ASTM A266/A266M-03a(2008)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Carbon Steel Forgings for Pressure Vessel Components
Standard Specification for Carbon Steel Forgings for Pressure Vessel Components
ABSTRACT
This specification covers four grades of carbon steel forgings for boiler and pressure vessel components, and associated equipment. Materials shall be manufactured by melting process and hot-worked forging. Heat and product analyses shall be performed wherein forgings shall conform to chemical requirements for carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulphur, and silicon. Mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and reduction of area shall be inspected as well. The requirements for annealed, normalized, or normalized and tempered steel forgings, and that for quenched and tempered steel forgings have been specified separately.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers four grades of carbon steel forgings for boilers, pressure vessels, and associated equipment.
Note 1—Designations have been changed as follows: Current
Formerly
Grade 1Class 1 Grade 2Class 2 Grade 3Class 3 Grade 4Class 4
1.2 Supplementary requirements are provided for use when additional testing or inspection is desired. These shall apply only when specified individually by the purchaser in the order.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-pound units.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A266/A266M – 03a (Reapproved 2008)
Standard Specification for
Carbon Steel Forgings for Pressure Vessel Components
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA266/A266M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
2 E165 PracticeforLiquidPenetrantExaminationforGeneral
1.1 This specification covers four grades of carbon steel
Industry
forgings for boilers, pressure vessels, and associated equip-
E381 Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets,
ment.
Blooms, and Forgings
NOTE 1—Designations have been changed as follows:
2.2 Other Standard:
Current Formerly
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX, Weld-
Grade 1 Class 1
ing Qualifications
Grade 2 Class 2
Grade 3 Class 3
Grade 4 Class 4 3. Ordering Information and General Requirements
1.2 Supplementary requirements are provided for use when 3.1 In addition to the ordering information required by
additional testing or inspection is desired. These shall apply
Specification A788/A788M, the purchaser shall include with
only when specified individually by the purchaser in the order. the inquiry and order a detailed drawing, sketch, or written
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
description of the forging.
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in 3.2 Material supplied to this specification shall conform to
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
the requirements of Specification A788/A788M, which out-
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining lines additional ordering information, manufacturing require-
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
ments, testing and retesting methods and procedures, marking,
with the standard. certification,productanalysisvariations,andadditionalsupple-
1.4 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specifica-
mentary requirements.
tion designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch- 3.3 If the requirements of this specification are in conflict
pound units. with the requirements of Specification A788/A788M, the
requirements of this specification shall prevail.
2. Referenced Documents
3.4 For hubbed flanges and tube sheets ordered for ASME
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code application, Supplementary
A275/A275M Practice for Magnetic Particle Examination
RequirementS12ofSpecificationA788/A788Mshallbespeci-
of Steel Forgings
fied in addition to Supplementary Requirement S8 of this
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
specification.
of Steel Products
4. Materials and Manufacture
A788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Re-
quirements 4.1 The steel shall be made in accordance with the Melting
Process Section of Specification A788/A788M. A sufficient
discard shall be made to secure freedom from injurious pipe
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
and undue segregation.
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
4.2 The material shall be forged as close as practical to the
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets.
Current edition approved March 1, 2008. Published April 2008. Originally
specified shape and size.
approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as A266/A266M – 03a.
4.3 The finished product shall be a hot-worked forging as
DOI: 10.1520/A0266_A0266M-03AR08.
defined by Specification A788/A788M.
