ASTM D5580-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, p/m-Xylene, o-Xylene, C9 and Heavier Aromatics, and Total Aromatics in Finished Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, <emph type="ital"> p/m</emph>-Xylene, <emph type="ital">o</emph>-Xylene, C<inf>9</inf> and Heavier Aromatics, and Total Aromatics in Finished Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Regulations limiting the concentration of benzene and the total aromatic content of finished gasoline have been established for 1995 and beyond in order to reduce the ozone reactivity and toxicity of automotive evaporative and exhaust emissions. Test methods to determine benzene and the aromatic content of gasoline are necessary to assess product quality and to meet new fuel regulations.
5.2 This test method can be used for gasolines that contain oxygenates (alcohols and ethers) as additives. It has been determined that the common oxygenates found in finished gasoline do not interfere with the analysis of benzene and other aromatics by this test method.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, the xylenes, C9 and heavier aromatics, and total aromatics in finished motor gasoline by gas chromatography.
1.2 The aromatic hydrocarbons are separated without interferences from other hydrocarbons in finished gasoline. Nonaromatic hydrocarbons having a boiling point greater than n-dodecane may cause interferences with the determination of the C9 and heavier aromatics. For the C8 aromatics, p-xylene and m-xylene co-elute while ethylbenzene and o-xylene are separated. The C9 and heavier aromatics are determined as a single group.
1.3 This test method covers the following concentration ranges, in liquid volume %, for the preceding aromatics: benzene, 0.1 to 5 %; toluene, 1 to 15 %; individual C8 aromatics, 0.5 to 10 %; total C9 and heavier aromatics, 5 to 30 %, and total aromatics, 10 to 80 %.
1.4 Results are reported to the nearest 0.01 % by either mass or by liquid volume.
1.5 Many of the common alcohols and ethers that are added to gasoline to reduce carbon monoxide emissions and increase octane, do not interfere with the analysis. Ethers such as methyl tert-butylether (MTBE), ethyl tert-butylether (ETBE), tert-amylmethylether (TAME), and diisopropylether (DIPE) have been found to elute from the precolumn with the nonaromatic hydrocarbons to vent. Other oxygenates, including methanol and ethanol elute before benzene and the aromatic hydrocarbons. 1-Methylcyclopentene has also been found to elute from the precolumn to vent and does not interfere with benzene.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5580 − 13
StandardTest Method for
Determination of Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, p/m-
Xylene, o-Xylene, C and Heavier Aromatics, and Total
9
1
Aromatics in Finished Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5580; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
1.1 This test method covers the determination of benzene,
only.
toluene, ethylbenzene, the xylenes, C and heavier aromatics,
9
and total aromatics in finished motor gasoline by gas chroma- 1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
tography.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
1.2 The aromatic hydrocarbons are separated without inter-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ferences from other hydrocarbons in finished gasoline. Non-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
aromatic hydrocarbons having a boiling point greater than
n-dodecane may cause interferences with the determination of
2. Referenced Documents
the C and heavier aromatics. For the C aromatics, p-xylene
9 8
2
and m-xylene co-elute while ethylbenzene and o-xylene are 2.1 ASTM Standards:
separated. The C and heavier aromatics are determined as a
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API
9
single group. Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Prod-
ucts by Hydrometer Method
1.3 This test method covers the following concentration
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API
ranges, in liquid volume %, for the preceding aromatics:
Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
benzene, 0.1 to 5 %; toluene, 1 to 15 %; individual C
8
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
aromatics, 0.5 to 10 %; total C and heavier aromatics, 5 to
9
Petroleum Products
30 %, and total aromatics, 10 to 80 %.
D4307 Practice for Preparation of Liquid Blends for Use as
1.4 Resultsarereportedtothenearest0.01 %byeithermass
Analytical Standards
or by liquid volume.
E355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Relation-
1.5 Many of the common alcohols and ethers that are added ships
to gasoline to reduce carbon monoxide emissions and increase
octane,donotinterferewiththeanalysis.Etherssuchasmethyl
3. Terminology
tert-butylether (MTBE), ethyl tert-butylether (ETBE), tert-
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
amylmethylether (TAME), and diisopropylether (DIPE) have
3.1.1 aromatic—any organic compound containing a ben-
been found to elute from the precolumn with the nonaromatic
zene ring.
hydrocarbons to vent. Other oxygenates, including methanol
3.1.2 low-volume connector—aspecialunionforconnecting
and ethanol elute before benzene and the aromatic hydrocar-
two lengths of narrow bore tubing 1.6-mm (0.06-in.) outside
bons. 1-Methylcyclopentene has also been found to elute from
diameterandsmaller;sometimesthisisreferredtoaszerodead
the precolumn to vent and does not interfere with benzene.
volume union.
3.1.3 narrow bore tubing—tubing used to transfer compo-
nents prior to or after separation; usually 0.5-mm (0.02-in.)
