ASTM D5426-12(2017)
(Practice)Standard Practices for Visual Inspection and Grading of Fabrics Used for Inflatable Restraints
Standard Practices for Visual Inspection and Grading of Fabrics Used for Inflatable Restraints
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 These practices are suitable for incorporation in a specification. Any reference to material or cushion specification in these practices shall mean any similar agreement between the purchaser and supplier relating to the inspection and acceptance of fabric intended for inflatable restraint use.
5.2 These practices constitute the terminology, conditions, equipment, and procedures by which rolls of inflatable restraint fabrics or cut parts are inspected and graded.
5.3 A specification incorporating these practices may deviate from them to account for considerations of fabric property, material handling equipment, or inflatable restraint cushion design, or a combination thereof. Whenever such deviations from standard occur, they are recorded in the report.
5.4 These practices acknowledge that, in the normal course of production, acceptable rolls of fabric will be produced containing imperfections; subsequently, pieces will be cut from the rolls and those pieces that contain imperfections restricted in Tables 1-5 will be culled at that time.
5.5 The accuracy in the results from visually inspecting fabric using these practices is affected by the ability of the inspector to detect, identify, and evaluate the severity of an imperfection in a moving fabric or in a cut part. Such ability can be affected by visual acuity, viewing distance, fabric traverse speed, lighting conditions, inspector discipline and training, and the availability and accuracy of suitable visual aids.
5.6 Systematic bias may result from using these practices whenever the precision or scale of the visual aids used to identify and quantify imperfections differs between the purchaser and supplier.
SCOPE
1.1 These practices cover procedures for the inspection and grading of coated and uncoated woven flat and one-piece woven (OPW) fabrics, and for the inspection and culling of cut parts made of such fabrics, all of which are used in the manufacture of inflatable restraint cushions.
1.2 For ease of reference, the scope, summary of practice, significance and use, apparatus, sampling, procedure, and report sections are listed separately for each inspection practice.
Inspection Practice
Section
Fabric Rolls
7
Cut Pieces & OPW
8
1.3 These practices can be used to distinguish those fabric imperfections that may adversely affect inflatable restraint cushion fabrication or performance from those imperfections that will not.
1.4 Procedures and apparatus other than those stated in these practices may be used by agreement of the purchaser and supplier with the specific deviations from these practices acknowledged in the report.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D5426 −12 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Practices for
Visual Inspection and Grading of Fabrics Used for Inflatable
Restraints
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5426; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D6799 Terminology Relating to Inflatable Restraints
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
1.1 These practices cover procedures for the inspection and
Reference Photographs of Imperfections
grading of coated and uncoated woven flat and one-piece
woven (OPW) fabrics, and for the inspection and culling of cut
3. Terminology
parts made of such fabrics, all of which are used in the
3.1 For all terminology relating to D13.20, Inflatable
manufacture of inflatable restraint cushions.
restraints, refer to Terminology D6799.
1.2 For ease of reference, the scope, summary of practice,
3.1.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard:
significance and use, apparatus, sampling, procedure, and
abrasion,airsplice,bleedthrough,blip,brokenfilament,bruise,
report sections are listed separately for each inspection prac-
coating slub, coating streak, coating transfer, contamination,
tice.
cushion, defect, filling bar, finished, foreign matter, grading,
Inspection Practice Section
hard contamination, heavy coating streak, hole, imperfection,
Fabric Rolls 7 inflatable restraint, inspection, light coating, light coating
Cut Pieces & OPW 8
streak, long float, loop, major imperfection, minor
1.3 These practices can be used to distinguish those fabric
imperfection, missing coating, missing yarn, misweave,
imperfections that may adversely affect inflatable restraint
module, rework, sharp crease, short float, short knot, soft
cushion fabrication or performance from those imperfections
contamination, spit mark, stain, stitching, tight yarn, yarn
that will not.
streak.