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specifi-
cation SA–266/ SA–266M in Section II of that code.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnual Book ofASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 345 East 47th
the ASTM website. St., New York, NY 10017.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A266/A266M – 03a (2008)
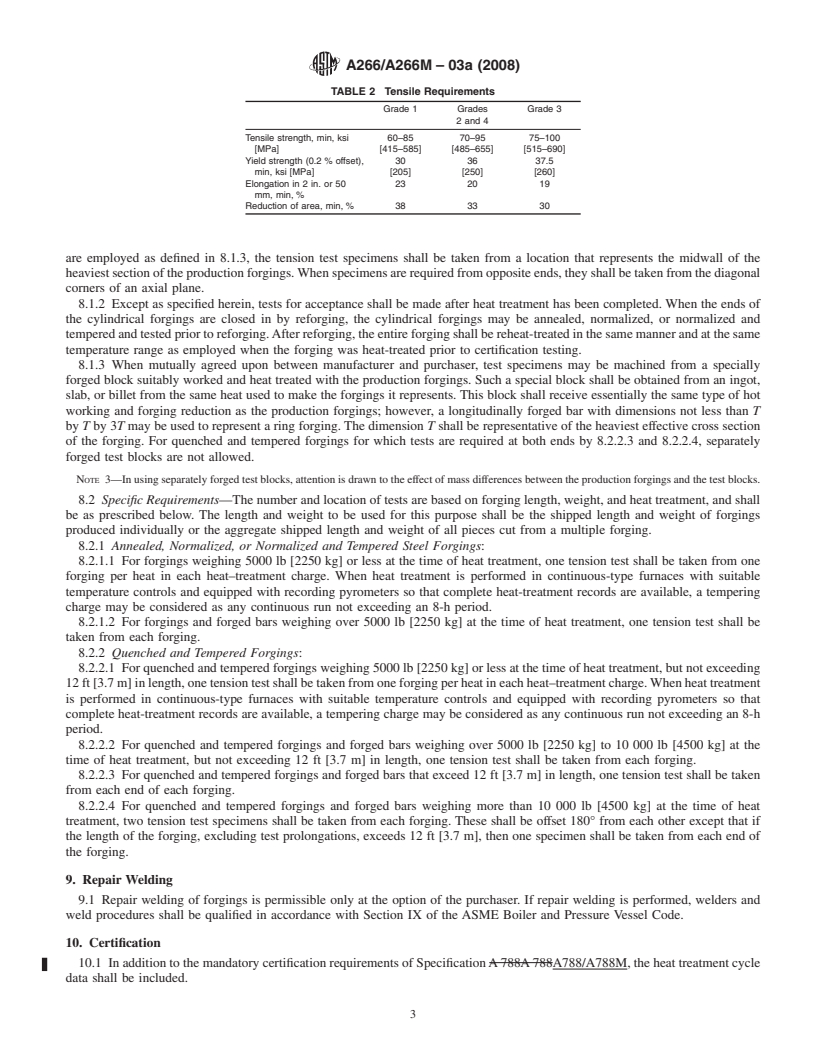
TABLE 2 Tensile Requirements
5. Machining
Grade 1 Grades Grade 3
5.1 Surfaces shall be machined as designated by the pur-
2 and 4
chaser. Unmachined surfaces shall be sufficiently free of scale
Tensile strength, min, ksi 60–85 70–95 75–100
to permit inspection.
[MPa] [415–585] [485–655] [515–690]
5.2 Machiningmaybeperformedeitherpriortoorafterheat
Yield strength (0.2 % offset), 30 36 37.5
min, ksi [MPa] [205] [250] [260]
treatment at the option of the manufacturer unless specified in
Elongation in 2 in. or 50 23 20 19
accordance with Supplementary Requirement S1.
mm, min, %
Reduction of area, min, % 38 33 30
6. Heat Treatment
6.1 After forging and before reheating for heat treatment,
the forgings shall be cooled in such a manner as to prevent
injury and to accomplish transformation. 8.1.1 Except when otherwise specified in accordance with
Supplementary Requirement S2, the longitudinal axis of the
6.2 All forgings shall be annealed, normalized, or normal-
ized and tempered, but alternatively may be liquid quenched specimensshallbeparalleltothedirectionofmajorworkingof
theforging.Forupset-discforgings,thelongitudinalaxisofthe
and tempered when mutually agreed upon between the manu-
facturer and the purchaser. When tempering is performed, it test specimen shall be in the tangential direction.
