ASTM D1822-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining the Tensile-Impact Resistance of Plastics
Standard Test Method for Determining the Tensile-Impact Resistance of Plastics
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Tensile-impact energy is the energy required to break a standard tension-impact specimen in tension by a single swing of a standard calibrated pendulum under a set of standard conditions (see Note 2). To compensate for the minor differences in cross-sectional area of the specimens, the energy to break is normalized to units of kilojoules per square metre (or foot-pounds-force per square inch) of minimum cross-sectional area. An alternative approach to normalizing the impact energy that compensates for these minor differences and still retains the test unit as joules (foot-pounds) is shown in Section 10. For a perfectly elastic material, the impact energy is usually reported per unit volume of material undergoing deformation. However, since much of the energy to break the plastic materials for which this test method is written is dissipated in drawing of only a portion of the test region, such normalization on a volume basis is not feasible. In order to observe the effect of elongation or rate of extension, or both, upon the result, the test method permits two specimen geometries. Results obtained with different capacity machines generally are not comparable.
5.1.1 With the Type S (short) specimen the extension is comparatively low, while with the Type L (long) specimen the extension is comparatively high. In general, the Type S specimen (with its greater occurrence of brittle fracture) gives greater reproducibility, but less differentiation among materials.
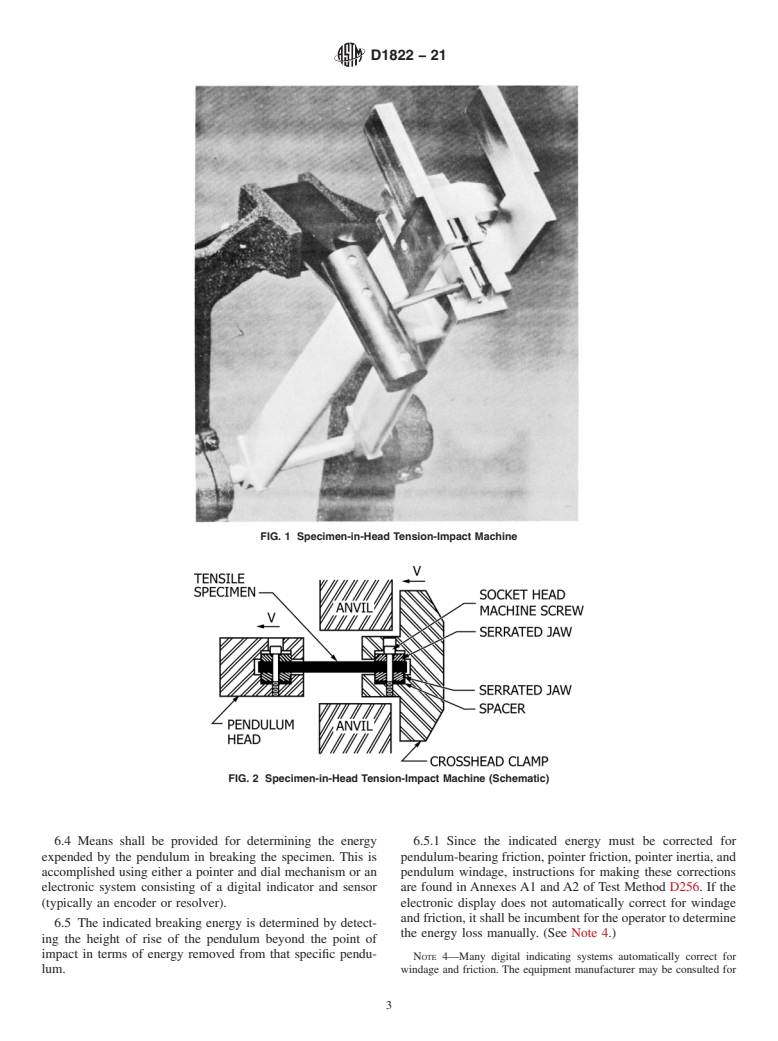
Note 2: Friction losses are largely eliminated by careful design and proper operation of the testing machine.
5.2 Scatter of data is sometimes attributed to different failure mechanisms within a group of specimens. Some materials exhibit a transition between different failure mechanisms. If so, the elongation will be critically dependent on the rate of extension encountered in the test. The impact energy values for a group of such specimens will have an abnormally large dispersion.