1.4 Procedures and apparatus other than those stated in
3.2 For all other terms related to textiles, see Terminology
these practices may be used by agreement of the purchaser and
D123.
supplier with the specific deviations from these practices
acknowledged in the report. 4. Summary of Practices
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the 4.1 Rolls of finished or coated fabric are examined for
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information imperfections as the fabric traverses an inspection station.
only. They are graded per Tables Tables 1-5 .
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.2 Cut pieces are inspected individually for imperfections.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Cut pieces containing imperfections are culled from use for
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
later review.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5. Significance and Use
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.1 These practices are suitable for incorporation in a
2. Referenced Documents
specification. Any reference to material or cushion specifica-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tion in these practices shall mean any similar agreement
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
between the purchaser and supplier relating to the inspection
and acceptance of fabric intended for inflatable restraint use.
These practices are under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.20 on Inflatable Restraints.
5.2 These practices constitute the terminology, conditions,
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2017. Published March 2017. Originally
equipment,andproceduresbywhichrollsofinflatablerestraint
approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D5426 – 12. DOI:
fabrics or cut parts are inspected and graded.
10.1520/D5426-12R17.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service ast service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standardsvolume information, refer to the standrd’s Document Summary page on Available from: ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
the ASTM website. ADJD5426. Original adjunct produced in 1996.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5426−12 (2017)
TABLE 1 Coating Non-Uniformity
Limits
Imperfection Definition
Minimum Maximum
A
Maximum Size
B
Separation Frequency
Soft the presence of materials not specified as part of the coating 15 mm diameter 2; but none within
contamination or fabric within or on the coating layer, such material visibly the line where two
appearing to be of small size, smooth in surface texture, and OPW inflatable
of a thickness that does not protrude significantly above the layers interface
surface of the coating layer. Examples are dirt, smudge, lint,
human hair, yarn filaments, and flies and similarly small
insects. Soft contamination not listed herein shall be from a
known source which is demonstrated to have no adverse
effect on fabric properties.
Hard the presence of non-coating material within or on the coating none none allowed
contamination layer, such material visibly appearing to be of small size,
smooth in surface texture, and of a thickness that protrudes
significantly above the surface of the coating layer.
Examples are metal filings, glass, plastic, or wood splinters.
Missing portions of the coated layer containing exposed base fabric or 15 mm diameter 2; but none within
coating scrape marks in the coated layer the line where two
OPW inflatable
layers interface
-or- -or-
5 mm diameter 5; but none within
the line where two
OPW inflatable
layers interface
Coating the presence of coating material on the uncoated side, none allowed
transfer covering one or more yarns
Bleedthrough the presence of coating material on the uncoated side, 35-mm length 500 mm 2
between two yarns without covering either yarn
Coating slub an irregularly shaped lump of coating material on the surface 15 mm diameter 2 per 400 cm
of the coated layer resembling a yarn slub
Spit mark an essentially round spot of coating material on the surface of 15 mm diameter 2 per 400 cm
the coated layer in which the coating spot is visibly at a -or- -or-
higher rate of coverage than the surrounding material. 5 mm diameter 5 per 400 cm
Heavy a narrow area of fabric, generally in the shape of a line 5 mm wide No limit
coating oriented in the warp direction of the fabric, in which the
streak coating layer is visibly at a higher rate of coverage than the
surrounding material.
Light a narrow area of light (not missing) and heavy coating 5 mm wide 3; but none within
coating associated with localized creasing in the fabric, visibly at a the line where two
crease lower rate of coverage than the surrounding material. OPW inflatable
layers interface
Light a narrow area of light coating (not missing), generally in the 5mmwide 1
coating shape of a line oriented in the warp direction of the fabric.
streak
Light coating a localized amorphous area of fabric in which the coating layer 50 × 100 mm 1
(except light is visibly at a lower rate than the surrounding material. -or- -or-
coating streak) 10 mm dia 5
A
For diameter call outs, an equivalent area is permissible
B
Per linear m (yd), or unit of area indicated. For cut pieces, limits apply to cut pieces# 2 meters in longest dimension. For cut pieces > 2 meters in longest dimension,
multiply limits by 1.5. Per linear m (yd), cut piece, or unit of area indicated.
