ASTM D178-22
(Specification)Standard Specification for Rubber Insulating Matting
Standard Specification for Rubber Insulating Matting
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the acceptance testing of insulating rubber matting that are used as a floor covering for the personal protection of workers. The sheeting shall be made from any elastomer or combination of elastomeric compounds. Two types of matting, differing in chemical and physical characteristics, are provided and are designated as Type I, which has been properly vulcanized, and Type II, which has one or more of the following special properties: (A) ozone resistance; (B) flame resistance; and (C) oil resistance. Five classes of matting, designated as Classes 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4, are assigned according to electrical protection characteristics. When evaluated in accordance with the test procedures detailed herein, the matting shall adhere to the following property requirements: electrical properties such as phase-phase maximum use voltage, AC and DC proof-test voltages, AC and DC dielectric breakdown test voltages, and AC and DC electrode clearances; an physical and chemical properties such as moisture absorption, oil resistance, tensile strength, tension set, elongation, resistance to accelerated heat aging, and flame resistance.
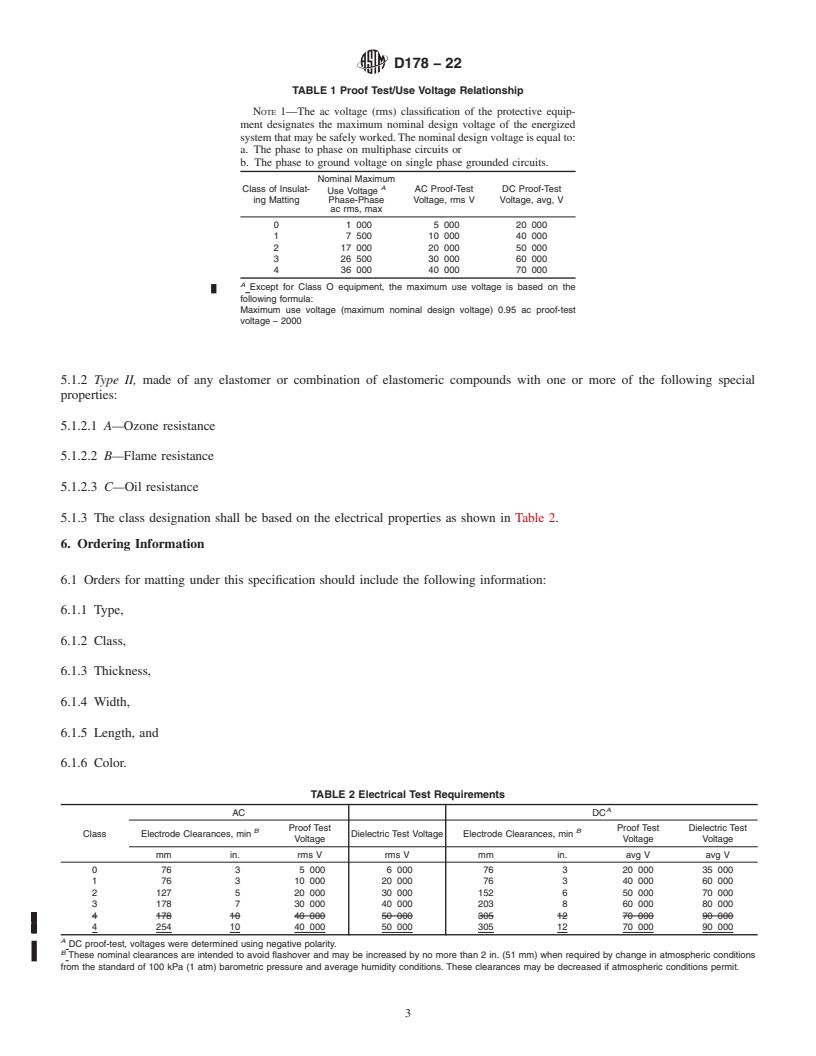
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
X1.3 Significance and Use
X1.3.1 Tests made on a cellular plastic under conditions herein prescribed can be of considerable value in comparing the rate of burning and/or extent and time of burning of different materials, in controlling manufacturing processes, or as a measure of deterioration or change in burning characteristics prior to or during use.