8.1.1.1 The longitudinal axis of the specimen shall be
shall be at a subcritical temperature, but no less than 1100°F
[595°C]. located midway between the parallel surfaces of the test
extensionifaddedtotheperipheryofdisksormidwaybetween
6.3 A multiple stage austenitizing procedure may be used
whereby the forging is first fully austenitized and liquid the center and surface of solid forgings. For hollow forgings,
the longitudinal axis of the specimens shall be located midway
quenched, followed by reheating within the intercritical tem-
perature range to partially reaustenitize, and again liquid between the center and outer surfaces of the wall. When
quenched. On completion of the austenitizing/quenching separately forged test blocks are employed as defined in 8.1.3,
the tension test specimens shall be taken from a location that
cycles, tempering at a temperature between 1100°F [595°C]
and the lower critical temperature shall follow. representsthemidwalloftheheaviestsectionoftheproduction
forgings. When specimens are required from opposite ends,
NOTE 2—Although liquid quenching from the austenitizing tempera-
they shall be taken from the diagonal corners of an axial plane.
turesismoreeffectiveinenhancingimpactproperties,aircoolingfromthe
8.1.2 Except as specified herein, tests for acceptance shall
austenitizing temperatures is also beneficial and may be used instead of
be made after heat treatment has been completed. When the
the normalizing procedure in 6.2.
ends of the cylindrical forgings are closed in by reforging, the
7. Chemical Composition
cylindrical forgings may be annealed, normalized, or normal-
7.1 Heat Analysis—The heat analysis obtained from sam- ized and tempered and tested prior to reforging. After reforg-
pling in accordance with Specification A788/A788M shall ing, the entire forging shall be reheat-treated in the same
comply with Table 1 except that the additional features of manner and at the same temperature range as employed when
Supplementary Requirements S11 and S12 shall also apply as the forging was heat-treated prior to certification testing.
individually specified in the ordering information. 8.1.3 When mutually agreed upon between manufacturer
7.2 Product Analysis—The purchaser may use the product and purchaser, test specimens may be machined from a
analysis provision of Specification A788/A788M to obtain a specially forged block suitably worked and heat treated with
product analysis from a forging representing each heat or the production forgings. Such a special block shall be obtained
multiple heat. from an ingot, slab, or billet from the same heat used to make
the forgings it represents. This block shall receive essentially
8. Mechanical Properties
the same type of hot working and forging reduction as the
8.1 General Requirements—Except when otherwise speci- production forgings; however, a longitudinally forged bar with
dimensionsnotlessthan Tby Tby3Tmaybeusedtorepresent
fied in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S2, the
a ring forging. The dimension T shall be representative of the
material shall conform to the requirements for mechanical
heaviest effective cross section of the forging. For quenched
propertiesprescribedinTable2whentestedinaccordancewith
and tempered forgings for which tests are required at both ends
the latest issue of Test Methods and Definitions A370. The
by 8.2.2.3 and 8.2.2.4, separately forged test blocks are not
largest obtainable tension test specimen as specified in Test
allowed.
Method
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:A 266/A 266M–03a Designation: A266/A266M – 03a (Reapproved 2008)
Standard Specification for
Carbon Steel Forgings for Pressure Vessel Components
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA266/A266M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope *
1.1 This specification covers four grades of carbon steel forgings for boilers, pressure vessels, and associated equipment.
NOTE 1—Designations have been changed as follows:
Current Formerly
Grade 1 Class 1
Grade 2 Class 2
Grade 3 Class 3
Grade 4 Class 4
1.2 Supplementary requirements are provided for use when additional testing or inspection is desired. These shall apply only
when specified individually by the purchaser in the order.
1.3The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text
and tables, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system
must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the
specification.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-pound
units.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A275/A275M Test MethodPractice for Magnetic Particle Examination of Steel Forgings
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A788788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Requirements
E112 Test Methods for Determining the Average Grain Size
E165 Test Method for Liquid Penetrant Examination Practice for Liquid Penetrant Examination for General Industry
E381 Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets, Blooms, and Forgings
2.2 Other Standard:
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX, Welding Qualifications
3. Ordering Information and General Requirements
3.1 In addition to the ordering information required by SpecificationA788A788A788/A788M, the purchaser shall include with
the inquiry and order a detailed drawing, sketch, or written description of the forging.