5.3 A specification incorporating these practices may devi- containingimperfections;subsequently,pieceswillbecutfrom
ate from them to account for considerations of fabric property, the rolls and those pieces that contain imperfections restricted
material handling equipment, or inflatable restraint cushion in Tables 1-5 will be culled at that time.
design, or a combination thereof. Whenever such deviations
5.5 The accuracy in the results from visually inspecting
from standard occur, they are recorded in the report.
fabric using these practices is affected by the ability of the
5.4 These practices acknowledge that, in the normal course inspector to detect, identify, and evaluate the severity of an
of production, acceptable rolls of fabric will be produced imperfection in a moving fabric or in a cut part. Such ability
D5426−12 (2017)
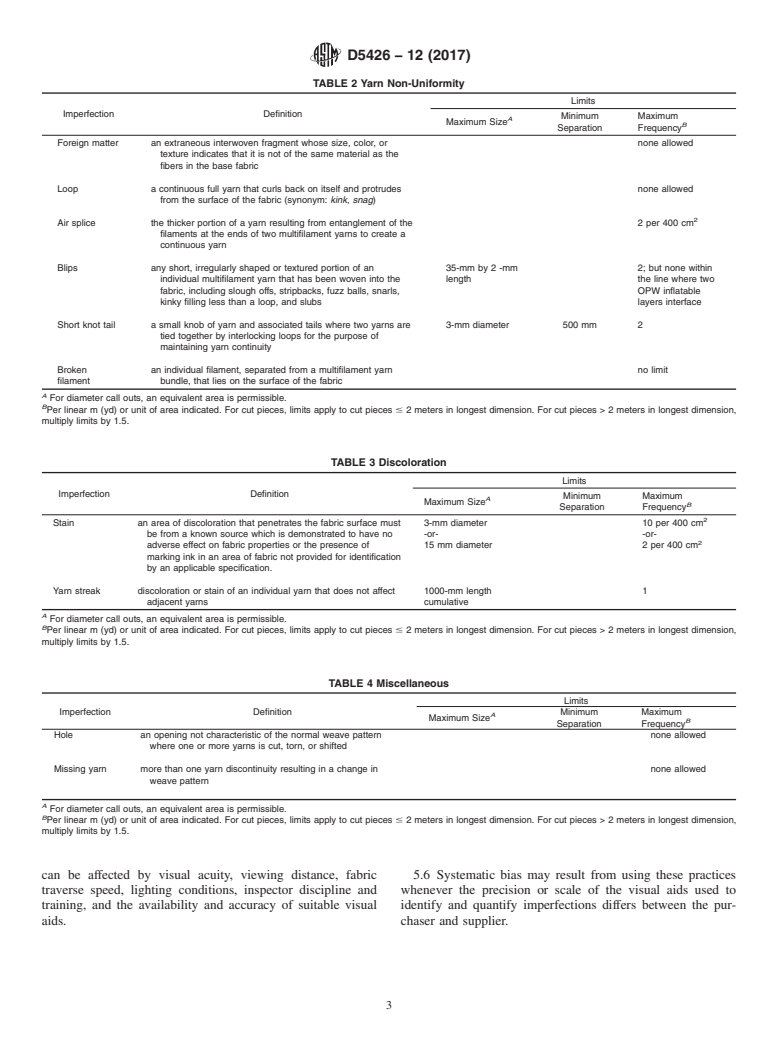
TABLE 2 Yarn Non-Uniformity
Limits
Imperfection Definition
Minimum Maximum
A
Maximum Size
B
Separation Frequency
Foreign matter an extraneous interwoven fragment whose size, color, or none allowed
texture indicates that it is not of the same material as the
fibers in the base fabric
Loop a continuous full yarn that curls back on itself and protrudes none allowed
from the surface of the fabric (synonym: kink, snag)
Air splice the thicker portion of a yarn resulting from entanglement of the 2 per 400 cm
filaments at the ends of two multifilament yarns to create a
continuous yarn
Blips any short, irregularly shaped or textured portion of an 35-mm by 2 -mm 2; but none within
individual multifilament yarn that has been woven into the length the line where two
fabric, including slough offs, stripbacks, fuzz balls, snarls, OPW inflatable
kinky filling less than a loop, and slubs layers interface
Short knot tail a small knob of yarn and associated tails where two yarns are 3-mm diameter 500 mm 2
tied together by interlocking loops for the purpose of
maintaining yarn continuity
Broken an individual filament, separated from a multifilament yarn no limit
filament bundle, that lies on the surface of the fabric
A
For diameter call outs, an equivalent area is permissible.
