ASTM D4986-98
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Horizontal Burning Characteristics of Cellular Polymeric Materials
Standard Test Method for Horizontal Burning Characteristics of Cellular Polymeric Materials
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes a small-scale apparatus test procedure for comparing the relative rate of burning and the extent and time of burning of cellular polymeric materials.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This test method should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response to heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of this test method may be used as elements of a fire risk assessment which then takes into account all of the factors that are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard and of a particular end use.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific hazard statement, see Note 1.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4986 – 98
Standard Test Method for
Horizontal Burning Characteristics of Cellular Polymeric
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4986; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (ϵ) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* Burning Characteristics of Small Specimens Subjected to
a Small Flame
1.1 This fire-test-response test method describes a small-
scale horizontally oriented burning test procedure for compar-
3. Terminology
ing the relative rate of burning and the extent and time of
3.1 Definitions—Fordefinitionsoffire-relatedtermsusedin
burning of cellular polymeric materials having a density less
this test method, refer to Terminology E 176E 176.
than 250 kg/m .
3.2 afterflame time, n—the length of time for which a
1.2 The classification system described in theAppendix X1
material continues to flame, under specified conditions, after
is intended for quality assurance and the preselection of
the ignition source has been removed.
component materials for products.
3.3 afterglow time, n—the length of time for which a
1.3 This standard measures and describes the response of
materialcontinuestoglowunderspecifiedtestconditions,after
materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under
the ignition source has been removed or cessation of flaming,
controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all
or both.
factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the
3.4 flame, vb—to undergo combustion in the gaseous phase
materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
with emission of light.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.5 glow, n—visible light, other than from flaming, emitted
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
by a solid undergoing combustion.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4. Summary of Test Method
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific
4.1 This test method for measuring the burning characteris-
hazard statement, see Note 2.
tics of cellular polymeric materials employs a small standard
NOTE 1—This test method and ISO 9772 are equivalent.
test specimen 50 by 150 mm. The specimen is supported
horizontally. One end is exposed to a specified gas flame for 60
2. Referenced Documents
s and the extent of burning is measured.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 4483 Practice for Determining Precision for Test Method 5. Significance and Use
Standards in the Rubber and Carbon Black Industries
5.1 This test method provides a means of measuring the
D 5025 Specification for Laboratory Burner Used for
time and extent of burning for cellular polymeric materials. It
Small-Scale Burning Tests on Plastic Materials
also provides a means of measuring burning rates for materials
E 176 Terminology to Fire Standards
that continue to burn past the specified gage marks.
E 437 Specification for Industrial Wire Cloth and Screens
5.2 This test method provides a means of comparing the
(Square Opening Series)
burning characteristics of materials of like thickness density,
2.2 ISO Standard:
cell size, and skin irregularities, including the effect of falling
ISO 9772 Cellular Plastics—Determination of Horizontal
particles of cellular polymeric materials. It may be used for
quality control, specification acceptance, and for research and
development. Such materials may be filled or reinforced, rigid
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD-20onPlastics
or flexible, cut or formed.
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.30 on Thermal Properties.
5.3 In this test method, the specimens are subjected to one
Current edition approved July 10, 1998. Published January 1999. Originally
published as D 4986 – 89. Last previous edition D 4986 – 95.
ormorespecificsetsoflaboratoryfiretestexposureconditions.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.03.
4 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.07. Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd Street, 13th
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 4986 – 98
If different test conditions are substituted or if the anticipated 6.6 Support Fixture—Any fixture that will support the wire
end-use conditions are changed, it may not be possible from cloth horizontally, 136 1 mm above the burner wing top and
this test method to predict changes in the performance charac- 1756 25 mm above the base of the test chamber. Fig. 2 shows
teristics measured. Therefore, the results are strictly valid only one acceptable arrangement.
forthefiretestexposureconditionsdescribedinthisprocedure. 6.7 Timing Device(s)—Accurate to 61s.
5.4 This test method is not intended to be a criterion for fire 6.8 Linear Measuring Device—Graduated in millimeters.
hazard. The fire hazard created by materials depends upon the 6.9 Cotton—A supply of dry, absorbent 100 % cotton.
form and end use of the material. Assessment of fire hazard 6.10 Desiccator—Containing a suitable drying agent, ca-
includes, but is not limited to, many factors such as flame pable of maintaining a relative humidity not exceeding 20 % at
spread, burning rate, ease of ignition, fuel contribution, heat 236 2°C.
evolution, products of combustion, and others. 6.11 Conditioning Room or Chamber—Capable of being
maintained at 236 2°C and a relative humidity of 5065%.