inside diameter and smaller.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
2
Subcommittee D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 2013. Published October 2013. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D5580 – 02 (2007). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D5580-13. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
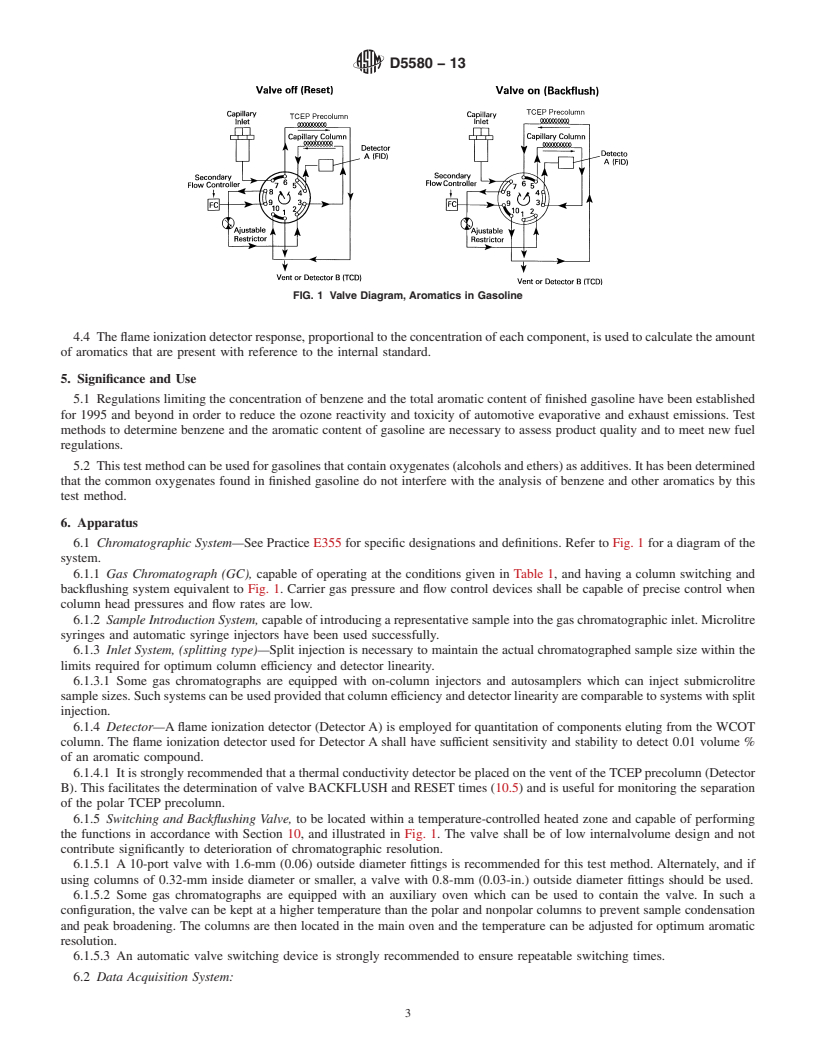
D5580 − 13
FIG. 1 Valve Diagram, Aromatics in Gasoline
3.1.4 split ratio—in capillary gas chromatography, the ratio o-xylene has eluted, the flow through the nonpolar WCOT
of the total flow of carrier gas to the sample inlet versus the columnisreversedtobackflushtheC andheavieraromaticsto
9
flow of the carrier gas to the capillary column, expressed by: the flame ionization detector.
split ratio 5 ~S1C!/C (1) 4.3 From the first analysis, the peak area
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5580 − 02 (Reapproved 2007) D5580 − 13
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, p/m-
Xylene, o-Xylene, C and Heavier Aromatics, and Total
9
1
Aromatics in Finished Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5580; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, the xylenes, C and heavier aromatics, and
9
total aromatics in finished motor gasoline by gas chromatography.
1.2 The aromatic hydrocarbons are separated without interferences from other hydrocarbons in finished gasoline. Nonaromatic
hydrocarbons having a boiling point greater than n-dodecane may cause interferences with the determination of the C and heavier
9
aromatics. For the C aromatics, p-xylene and m-xylene co-elute while ethylbenzene and o-xylene are separated. The C and
8 9
heavier aromatics are determined as a single group.
1.3 This test method covers the following concentration ranges, in liquid volume %, for the preceding aromatics: benzene, 0.1
to 5 %; toluene, 1 to 15 %; individual C aromatics, 0.5 to 10 %; total C and heavier aromatics, 5 to 30 %, and total aromatics,
8 9
10 to 80 %.
1.4 Results are reported to the nearest 0.01 % by either mass or by liquid volume.
1.5 Many of the common alcohols and ethers that are added to gasoline to reduce carbon monoxide emissions and increase
octane, do not interfere with the analysis. Ethers such as methyl tert-butylether (MTBE), ethyl tert-butylether (ETBE),
tert-amylmethylether (TAME), and diisopropylether (DIPE) have been found to elute from the precolumn with the nonaromatic
hydrocarbons to vent. Other oxygenates, including methanol and ethanol elute before benzene and the aromatic hydrocarbons.
1-Methylcyclopentene has also been found to elute from the precolumn to vent and does not interfere with benzene.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2007Sept. 15, 2013. Published January 2008 October 2013. Originally approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 20022007
as D5580D5580 – 02 (2007).–02. DOI: 10.1520/D5580-02R07.10.1520/D5580-13.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5580 − 13
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products by
Hydrometer Method
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4307 Practice for Preparation of Liquid Blends for Use as Analytical Standards
E355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Relationships
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 aromatic—any organic compound containing a benzene ring.
3.1.2 low-volume connector—a special union for connecting two lengths of narrow bore tubing 1.6-mm (0.06-in.) outside
diameter and smaller; sometimes this is referred to as zero dead volume union.
3.1.3 narrow bore tubing—tubing used to transfer components prior to or after separation; usually 0.5-mm (0.02-in.) inside
diameter and smaller.
3.1.4 split ratio—in capillary gas chromatography, the ratio of the total flow of carrier gas to the sample inlet versus the flow
of the carrier gas to the capillary column, expressed by:
split ratio 5 S1C /C (1)
~ !
where:
S = flow rate at the splitter vent and
C = flow rate at the column ou
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.