3.2 Material supplied to this specification shall conform to the requirements of SpecificationA788A788A788/A788M, which
outlines additional ordering information, manufacturing requirements, testing and retesting methods and procedures, marking,
certification, product analysis variations, and additional supplementary requirements.
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel, Stainless Steel,Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 2003. Published October 2003. Originally approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as A 266/A 266M–03.
Current edition approved March 1, 2008. Published April 2008. Originally approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as A266/A266M – 03a. DOI:
10.1520/A0266_A0266M-03AR08.
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specification SA–266/ SA–266M in Section II of that code.
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Available from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 345 East 47th St., New York, NY 10017.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A266/A266M – 03a (2008)
3.3 If the requirements of this specification are in conflict with the requirements of SpecificationA788A788A788/A788M, the
requirements of this specification shall prevail.
3.4 For hubbed flanges and tube sheets ordered for ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code application, Supplementary
Requirement S12 of Specification A 788A 788A788/A788M shall be specified in addition to Supplementary Requirement S8 of
this specification.
4. Materials and Manufacture
4.1 The steel shall be made in accordance with the Melting Process Section of Specification A 788A 788A788/A788M. A
sufficient discard shall be made to secure freedom from injurious pipe and undue segregation.
4.2 The material shall be forged as close as practical to the specified shape and size.
4.3 The finished product shall be a hot-worked forging as defined by Specification A 788A 788A788/A788M.
5. Machining
5.1 Surfaces shall be machined as designated by the purchaser. Unmachined surfaces shall be sufficiently free of scale to permit
inspection.
5.2 Machining may be performed either prior to or after heat treatment at the option of the manufacturer unless specified in
accordance with Supplementary Requirement S1.
6. Heat Treatment
6.1 After forging and before reheating for heat treatment, the forgings shall be cooled in such a manner as to prevent injury and
to accomplish transformation.
6.2 All forgings shall be annealed, normalized, or normalized and tempered, but alternatively may be liquid quenched and
tempered when mutually agreed upon between the manufacturer and the purchaser. When tempering is performed, it shall be at
a subcritical temperature, but no less than 1100°F [595°C].
6.3 A multiple stage austenitizing procedure may be used whereby the forging is first fully austenitized and liquid quenched,
followed by reheating within the intercritical temperature range to partially reaustenitize, and again liquid quenched. On
completion of the austenitizing/quenching cycles, tempering at a temperature between 1100°F [595°C] and the lower critical
temperature shall follow.
NOTE 2—Although liquid quenching from the austenitizing temperatures is more effective in enhancing impact properties, air cooling from the
austenitizing temperatures is also beneficial and may be used instead of the normalizing procedure in 6.2.
7. Chemical Composition
7.1 Heat Analysis—The heat analysis obtained from sampling in accordance with SpecificationA788A788A788/A788M shall
comply with Table 1 except that the additional features of Supplementary Requirements S11 and S12 shall also apply as
individually specified in the ordering information.
7.2 Product Analysis—The purchaser may use the product analysis provision of Specification A 788A 788A788/A788M to
obtain a product analysis from a forging representing each heat or multiple heat.
8. Mechanical Properties
8.1 General Requirements—Except when otherwise specified in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S2, the material
shall conform to the requirements for mechanical properties prescribed in Table 2 when tested in accordance with the latest issue
of Test Methods and Definitions A 370A370. The largest obtainable tension test specimen as specified in Test Methods and
Definitions A 370A370 shall be used.
8.1.1 Except when otherwise specified in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S2, the longitudinal axis of the
specimens shall be parallel to the direction of major working of the forging. For upset-disc forgings, the longitudinal axis of the
test specimen shall be in the tangential direction.