X1.3.2 This test method is not intended to be a criterion for fire hazard. The fire hazard created by materials depends upon the form and end use of the material. Assessment of fire hazard includes, but is not limited to, many factors, such as, ease of ignition, burning rate, flame spread, fuel contribution, intensity of burning, and products of combustion.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers acceptance testing of rubber insulating matting for use as a floor covering for protection of workers.
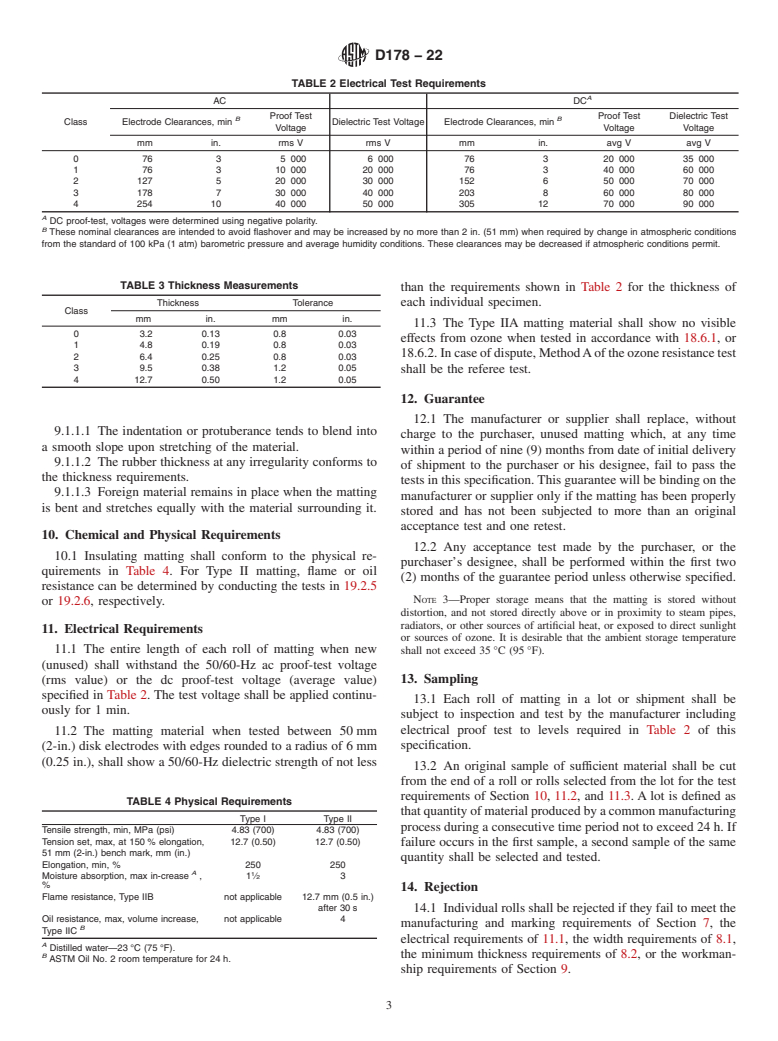
1.2 Two types of matting, differing in chemical and physical characteristics, are provided and are designated as Type I and Type II matting.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat applies only to the test method portion, Sections 17 to 19, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1: Rubber insulating matting should remain flexible for use through normal temperature ranges.
Note 2: Rubber as used in this specification is a generic term that includes elastomers and elastomer compounds, regardless of origin.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D178 −22
Standard Specification for
1
Rubber Insulating Matting
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D178; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope D412 Test Methods forVulcanized Rubber andThermoplas-
tic Elastomers—Tension
1.1 This specification covers acceptance testing of rubber
D471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
insulating matting for use as a floor covering for protection of
D518 Test Method for Rubber Deterioration—Surface
workers.
3
Cracking (Withdrawn 2007)
1.2 Twotypesofmatting,differinginchemicalandphysical
D570 Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics
characteristics, are provided and are designated as Type I and
D573 Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air
Type II matting.
Oven
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat applies only to the
D1692 Method of Test for Rate of Burning or Extent and
test method portion, Sections 17 to 19, of this specification: Time of Burning of Cellular Plastics Using a Specimen
3
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety
Supported by a Horizontal Screen (Withdrawn 1976)
4
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
2.2 American National Standard:
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety,
ANSIC84.1 VoltageRatingsforElectricPowerSystemsand
health, and environmental practices and determine the appli- Equipment (60 Hz)
cability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3. Terminology
NOTE 1—Rubber insulating matting should remain flexible for use
3.1 Definitions:
through normal temperature ranges.