6. Apparatus 6.12 Conditioning Oven—A full-draft circulating air oven
capable of being maintained at 706 2°C.
6.1 Test Chamber—A laboratory hood free of induced or
6.13 Dial Gage Micrometer—For measuring thicknesses
forced draft during test. The hood shall be totally enclosed,
with a 650-mm pressure ft exerting a pressure of
with a heat-resistant transparent window for observing the test.
0.1756 0.035 kPa.
Alternatively, the test may be conducted in a cabinet placed
inside the hood. The cabinet should be constructed of noncom-
7. Test Specimen
bustible materials and should have a transparent window for
7.1 Thestandardtestspecimenshallbe1506 10by506 1
observing the test. The cabinet must provide adequate ventila-
mm, in the thickness appropriate to the objectives of the
tion for characteristic burning, but must not allow drafts across
determination. Specimens tested in accordance with this test
the burning specimen; therefore, a suitable damper may be
method are limited to a maximum thickness of 13 mm.
necessary.
Materials supplied in thicknesses over 13 mm, shall be cut to
6.2 Laboratory Burner—Burner shall be constructed in
136 1 mm thickness with the skin on one side.
accordance with Specification D 5025D 5025.
7.2 The surfaces of the specimen must be smooth and
6.3 Wing Top—Wing top, having an opening 4861mmin
unbroken. Any loose particles shall be removed. The corner
lengthby1.36 0.05mminwidthfittedtotheburner.(SeeFig.
radius must not exceed 1.3 mm. Specimens with skin shall be
1.)
tested skin side down.
6.4 Gas Supply—Methane gas, technical grade or natural
7.3 Fivespecimensper typeof conditioningaretobetested,
gas having a heat content of 376 1 MJ/m with suitable
ten specimens in all.
regulator and meter for uniform gas flow.
6.5 Wire Cloth—Low-carbon, plain, steel wire, 6.4-mm
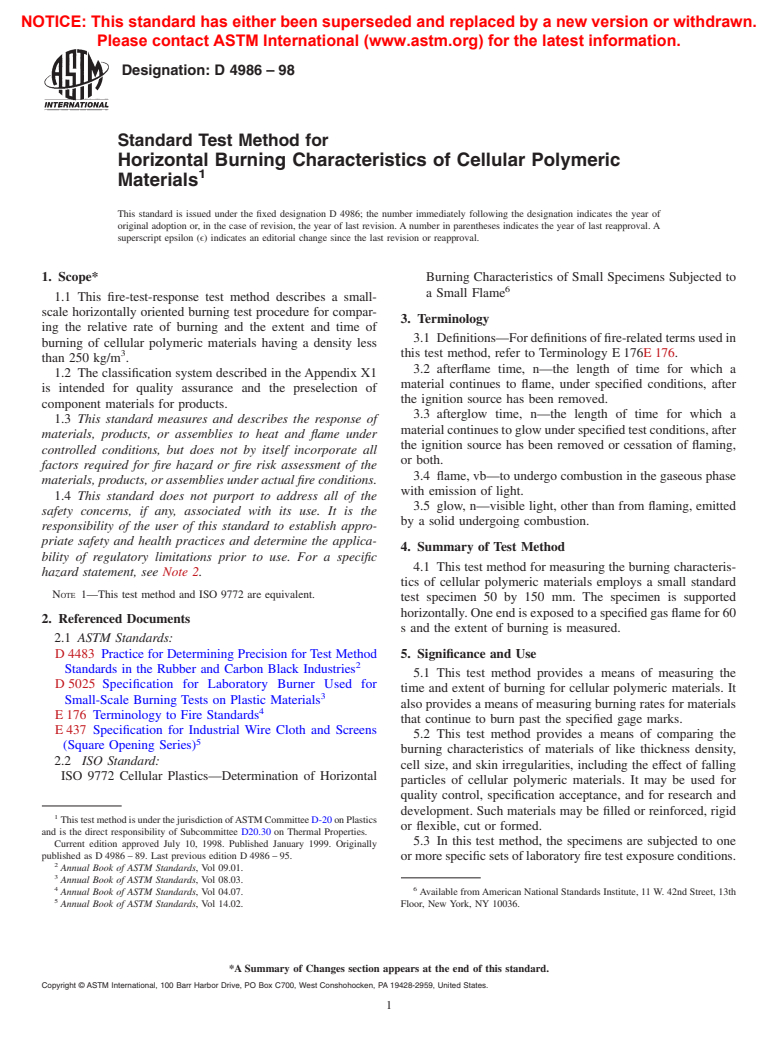
8. Conditioning
mesh of 0.906 0.05-mm wire diameter. The cloth mesh and
wire diameter shall be determined in accordance with Specifi- 8.1 Condition specimen sets as follows:
cationE 437E 437,AppendixX3.Thewireclothshallbecutto 8.1.1 Condition one set of five specimens for at least 48 h at
approximately 215 by 75 mm and shall be formed to provide a atemperatureof236 2°Candarelativehumidityof5065%
90° bend at one end, 13 mm high. (See Fig. 1.) prior to testing.