B
Per linear m (yd) or unit of area indicated. For cut pieces, limits apply to cut pieces# 2 meters in longest dimension. For cut pieces > 2 meters in longest dimension,
multiply limits by 1.5.
TABLE 3 Discoloration
Limits
Imperfection Definition
Minimum Maximum
A
Maximum Size
B
Separation Frequency
Stain an area of discoloration that penetrates the fabric surface must 3-mm diameter 10 per 400 cm
be from a known source which is demonstrated to have no -or- -or-
adverse effect on fabric properties or the presence of 15 mm diameter 2 per 400 cm
marking ink in an area of fabric not provided for identification
by an applicable specification.
Yarn streak discoloration or stain of an individual yarn that does not affect 1000-mm length 1
adjacent yarns cumulative
A
For diameter call outs, an equivalent area is permissible.
B
Per linear m (yd) or unit of area indicated. For cut pieces, limits apply to cut pieces# 2 meters in longest dimension. For cut pieces > 2 meters in longest dimension,
multiply limits by 1.5.
TABLE 4 Miscellaneous
Limits
Imperfection Definition Minimum Maximum
A
Maximum Size
B
Separation Frequency
Hole an opening not characteristic of the normal weave pattern none allowed
where one or more yarns is cut, torn, or shifted
Missing yarn more than one yarn discontinuity resulting in a change in none allowed
weave pattern
A
For diameter call outs, an equivalent area is permissible.
B
Per linear m (yd) or unit of area indicated. For cut pieces, limits apply to cut pieces# 2 meters in longest dimension. For cut pieces > 2 meters in longest dimension,
multiply limits by 1.5.
can be affected by visual acuity, viewing distance, fabric 5.6 Systematic bias may result from using these practices
traverse speed, lighting conditions, inspector discipline and whenever the precision or scale of the visual aids used to
training, and the availability and accuracy of suitable visual identify and quantify imperfections differs between the pur-
aids. chaser and supplier.
D5426−12 (2017)
TABLE 5 Weave Non-Uniformity
Limits
Imperfection Definition
Minimum Maximum
A
Maximum Size
B
Separation Frequency
Abrasion a localized concentration of multiple broken filaments. none allowed
Fold over a hard ridge where a layer is overlapped upon itself where if none allowed
applicable coating integrity is compromised
Long float a warp or filling yarn extending over six or more filling or warp none allowed
yarns with which it should be interlaced
Short float a warp or filling yarn extending over five or fewer filling or warp 5 per 400 cm ; but
yarns with which it should be interlaced none within the line
where two OPW
inflatable layers
interface
Bruise a shift in the squareness of the weave pattern in an area that 35-mm diameter 500 mm 2
has been subjected to impact or pressure
Tight yarn a yarn with less crimp than surrounding fibers that may create 35-mm length 500 mm 2
puckering, which may appear to be shinier or to lie straighter
in the weave pattern, or a combination thereof
Misweave a change in the weave pattern visually indicated by incorrect 1000-mm length 1
interlacing or incorrect insertion of a single unbroken yarn or
a single missing yarn. (includes mispick, missing yarn,
wrong draw, jerk-in).)
Filling bar a temporary change in the filling-wise density of the weave
pattern that:(synonym: stop/start mark)
1. is in compliance with the specified count no limit
2. is not in compliance with the specified count none allowed
Stitching (OPW only) the presence of an inter-lace between two layers none allowed
of fabric in an area not provided for interlacing by an
applicable specification.