NOTE 2—Rubber as used in this specification is a generic term that 3.1.1 user, n—as used in 4.3.1, the entity employing the
includes elastomers and elastomer compounds, regardless of origin.
actual worker(s) utilizing the equipment; if no separate
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor- employer, then the individual.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.2 voltage, maximum retest, n—voltage, either ac rms or
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
dc avg, which is equal to the proof-test voltage for new
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
protective equipment.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.1.3 voltage, retest, n—voltage, either ac rms or dc avg,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
that used protective equipment must be capable of withstand-
2. Referenced Documents ing for a specified test period without breakdown.
2
3.1.4 voltage, nominal design, n—a nominal value consis-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tent with the latest revision of ANSI C84.1, assigned to the
D149 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and
circuit or system for the purpose of conveniently designating
DielectricStrengthofSolidElectricalInsulatingMaterials
its voltage class.
at Commercial Power Frequencies
D297 Test Methods for Rubber Products—ChemicalAnaly-
3.1.5 voltage, maximum use, n—the ac voltage (rms) clas-
sis
sification of the protective equipment that designates the
maximum nominal design voltage of the energized system that
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F18 on
may be safely worked. The nominal design voltage is equal to
Electrical Protective Equipment for Workers and is the direct responsibility of
phase-to-phase voltage on multiphase circuits.
Subcommittee F18.25 on Insulating Cover-Up Equipment. This standard replaces
3.1.5.1 If there is no multiphase exposure in a system area,
ANSI Standard J 6.7, which is no longer available.
and the voltage exposure is limited to phase (polarity on dc
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2022. Published January 2023. Originally
approved in 1923. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as D178 – 19. DOI:
10.1520/D0178-22.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.astm.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshoh
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D178 − 19 D178 − 22
Standard Specification for
1
Rubber Insulating Matting
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D178; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers acceptance testing of rubber insulating matting for use as a floor covering for protection of workers.
1.2 Two types of matting, differing in chemical and physical characteristics, are provided and are designated as Type I and Type
II matting.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat applies only to the test method portion, Sections 17 to 19, of this specification: This
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—Rubber insulating matting should remain flexible for use through normal temperature ranges.
NOTE 2—Rubber as used in this specification is a generic term that includes elastomers and elastomer compounds, regardless of origin.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D149 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and Dielectric Strength of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials at
Commercial Power Frequencies
D297 Test Methods for Rubber Products—Chemical Analysis
D412 Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers—Tension
D471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
3
D518 Test Method for Rubber Deterioration—Surface Cracking (Withdrawn 2007)
D570 Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics
D573 Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air Oven
D1692 Method of Test for Rate of Burning or Extent and Time of Burning of Cellular Plastics Using a Specimen Supported by
3
a Horizontal Screen (Withdrawn 1976)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F18 on Electrical Protective Equipment for Workers and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F18.25 on Insulating Cover-Up Equipment. This standard replaces ANSI Standard J 6.7, which is no longer available.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2019Dec. 1, 2022. Published February 2019January 2023. Originally approved in 1923. Last previous edition approved in 20102019 as
D178 – 01D178 – 19.(2010). DOI: 10.1520/D0178-19. 10.1520/D0178-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D178 − 22
4
2.2 American National Standard:
ANSI C84.1 Voltage Ratings for Electric Power Systems and Equipment (60 Hz)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 user, n—as used in 4.3.1, the entity employing the actual worker(s) utilizing the equipment; if no separate employer, then
the individual.
3.1.2 voltage, maximum retest, n—voltage, either ac rms or dc avg, which is equal to the proof-test voltage for new protective
equipment.
3.1.3 voltage, retest, n—voltage, either ac rms or dc avg, that used protective equipment must be capable of withstanding for a
specified test period without breakdown.
3.1.4 voltage, nominal design, n—a nominal value consistent with the latest revision of ANSI C84.1, assigned to the circuit or
system for the purpose of conveniently designating its voltage class.
3.1.5 voltage, maximum use, n—the ac voltage (rms) classification of the protective equipment that designates the maximum
nominal design voltage of the energized system that may be safely worked. The nominal design voltage is
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.