ASTM D6406-99(2014)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Analysis of Sugar in Vegetable Tanning Materials
Standard Test Method for Analysis of Sugar in Vegetable Tanning Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
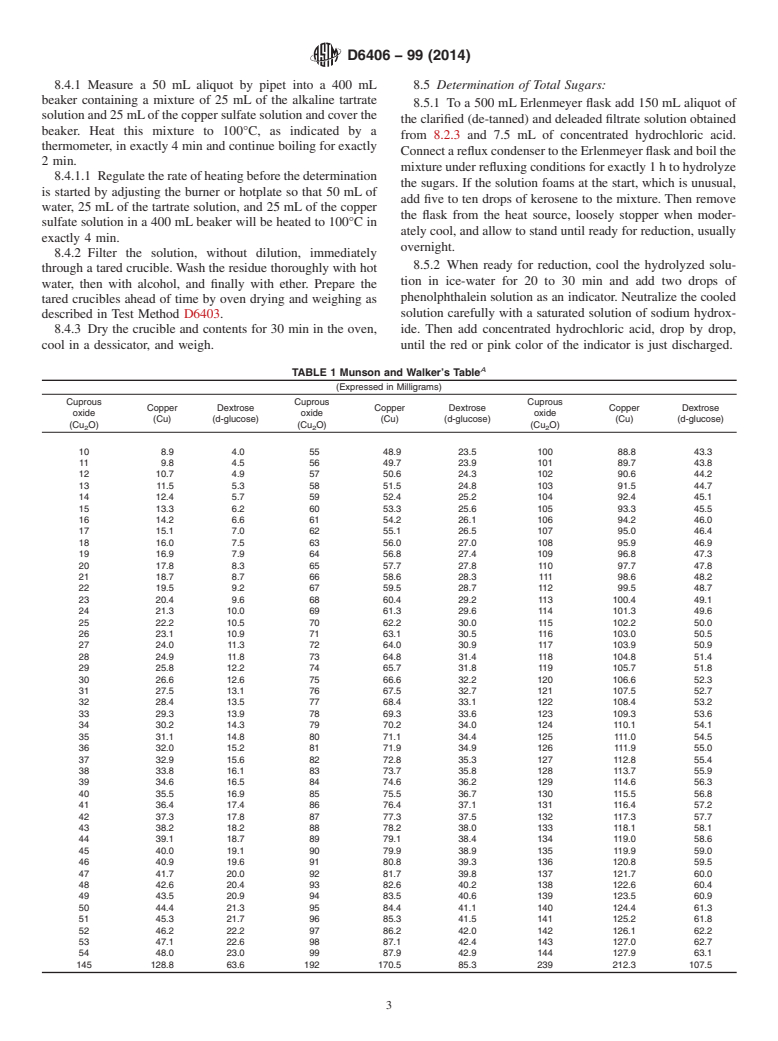
5.1 This test method is used to determine the quantity of sugar present in vegetable tanning materials or vegetable tannin extracts. The amount of the reducing sugars, total sugars, and non-reducing sugars in a sample of material or extract can be determined by this method.
5.2 Because of the possibility of errors in this test method it is essential that the method be followed exactly in order to obtain reproducible results both among specimens within a laboratory and for analyses between laboratories.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers determining the sugars present in vegetable tanning materials.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6406 − 99 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Method for
1
Analysis of Sugar in Vegetable Tanning Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6406; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers determining the sugars present 3.1 Definitions:
in vegetable tanning materials. 3.1.1 dextrose—d-glucose.
3.1.2 glucose—a simple sugar with formula C H O , and
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
6 12 6
known to exist in d-, l-, and racemic forms. The term
standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for
commonly refers to the sweet, colorless, water-soluble dextro-
information only.
rotatoryformthatoccurswidelyinnatureandistheusualform
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
in which carbohydrate is assimilated by animals. The term
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
glucose can also refer to a light-colored syrup made from corn
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
starch.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.3 sugar—any of various water-soluble compounds that
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
vary widely in sweetness and comprise the oligosaccharides
including sucrose.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4. Summary of Test Method
D4901 Practice for Preparation of Solution of Liquid Veg-
4.1 An analytical strength solution (that is, 4.00 6 0.25 g
etable Tannin Extracts
tanninperlitre)ofthetanningmaterialisanalyzedforreducing
D4905 Practice for Preparation of Solution of Solid, Pasty
sugars and total sugars by the Munson and Walker procedure.
and Powdered Vegetable Tannin Extracts
D6401 Test Method for Determining Non-Tannins and Tan-
5. Significance and Use
nin in Extracts of Vegetable Tanning Materials
D6403 Test Method for Determining Moisture in Raw and
5.1 This test method is used to determine the quantity of
Spent Materials
sugar present in vegetable tanning materials or vegetable
D6404 Practice for Sampling Vegetable Materials Contain-
tannin extracts. The amount of the reducing sugars, total
ing Tannin
sugars, and non-reducing sugars in a sample of material or
D6405 Practice for Extraction of Tannins from Raw and
extract can be determined by this method.