NOTE—Dimensions in millimetres.
FIG. 1 Test Specimen and Specimen Support Gauze
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 4986 – 98
FIG. 2 Support Gauze Holder
8.1.2 Condition a second set of five specimens in a circu-
lating air oven for 16862hat706 2°C, and then cool in a
desiccator for at least4hat room temperature prior to testing.
8.2 All specimens shall be tested in a laboratory atmosphere
of 15 to 35°C and 45 to 75 % relative humidity.
9. Procedure
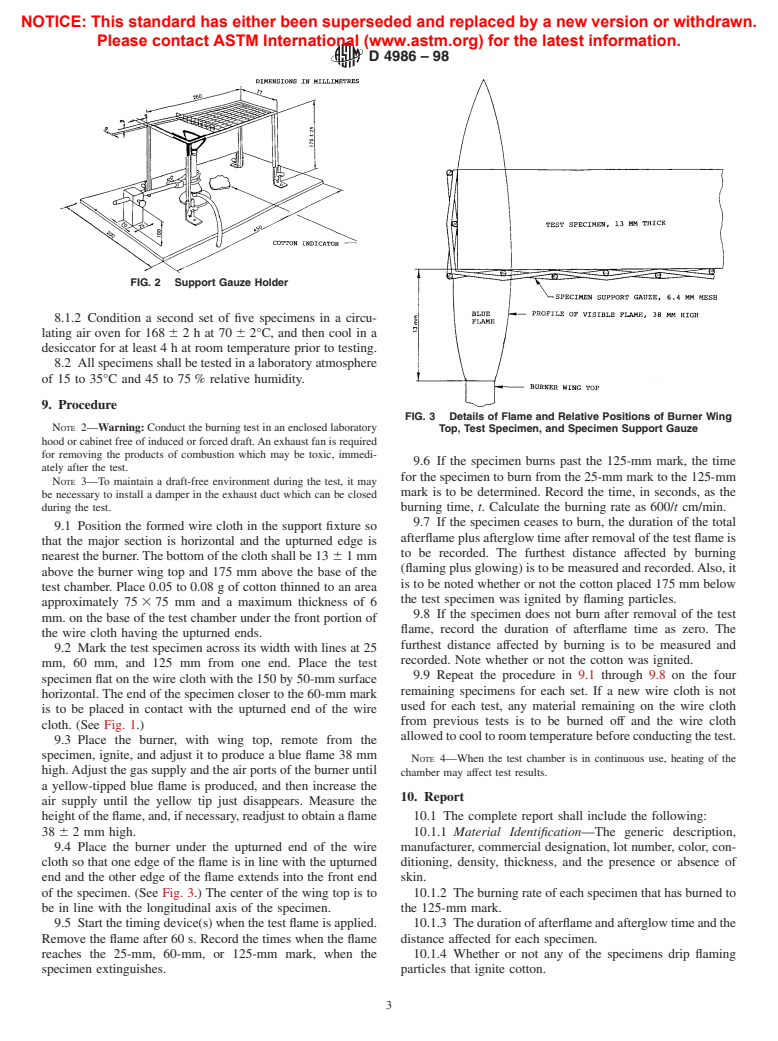
FIG. 3 Details of Flame and Relative Positions of Burner Wing
NOTE 2—Warning: Conduct the burning test in an enclosed laboratory Top, Test Specimen, and Specimen Support Gauze
hood or cabinet free of induced or forced draft.An exhaust fan is required
for removing the products of combustion which may be toxic, immedi-
9.6 If the specimen burns past the 125-mm mark, the time
ately after the test.
for the specimen to burn from the 25-mm mark to the 125-mm
NOTE 3—To maintain a draft-free environment during the test, it may
mark is to be determined. Record the time, in seconds, as the
be necessary to install a damper in the exhaust duct which can be closed
during the test. burning time, t. Calculate the burning rate as 600/t cm/min.