A
For diameter call outs, an equivalent area is permissible.
B
Per linear m (yd) or unit of area indicated. For cut pieces, limits apply to cut pieces# 2 meters in longest dimension. For cut pieces > 2 meters in longest dimension,
multiply limits by 1.5.
6. Visual Aids 7.2.1 Rolls of fabric are visually inspected for the presence
of imperfections and graded at an inspection station. Rolls of
6.1 A calibrated measuring device or clear template of
fabric are unwound and rewound as the fabric traverses the
sufficient size to contain an array of circles whose diameters
inspection station, with provision for interruption of the tra-
equal the length, diameter, separation, or area limits listed in
verse for stationary inspection.
Tables 1-5, with labeling corresponding to the terminology for
NOTE 1—In accordance with an applicable material specification, fabric
each imperfection: 3, 10, 15, 35, 50, 200, 225, 300, 400 and
is inspected full width or within a specified distance of the outer edge of
500 mm. The template should be positioned such that the
the selvage, or if its in one-piece woven fabric within a specified distance
maximum number of imperfections is captured.
ofthevisiblelinecreatedwherethetwoinflatablelayersinitiallyinterlace.
6.1.1 Dimensions on the measuring device
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5426 − 12 D5426 − 12 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Practices for
Visual Inspection and Grading of Fabrics Used for Inflatable
Restraints
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5426; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 These practices cover procedures for the inspection and grading of coated and uncoated woven flat and one-piece woven
(OPW) fabrics, and for the inspection and culling of cut parts made of such fabrics, all of which are used in the manufacture of
inflatable restraint cushions.
1.2 For ease of reference, the scope, summary of practice, significance and use, apparatus, sampling, procedure, and report
sections are listed separately for each inspection practice.
Inspection Practice Section
Fabric Rolls 7
Cut Pieces & OPW 8
1.3 These practices can be used to distinguish those fabric imperfections that may adversely affect inflatable restraint cushion
fabrication or performance from those imperfections that will not.
1.4 Procedures and apparatus other than those stated in these practices may be used by agreement of the purchaser and supplier
with the specific deviations from these practices acknowledged in the report.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
D6799 Terminology Relating to Inflatable Restraints
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
Reference Photographs of Imperfections
3. Terminology
3.1 For all terminology relating to D13.20, Inflatable restraints, refer to Terminology D6799.
3.1.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard: abrasion, air splice, bleedthrough, blip, broken filament, bruise, coating
slub, coating streak, coating transfer, contamination, cushion, defect, filling bar, finished, foreign matter, grading, hard
contamination, heavy coating streak, hole, imperfection, inflatable restraint, inspection, light coating, light coating streak, long
float, loop, major imperfection, minor imperfection, missing coating, missing yarn, misweave, module, rework, sharp crease, short
float, short knot, soft contamination, spit mark, stain, stitching, tight yarn, yarn streak.
3.2 For all other terms related to textiles, see Terminology D123.
These practices are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D13 on Textiles and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.20 on Inflatable Restraints.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2012Feb. 1, 2017. Published January 2013March 2017. Originally approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 20082012 as
ε1
D5426 – 08D5426 – 12. . DOI: 10.1520/D5426-12.10.1520/D5426-12R17.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service ast service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standardsvolume information, refer to the standrd’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Available from: ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No. ADJD5426. Original adjunct produced in 1996.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5426 − 12 (2017)
4. Summary of Practices
4.1 Rolls of finished or coated fabric are examined for imperfections as the fabric traverses an inspection station. They are
graded per Tables Tables 1-5 .
4.2 Cut pieces are inspected individually for imperfections. Cut pieces containing imperfections are culled from use for later
review.
