ASTM D852-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Solidification Point of Benzene
Standard Test Method for Solidification Point of Benzene
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method may be used as a criteria for determining the purity of benzene. The closer the solidification point reaches that of pure benzene, the purer the sample.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the solidification point of benzene.
1.2 The following applies for the purposes of determining the conformance of the test results using this test method to applicable specifications, results shall be rounded off in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E29.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
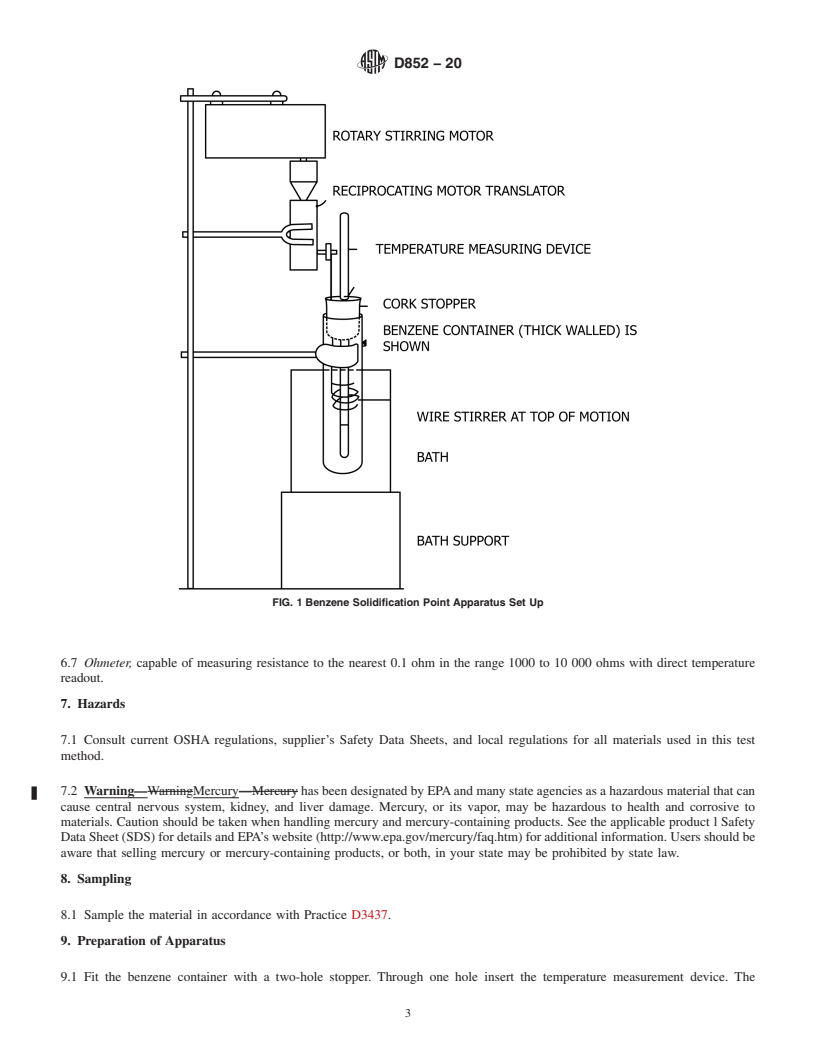
1.4 Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state or country may be prohibited by law.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 7.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D852 −20
Standard Test Method for
1
Solidification Point of Benzene
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D852; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the solidi- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
fication point of benzene. D1015 Test Method for Freezing Points of High-Purity
3
Hydrocarbons (Withdrawn 2019)
1.2 The following applies for the purposes of determining
D1016 Test Method for Purity of Hydrocarbons from Freez-
the conformance of the test results using this test method to
3
ing Points (Withdrawn 2019)
applicable specifications, results shall be rounded off in accor-
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
dance with the rounding-off method of Practice E29.
D3437 Practice for Sampling and Handling Liquid Cyclic
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Products
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
D6809 Guide for Quality Control and Quality Assurance
standard.
Procedures for Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Ma-
1.4 Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regu- terials
latory agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
demonstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to
Determine Conformance with Specifications
materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
and mercury containing products. See the applicable product
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional information. Users
2.2 Other Document:
should be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury contain-
OSHA Regulations, 29 CFR paragraphs 1910.1000 and
4
ing products into your state or country may be prohibited by
1910.1200
law.
3. Terminology
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 Definitions:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.1 solidification point, n—an empirical constant defined
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
as the temperature at which the liquid phase of a substance is
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
in approximate equilibrium with a relatively small portion of
For specific hazard statements, see Section 7.
the solid phase.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Solidification point is distinguished
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
from freezing point which is described in Test Method D1015.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
An interpretation of mol percent purity in terms of freezing
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
point is given in Test Method D1016.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Aromatic, Industrial, Specialty and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsi- the ASTM website.
3
bility of Subcommittee D16.01 on Benzene, Toluene, Xylenes, Cyclohexane and The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
Their Derivatives. www.astm.org.
4
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2020. Published October 2020. Originally AvailablefromU.S.GovernmentPrintingOfficeSuperintendentofDocuments,
approved in 1945. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D852 – 16. DOI: 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
10.1520/D0852-20. www.access.gpo.gov.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D852 − 20
FIG. 1 Benzene Solidification Point Apparatus Set Up
4. Summary of Test Method 6.3 Ice Bath, a 1-L beaker, or similar suitable container,
having an effective depth of at least 127 mm and filled with
4.1 S
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D852 − 16 D852 − 20
Standard Test Method for
1
Solidification Point of Benzene
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D852; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the solidification point of benzene.
1.2 In The following applies for the purposes of determining the conformance of the test results using this test method to
applicable specifications, results shall be rounded off in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E29.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 Warning—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause serious
medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should
be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for
additional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state or country
may be prohibited by law.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 7.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3
D1015 Test Method for Freezing Points of High-Purity Hydrocarbons (Withdrawn 2019)
3
D1016 Test Method for Purity of Hydrocarbons from Freezing Points (Withdrawn 2019)
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D3437 Practice for Sampling and Handling Liquid Cyclic Products
D6809 Guide for Quality Control and Quality Assurance Procedures for Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Materials
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic, Industrial, Specialty and Related Chemicals and is the direct
responsibility of Subcommittee D16.01 on Benzene, Toluene, Xylenes, Cyclohexane and Their Derivatives.
Current edition approved June 1, 2016Oct. 1, 2020. Published July 2016October 2020. Originally approved in 1945. Last previous edition approved in 20132016 as
D852 – 13.D852 – 16. DOI: 10.1520/D0852-16.10.1520/D0852-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D852 − 20
2.2 Other Document:
4
OSHA Regulations, 29 CFR paragraphs 1910.1000 and 1910.1200
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 solidification point, n—an empirical constant defined as the temperature at which the liquid phase of a substance is in
approximate equilibrium with a relatively small portion of the solid phase.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
Solidification point is distinguished from freezing point which is described in Test Method D1015. An interpretation of mol percent
purity in terms of freezing point is given in Test Method D1016.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Solidification point is measured by noting the maximum temperature reached during a controlled cooling cycle after the
appearance of
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.