8.1.1.1 The longitudinal axis of the specimen shall be located midway between the parallel surfaces of the test extension if
added to the periphery of disks or midway between the center and surface of solid forgings. For hollow forgings, the longitudinal
axisofthespecimensshallbelocatedmidwaybetweenthecenterandoutersurfacesofthewall.Whenseparatelyforgedtestblocks
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
Grades 1 and 2 Grade 3 Grade 4
Carbon, max 0.30 0.35 0.30
Manganese 0.40–1.05 0.80–1.35 0.80–1.35
Phosphorus, max 0.025 0.025 0.025
Sulfur, max 0.025 0.025 0.025
Silicon 0.15–0.35 0.15–0.35 0.15–0.35
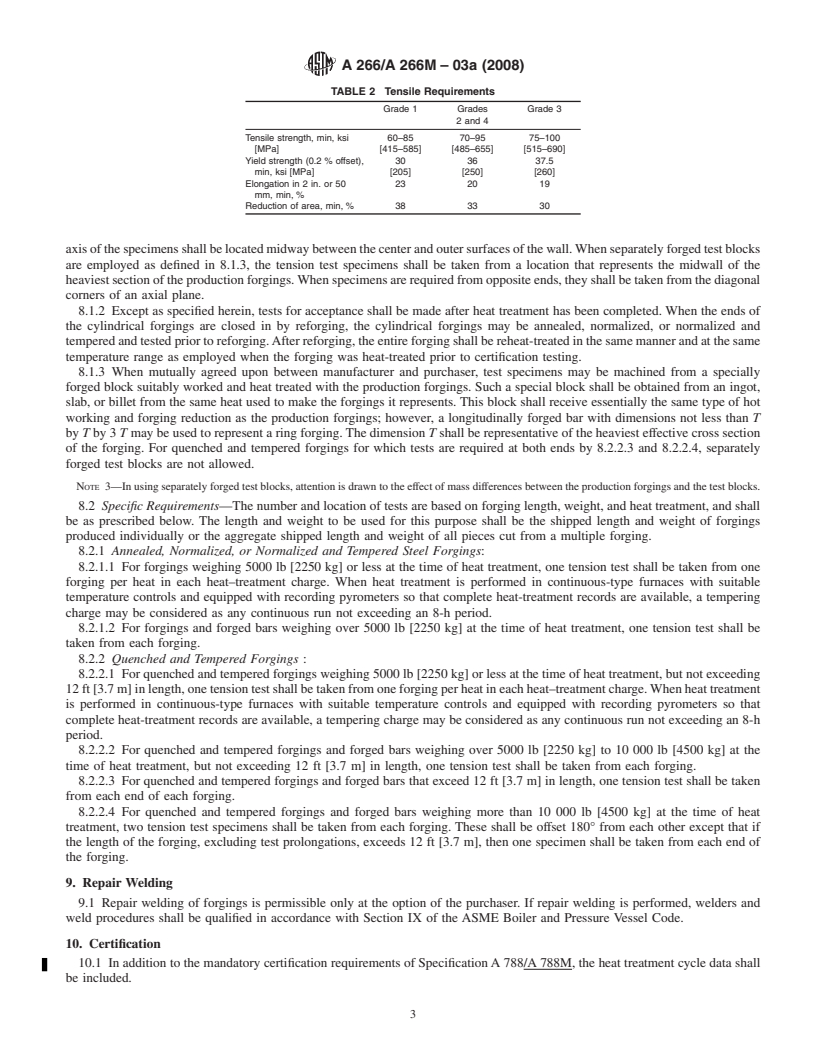
A266/A266M – 03a (2008)
TABLE 2 Tensile Requirements
Grade 1 Grades Grade 3
2 and 4
Tensile strength, min, ksi 60–85 70–95 75–100
[MPa] [415–585] [485–655] [515–690]
Yield strength (0.2 % offset), 30 36 37.5
min, ksi [MPa] [205] [250] [260]
Elongation in 2 in. or 50 23 20 19
mm, min, %
Reduction of area, min, % 38 33 30
are employed as defined in 8.1.3, the tension test specimens shall be taken from a location that represents the midwall of the
heaviestsectionoftheproductionforgings.Whenspecimensarerequiredfromoppositeends,theyshallbetakenfromthediagonal
corners of an axial plane.
