standard for Components for Personal Flotation
Where the procedure is not described in this specification or
Devices
special limits are desired, or both, the test procedures and
values must be arranged between the purchaser and the
3. Terminology
supplier.
3.1 Definitions:
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1.1 blend—mixture of polyolefin plastic(s) with other
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
polymer(s) in which at least 51 mass % is the polyolefin
only.
plastic(s).
NOTE 1—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
3.1.2 polyolefin plastics—material based on polymers made
by the polymerization of olefins or copolymerization of olefins
2. Referenced Documents
with other polymers, the polyolefin being at least 51 mass %.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.3 resin—solid, semi-solid, or pseudo-solid organic ma-
C518 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission
terial that has an indefinite and often high molecular weight,
Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
exhibits a tendency to flow when subject to stress, usually has
D412 Test Methods forVulcanized Rubber andThermoplas-
a softening or melting range, and usually fractures conchoid-
tic Elastomers—Tension
ally.
4. Classification (Types, Suffix Letters, and Suffix
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
Numbers)
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular
Plastics.
4.1 Types—This specification covers two types of flexible,
Current edition approved March 1, 2005. Published March 2005. Originally
closed-cell polyolefin foams designated as follows:
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 1996 as D4819 - 96. DOI:
10.1520/D4819-96R05.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from Department of Transportation, Washington, DC.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Underwriters Laboratories (UL), Corporate Progress, 333
the ASTM website. Pfingsten Rd., Northbrook, IL 60062.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D4819−96 (2005)
TABLE 1 Suffix Letter Designations
5. Ordering Information
A Heat resistance
5.1 When ordering, the product shall be described by
B Compression set under constant deflection
showing the type and suffix letters and number designations as
C Ozone or weather resistance
D Compression deflection
described in Section 4.
E Oil resistance
5.2 Minimum recommended properties for either type of
F Low temperature
G Tear resistance
foam shall include requirements for Compression Deflection
H Flex resistance
(Suffix D), Tensile Strength (Suffix T ), and Ultimate Elonga-
I Not assigned
J Abrasion resistance tion (Suffix T ).
K Adhesion capability
5.3 The properties selected and values set shall be selected
L Water absorption
M Flammability resistance
to ensure the required performance of the end product.
N Impact resistance
5.4 Specialrequirementsshallbelisted.Testproceduresand
O Electrical properties
P Staining resistance
limits shall be established by negotiation between the pur-
Q Not assigned
chaser and the supplier. Each special requirement shall be
R Resilience
listed as Z suffix letters followed by numerical subscripts.
R Shock absorption
S Thermal stability
T Tensile strength
6. Materials and Manufacture
T Ultimate elongation
U Not assigned
6.1 Cellular polyolefin foams furnished under this specifi-
V Thermal conductivity
cation shall be manufactured from any resin or blend of resins
W Density
that are members of the polyolefin family together with added
X Not assigned
Y Not assigned
compounding materials of such a nature and quality that the
Z Special requirements
finished product complies with this specification. In permitting
AA Buoyancy
choice in use of those materials by the producer, it is not
BB Compressive creep
CC Dynamic cushioning
intended to imply that the different resins are equivalent with
DD Open cell
respect to all physical properties. Special characteristics other
EE Not assigned
than those prescribed in this specification that may be desired
FF Water vapor transmission
for specific applications shall be listed in the product specifi-
cations, as they may influence the choice of the type of resin or
other materials used.
6.2 All materials and workmanship shall be in accordance
4.1.1 Type I—Closed cell foams made with polyolefin
with good commercial practice and the resulting cellular
plastics and either chemically or radiation crosslinked.
polyolefin shall be free from defects affecting serviceability.
4.1.2 Type II—Closed cell foams made with polyolefin
7. Color
plastics that are non-crosslinked.
7.1 Unless otherwise specified, the color of cellular poly-
4.2 Suffıx Letters—Suffix letters shall be added to the type
olefin foams shall be natural. The foam shall contain no
designation (4.1) singly or in combination to indicate the
colorants.
necessary requirements.
4.2.1 The significance of the approved suffix letters is given
8. Physical Properties
in Table 1.
8.1 The polyolefin foams shall conform to the requirements
4.2.2 Frequently used suffix letters for polyolefin foams are
given in the classification (see Section 4) and described in
given in Table 2. Where more than one test method exists for
Table 2 togethe
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.