Spent Materials
5.2 Because of the possibility of errors in this test method it
D6408 Test Method for Analysis of Tannery Liquors
is essential that the method be followed exactly in order to
2.2 ALCA Methods:
obtain reproducible results both among specimens within a
3
A30 Sugar in Tanning Materials
laboratory and for analyses between laboratories.
6. Apparatus and Reagents
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D31 on Leather
6.1 Saturated Solution of Normal Lead Acetate.
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D31.01 on Vegetable Leather. This
6.2 Dipotassium Hydrogen Phosphate, Anhydrous
method has been adapted from and is a replacement for MethodA30 of the Official
Methods of the American Leather Chemists Association.
(K HPO ), dried in an oven at 100°C for 16 h then stored in a
2 4
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2014. Published December 2014. Originally
tightly stoppered bottle.
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as D6406 – 99 (2009).
DOI: 10.1520/D6406-99R14.
6.3 Toluene, assay ≥ 99.5 %.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.4 Fehling’s Solutions, A and B.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
6.5 Hydrochloric Acid, concentrated (sp.gr. 1.18).
the ASTM website.
3
Official Methods of the American Leather Chemists Association. Available
6.6 Kerosene, commercial grade.
from the American Leather Chemists Association, University of Cincinnati, P.O.
Box 210014, Cincinnati, OH 45221-0014. 6.7 Saturated Solution of Sodium Hydroxide.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6406 − 99 (2014)
6.8 Phenolphthalein Solution, 0.5 g dissolved in 100 mL of 6.26 Balance,analyticalbalancewhichwillweighupto100
95 % ethanol. g with an accuracy of 6 0.1 mg (6 0.0001 g).
6.9 Tartaric Acid, powdered.
6.27 Drying Oven, a forced-air convection oven (or
mechanical-convection draft oven) capable of maintaining a
6.10 Copper Sulfate Solution, prepared by dissolving
temperature of 100 6 2.0°C.
69.278 g o
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6406 − 99 (Reapproved 2009) D6406 − 99 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Method for
1
Analysis of Sugar in Vegetable Tanning Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6406; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers determining the sugars present in vegetable tanning materials.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for
information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4901 Practice for Preparation of Solution of Liquid Vegetable Tannin Extracts
D4905 Practice for Preparation of Solution of Solid, Pasty and Powdered Vegetable Tannin Extracts
D6401 Test Method for Determining Non-Tannins and Tannin in Extracts of Vegetable Tanning Materials
D6403 Test Method for Determining Moisture in Raw and Spent Materials
D6404 Practice for Sampling Vegetable Materials Containing Tannin
D6405 Practice for Extraction of Tannins from Raw and Spent Materials
D6408 Test Method for Analysis of Tannery Liquors
2.2 ALCA Methods:
3
A30 Sugar in Tanning Materials
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 dextrose—d-glucose.
3.1.2 glucose—a simple sugar with formula C H O , and known to exist in d-, l-, and racemic forms. The term commonly
6 12 6
refers to the sweet, colorless, water-soluble dextrorotatory form that occurs widely in nature and is the usual form in which
carbohydrate is assimilated by animals. The term glucose can also refer to a light-colored syrup made from corn starch.
3.1.3 sugar—any of various water-soluble compounds that vary widely in sweetness and comprise the oligosaccharides
including sucrose.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 An analytical strength solution (that is, 4.00 6 0.25 g tannin per litre) of the tanning material is analyzed for reducing sugars
and total sugars by the Munson and Walker procedure.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is used to determine the quantity of sugar present in vegetable tanning materials or vegetable tannin
extracts. The amount of the reducing sugars, total sugars, and non-reducing sugars in a sample of material or extract can be
determined by this method.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D31 on Leather and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D31.01 on Vegetable Leather. This
method has been adapted from and is a replacement for Method A30 of the Official Methods of the American Leather Chemists Association.
Current edition approved April 1, 2009Nov. 1, 2014. Published July 2009December 2014. Originally approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 20042009 as
D6406 – 99 (2004).(2009). DOI: 10.1520/D6406-99R09.10.1520/D6406-99R14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Official Methods of the American Leather Chemists Association. Available from the American Leather Chemists Association, University of Cincinnati, P.O. Box 210014,
Cincinnati, OH 45221-0014.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6406 − 99 (2014)
5.2 Because of the possibility of errors in this test method it is essential that the method be followed exactly in order to obtain
reproducible results both among specimens within a laboratory and for analyses between laboratories.
6. Apparatus and Reagents
6.1 Saturated Solution of Normal Lead Acetate.
6.2 Dipotassium Hydrogen Phosphate, Anhydrous (K HPO ),dried in an oven at 100°C for 16 h then stored in a tightly
2 4
stoppered bottle.
6.3 Toluene, assay ≥ 99.5 %.
6.4 Fehling’s Solutions, A and B.
6.5 Hydrochloric Acid, concentrated (sp.gr. 1.18).
6.6 Kerosene, commercial grade.
6.7 Saturated Solution of Sodium Hydroxide.
6.8 Phenolphthalein Solution,
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.