TABLE 1 Coating Non-Uniformity
Limits
Imperfection Definition
Minimum Maximum
A
Maximum Size
B
Separation Frequency
Soft the presence of materials not specified as part of the coating 15 mm diameter 2; but none within
contamination or fabric within or on the coating layer, such material visibly the line where two
appearing to be of small size, smooth in surface texture, and OPW inflatable
of a thickness that does not protrude significantly above the layers interface
surface of the coating layer. Examples are dirt, smudge, lint,
human hair, yarn filaments, and flies and similarly small
insects. Soft contamination not listed herein shall be from a
known source which is demonstrated to have no adverse
effect on fabric properties.
Hard the presence of non-coating material within or on the coating none none allowed
contamination layer, such material visibly appearing to be of small size,
smooth in surface texture, and of a thickness that protrudes
significantly above the surface of the coating layer.
Examples are metal filings, glass, plastic, or wood splinters.
Missing portions of the coated layer containing exposed base fabric or 15 mm diameter 2; but none within
coating scrape marks in the coated layer the line where two
OPW inflatable
layers interface
-or- -or-
5 mm diameter 5; but none within
the line where two
OPW inflatable
layers interface
Coating the presence of coating material on the uncoated side, none allowed
transfer covering one or more yarns
Bleedthrough the presence of coating material on the uncoated side, 35-mm length 500 mm 2
between two yarns without covering either yarn
Coating slub an irregularly shaped lump of coating material on the surface 15 mm diameter 2 per 400 cm
of the coated layer resembling a yarn slub
Spit mark an essentially round spot of coating material on the surface of 15 mm diameter 2 per 400 cm
the coated layer in which the coating spot is visibly at a -or- -or-
higher rate of coverage than the surrounding material. 5 mm diameter 5 per 400 cm
Heavy a narrow area of fabric, generally in the shape of a line 5 mm wide No limit
coating oriented in the warp direction of the fabric, in which the
streak coating layer is visibly at a higher rate of coverage than the
surrounding material.
Light a narrow area of light (not missing) and heavy coating 5 mm wide 3; but none within
coating associated with localized creasing in the fabric, visibly at a the line where two
crease lower rate of coverage than the surrounding material. OPW inflatable
layers interface
Light a narrow area of light coating (not missing), generally in the 5 mm wide 1
coating shape of a line oriented in the warp direction of the fabric.
streak
Light coating a localized amorphous area of fabric in which the coating layer 50 × 100 mm 1
(except light is visibly at a lower rate than the surrounding material. -or- -or-
coating streak) 10 mm dia 5
A
For diameter call outs, an equivalent area is permissible
B