9.7 If the specimen ceases to burn, the duration of the total
9.1 Position the formed wire cloth in the support fixture so
afterflame plus afterglow time after removal of the test flame is
that the major section is horizontal and the upturned edge is
to be recorded. The furthest distance affected by burning
nearest the burner.The bottom of the cloth shall be 1361mm
(flaming plus glowing) is to be measured and recorded.Also, it
above the burner wing top and 175 mm above the base of the
is to be noted whether or not the cotton placed 175 mm below
test chamber. Place 0.05 to 0.08 g of cotton thinned to an area
the test specimen was ignited by flaming particles.
approximately 753 75 mm and a maximum thickness of 6
9.8 If the specimen does not burn after removal of the test
mm. on the base of the test chamber under the front portion of
flame, record the duration of afterflame time as zero. The
the wire cloth having the upturned ends.
furthest distance affected by burning is to be measured and
9.2 Mark the test specimen across its width with lines at 25
recorded. Note whether or not the cotton was ignited.
mm, 60 mm, and 125 mm from one end. Place the test
9.9 Repeat the procedure in 9.1 through 9.8 on the four
specimen flat on the wire cloth with the 150 by 50-mm surface
remaining specimens for each set. If a new wire cloth is not
horizontal. The end of the specimen closer to the 60-mm mark
used for each test, any material remaining on the wire cloth
is to be placed in contact with the upturned end of the wire
from previous tests is to be burned off and the wire cloth
cloth. (See Fig. 1.)
allowedtocooltoroomtemperaturebeforeconductingthetest.
9.3 Place the burner, with wing top, remote from the
specimen, ignite, and adjust it to produce a blue flame 38 mm
NOTE 4—When the test chamber is in continuous use, heating of the
high.Adjust the gas supply and the air ports of the burner until
chamber may affect test results.
a yellow-tipped blue flame is produced, and then increase the
10. Report
air supply until the yellow tip just disappears. Measure the
height of the flame, and, if necessary, readjust to obtain a flame 10.1 The complete report shall include the following:
386 2 mm high. 10.1.1 Material Identification—The generic description,
9.4 Place the burner under the upturned end of the wire manufacturer, commercial designation, lot number, color, con-
cloth so that one edge of the flame is in line with the upturned ditioning, density, thickness, and the presence or absence of
end and the other edge of the flame extends into the front end skin.
of the specimen. (See Fig. 3.) The center of the wing top is to 10.1.2 The burning rate of each specimen that has burned to
be in line with the longitudinal axis of the specimen. the 125-mm mark.
9.5 Start the timing device(s) when the test flame is applied. 10.1.3 Thedurationofafterflameandafterglowtimeandthe
Remove the flame after 60 s. Record the times when the flame distance affected for each specimen.
reaches the 25-mm, 60-mm, or 125-mm mark, when the 10.1.4 Whether or not any of the specimens drip flaming
specimen extinguishes. particles that ignite cotton.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 4986 – 98
10.1.5 Note any unusual burning phenomena, such as war- 11.2.3 All materials were prescreened for properties by one
page, shrinkage, melting, or other atypical responses. laboratory and then forwarded to a second laboratory. The
10.1.6 The statement: These data describe the response of second laboratory prepared all samples for testing and distrib-
materials to heat and flame under controlled laboratory condi- uted them to the other participating laboratories. The test
tions and should not be used for the appraisal or regulation of specimens only had to be conditioned in accordance with this
the fire hazards associated with them under actual fire condi- test method prior to actual testing.
tions. 11.2.4 Material testing order was randomized.
10.1.7 Ifthematerialwillbeclassified,indicatethecategory 11.2.5 The results of the precision calculations for repeat-
designation from the classification system in Appendix X1. ability and reproducibility are given in Table 1.
11.2.6 Repeatability—The repeatability, r, of this test
11. Precision and Bias
method has been established in Table 1. Two single test results
11.1 An interlaboratory test program was conducted to
obtained within one laboratory that differ by more than this
obtain precision data for this test method. Both precision and tabulated r (for any given material) must be considered to have
bias sections were prepared in accordance with Practice
come from different or nonidentical sample populations.
D 4483D 4483.
11.2.7 Reproducibility—The reproducibility, R, of this test
11.2 Test Method: method has been established in Table 1. Two single test results
11.2.1 The interlaboratory program was a Type 1 precision
obtained in different laboratories that dif
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.