5.2.1 Some mater...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the energy required to rupture standard tension-impact specimens of plastic materials. Rigid materials are suitable for testing by this method as well as specimens that are too flexible or thin to be tested in accordance with other impact test methods.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
Note 1: This test method and ISO 8256 address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D1822 − 21
Standard Test Method for
1
Determining the Tensile-Impact Resistance of Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1822; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D6988GuideforDeterminationofThicknessofPlasticFilm
Test Specimens
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the energy
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
required to rupture standard tension-impact specimens of
ASTM Test Methods
plasticmaterials.Rigidmaterialsaresuitablefortestingbythis
E456Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
method as well as specimens that are too flexible or thin to be
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
tested in accordance with other impact test methods.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
2.2 ISO Standards:
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
ISO 8256 Plastics—Determination of Tensile-Impact
only.
Strength
NOTE 1—This test method and ISO 8256 address the same subject
3. Terminology
matter, but differ in technical content.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 3.1 Definitions—Terms used in this standard are defined in
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the accordance with Terminology D883, unless otherwise speci-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- fied. For terms relating to precision and bias and associated
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- issues,thetermsusedinthisstandardaredefinedinaccordance
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. with Terminology E456.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
4. Summary of Test Method
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.1 The energy utilized in this test method is delivered by a
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
single swing of a calibrated pendulum of a standardized
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
tension-impactmachine.Theenergytofractureaspecimen,by
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
shock in tension, is determined by the kinetic energy extracted
from the pendulum of the impact machine in the process of
2. Referenced Documents
breakingthespecimen.Oneendofthespecimenismountedin
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: the pendulum. The other end of the specimen is gripped by a
crosshead which travels with the pendulum until the instant of
D256Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum
impact (and instant of maximum pendulum kinetic energy),
Impact Resistance of Plastics
when the crosshead is arrested.
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D638Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
5. Significance and Use
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
D4000Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materi- 5.1 Tensile-impact energy is the energy required to break a
als standard tension-impact specimen in tension by a single swing
D5947Test Methods for Physical Dimensions of Solid of a standard calibrated pendulum under a set of standard
Plastics Specimens conditions (see Note 2). To compensate for the minor differ-
ences in cross-sectional area of the specimens, the energy to
break is normalized to units of kilojoules per square metre (or
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD20onPlastics
foot-pounds-forcepersquareinch)ofminimumcross-sectional
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.10 on Mechanical Properties.
area.Analternativeapproachtonormalizingtheimpactenergy
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2021. Published November 2021. Originally
that compensates for these minor differences and still retains
approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D1822-13.
DOI:10.1520/D1822–21.
thetestunitasjoules(foot-pounds)isshowninSection10.For
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
a perfectly elastic material, the impact energy is usually
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
reported per unit volume of material undergoing deformation.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. DOI: 10.1520/D1822-06. However, since much of the energy to break the plastic
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this st
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D1822 − 13 D1822 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Tensile-Impact Energy to Break Plastics and Electrical
Insulating MaterialsDetermining the Tensile-Impact
1
Resistance of Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1822; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the energy required to rupture standard tension-impact specimens of plastic or
electrical insulating materials. Rigid materials are suitable for testing by this method as well as specimens that are too flexible or
thin to be tested in accordance with other impact test methods.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
NOTE 1—This test method and ISO 8256 address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems,concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D256 Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materials
D5947 Test Methods for Physical Dimensions of Solid Plastics Specimens
D6988 Guide for Determination of Thickness of Plastic Film Test Specimens
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 8256 Plastics—Determination of Tensile-Impact Strength
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.10 on Mechanical Properties.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2013Oct. 1, 2021. Published November 2013November 2021. Originally approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 20062013
as D1822 - 06.D1822 - 13. DOI:10.1520/D1822–13.DOI:10.1520/D1822–21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website. DOI: 10.1520/D1822-06.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1822 − 21
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of terms applying to this test method appear in Terms used in this standard are defined in accordance
with Terminology D883, unless otherwise specified. For terms relating to precision and bias and associated issues, the terms used
in this standard are defined in accordance with Terminology E456.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The energy utilized in this test method is delivered by a single swing of a calibrated pendulum of a standardized tension-impact
machine. The energy to fracture a specimen, by shock in tension, is determined by the kinetic energy extracted from the pendulum
of the impact machine in the process of breaking the specimen. One end of the specimen is mounted in the pendulum. The other
end of the specimen is gripped by a crosshead which travels with the pendulum until the instant of impact (and instant of maximum
pendulum kinetic energy), when the crosshead is arrested.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Tensile-impact energy is the energy required to break a standard tension-impact specimen in tension by a single swing of a
standard calibrat
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.