Per linear m (yd), or unit of area indicated. For cut pieces, limits apply to cut pieces # 2 meters in longest dimension. For cut pieces > 2 meters in longest dimension,
multiply limits by 1.5. Per linear m (yd), cut piece, or unit of area indicated.
D5426 − 12 (2017)
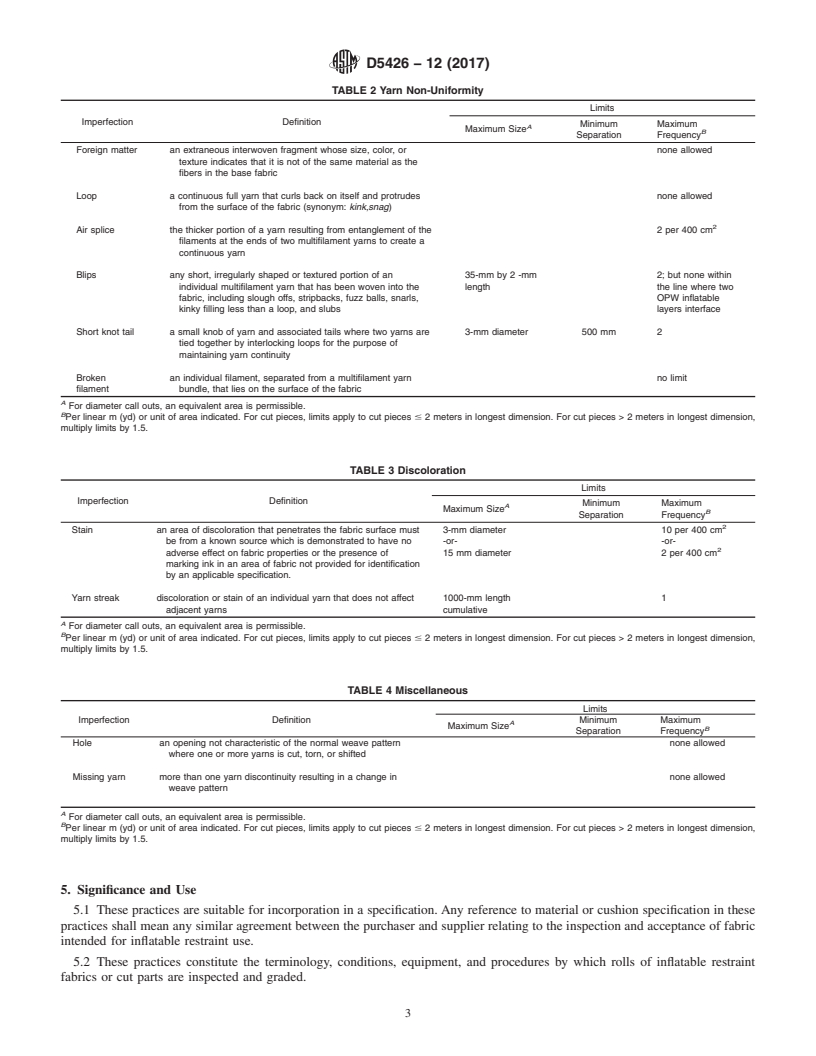
TABLE 2 Yarn Non-Uniformity
Limits
Imperfection Definition
Minimum Maximum
A
Maximum Size
B
Separation Frequency
Foreign matter an extraneous interwoven fragment whose size, color, or none allowed
texture indicates that it is not of the same material as the
fibers in the base fabric
Loop a continuous full yarn that curls back on itself and protrudes none allowed
from the surface of the fabric (synonym: kink,snag)
Air splice the thicker portion of a yarn resulting from entanglement of the 2 per 400 cm
filaments at the ends of two multifilament yarns to create a
continuous yarn
Blips any short, irregularly shaped or textured portion of an 35-mm by 2 -mm 2; but none within
individual multifilament yarn that has been woven into the length the line where two
fabric, including slough offs, stripbacks, fuzz balls, snarls, OPW inflatable
kinky filling less than a loop, and slubs layers interface
Short knot tail a small knob of yarn and associated tails where two yarns are 3-mm diameter 500 mm 2
tied together by interlocking loops for the purpose of
maintaining yarn continuity
Broken an individual filament, separated from a multifilament yarn no limit
filament bundle, that lies on the surface of the fabric
A
For diameter call outs, an equivalent area is permissible.
B
Per linear m (yd) or unit of area indicated. For cut pieces, limits apply to cut pieces # 2 meters in longest dimension. For cut pieces > 2 meters in longest dimension,
multiply limits by 1.5.
TABLE 3 Discoloration
Limits
Imperfection Definition
Minimum Maximum
A
Maximum Size
B
Separation Frequency
Stain an area of discoloration that penetrates the fabric surface must 3-mm diameter 10 per 400 cm
be from a known source which is demonstrated to have no -or- -or-
adverse effect on fabric properties or the presence of 15 mm diameter 2 per 400 cm
marking ink in an area of fabric not provided for identification
by an applicable specification.
Yarn streak discoloration or stain of an individual yarn that does not affect 1000-mm length 1
adjacent yarns cumulative
A
For diameter call outs, an equivalent area is permissible.
B
Per linear m (yd) or unit of area indicated. For cut pieces, limits apply to cut pieces # 2 meters in longest dimension. For cut pieces > 2 meters in longest dimension,
multiply limits by 1.5.
TABLE 4 Miscellaneous
Limits
Imperfection Definition Minimum Maximum
A
Maximum Size
B
Separation Frequency
Hole an opening not characteristic of the normal weave pattern none allowed
where one or more yarns is cut, torn, or shifted
Missing yarn more than one yarn discontinuity resulting in a change in none allowed
weave pattern
A
For diameter call outs, an equivalent area is permissible.
B
Per linear m (yd) or unit of area indicated. For cut pieces, limits apply to cut pieces # 2 meters in longest dimension. For cut pieces > 2 meters in longest dimension,
multiply limits by 1.5.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 These practices are suitable for incorporation in a specification. Any reference to material or cushion specification in these
practices shall mean any similar agreement between the purchaser and supplier relating to the inspection and acceptance of fabric
intended for inflatable restraint use.
5.2 These practices constitute the terminology, conditions, equipment, and procedures by which rolls of inflatable restraint
fabrics or cut parts are inspected and graded.
D5426 − 12 (2017)
TABLE 5 Weave Non-Uniformity
Limits
Imperfection Definition
Minimum Maximum
A
Maximum Size
B
Separation Frequency
Abrasion a localized concentration of multiple broken filaments. none allowed
Fold over a hard ridge where a layer is overlapped upon itself where if none allowed
applicable coating integrity is compromised
Long float a warp or filling yarn extending over six or more filling or warp none allowed
yarns with which it should be interlaced
Short float a warp or filling yarn extending over five or fewer filling or warp 5 per 400 cm ; but
yarns with which it should be interlaced none within the line
where two OPW
inflatable layers
interface
Bruise a shift in the squareness of the weave pattern in an area that 35-mm diameter 500 mm 2
has been subjected to impact or pressure
Tight yarn a yarn with less crimp than surrounding fibers that may create 35-mm length 500 mm 2
puckering, which may appear to be shinier or to lie straighter
in the weave pattern, or a combination thereof
Misweave a change in the weave pattern visually indicated by incorrect 1000-mm length 1
interlacing or incorrect insertion of a single unbroken yarn or
a single missing yarn. (includes mispick, missing yarn,
wrong draw, jerk-in).)
Filling bar a temporary change in the filling-wise density of the weave
pattern that:(synonym: stop/start mark)
1. is in compliance with the specified count no limit
2. is not in compliance with the specified count none allowed
Stitching (OPW only) the presence of an inter-lace between two layers none allowed
of fabric in an area not provided for interlacing by an
applicable specification.
A
For diameter call outs, an equivalent area is permissible.
B
Per linear m (yd) or unit of area indicated. For cut pieces, limits apply to cut pieces # 2 meters in longest dimension. For cut pieces > 2 meters in longest dimension,
multiply limits by 1.5.
5.3 A specification incorporating these practices may deviate from them to account for considerations of fabric property,
material handling equipment, or inflatable restraint cushion design, or a combination thereof. Whenever such deviations from
standard occur, they are recorded in the report.
5.4 These practices acknowledge that, in the normal course of production, acceptable rolls of fabric will be produced containing
imperfections; subsequently, pieces will be cut from the rolls and those pieces that contain imperfections restricted in Tables 1-5
will be culled at that time.
5.5 The accuracy in the results from visually inspecting fabric using these practices is affected by the ability of the inspector
to detect, identify, and evaluate the severity of an imperfection in a moving fabric or in a cut part. Such ability can be affected by
visual acuity, viewing distance, fabric traverse speed, lighting conditions, inspector discipline and training, and the availability and
accuracy of suitable visual aids.
5.6 Systematic bias may result from using these practices whenever the precision or scale of the visual aids used to identify and
quantify imperfections differs between the purchaser and supplier.
6. Visual Aids
6.1 A calibrated measuring device or clear template of sufficient size to contain an array of circles whose diameters equal the
length, diameter, separation, or area limits listed in Tables 1-5, with labeling corresponding to the terminology for each
imperfection: 3, 10, 15, 35, 50, 200, 225, 300, 400 and 500 mm. The template should be positioned such that the maximum number
of imperfections is captured.
6.1.1 Dimensions on the measuring device or template shall be traceable to the National Institute for Standards and Technology
(NIST) (or similarly recognized standards facility) via a master reference standard to ensure accuracy.
6.2 Re
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.