8.1.2 Except as specified herein, tests for acceptance shall be made after heat treatment has been completed. When the ends of
the cylindrical forgings are closed in by reforging, the cylindrical forgings may be annealed, normalized, or normalized and
temperedandtestedpriortoreforging.Afterreforging,theentireforgingshallbereheat-treatedinthesamemannerandatthesame
temperature range as employed when the forging was heat-treated prior to certification testing.
8.1.3 When mutually agreed upon between manufacturer and purchaser, test specimens may be machined from a specially
forged block suitably worked and heat treated with the production forgings. Such a special block shall be obtained from
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard Designation: A 266/A 266M – 03a (Reapproved 2008)
Designation:A266/A266M–03
Standard Specification for
Carbon Steel Forgings for Pressure Vessel Components
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA266/A266M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope *
1.1 This specification covers four grades of carbon steel forgings for boilers, pressure vessels, and associated equipment.
NOTE 1—Designations have been changed as follows:
Current Formerly
Grade 1 Class 1
Grade 2 Class 2
Grade 3 Class 3
Grade 4 Class 4
1.2 Supplementary requirements are provided for use when additional testing or inspection is desired. These shall apply only
when specified individually by the purchaser in the order.
1.3The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text
and tables, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system
must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the
specification.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-pound
units.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A 275/A 275M Test Method Practice for Magnetic Particle Examination of Steel Forgings
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A 788/A 788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Requirements
E 112 Test Methods for Determining the Average Grain Size
E 165 Test Method for Liquid Penetrant Examination
E 381 Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets, Blooms, and Forgings
2.2 Other Standard:
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX, Welding Qualifications
3. Ordering Information and General Requirements
3.1 InadditiontotheorderinginformationrequiredbySpecificationA 788/A 788M,thepurchasershallincludewiththeinquiry
and order a detailed drawing, sketch, or written description of the forging.
3.2 Material supplied to this specification shall conform to the requirements of Specification A 788/A 788M, which outlines
additional ordering information, manufacturing requirements, testing and retesting methods and procedures, marking, certification,
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel, Stainless Steel,Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets.
Current edition approved April 10, 2003.March 1, 2008. Published June 2003.April 2008. Originally approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 19992003 as
A266/A266M–99. A 266/A 266M – 03a.
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specification SA–266/ SA–266M in Section II of that code.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05.
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
Available from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 345 East 47th St., New York, NY 10017.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 266/A 266M – 03a (2008)
product analysis variations, and additional supplementary requirements.
3.3 If the requirements of this specification are in conflict with the requirements of Specification A 788/A 788M, the
requirements of this specification shall prevail.
3.4 For hubbed flanges and tube sheets ordered for ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code application, Supplementary
Requirement S12 of Specification A 788/A 788M shouldshall be specified in addition to Supplementary Requirement S8 of this
specification.
4. Materials and Manufacture
4.1 The steel shall be made in accordance with the Melting Process Section of SpecificationA 788/A 788M.Asufficient discard
shall be made to secure freedom from injurious pipe and undue segregation.
4.2 The material shall be forged as close as practical to the specified shape and size.
4.3 The finished product shall be a hot-worked forging as defined by Specification A 788/A 788M.
5. Machining
5.1 Surfaces shall be machined as designated by the purchaser. Unmachined surfaces shall be sufficiently free of scale to permit
inspection.
5.2 Machining may be performed either prior to or after heat treatment at the option of the manufacturer unless specified in
accordance with Supplementary Requirement S1.
6. Heat Treatment
6.1 After forging and before reheating for heat treatment, the forgings shall be cooled in such a manner as to prevent injury and
to accomplish transformation.
6.2 All forgings shall be annealed, normalized, or normalized and tempered, but alternatively may be liquid quenched and
tempered when mutually agreed upon between the manufacturer and the purchaser. When tempering is performed, it shall be at
a subcritical temperature, but no less than 1100°F [595°C].
6.3 A multiple stage austenitizing procedure may be used whereby the forging is first fully austenitized and liquid quenched,
followed by reheating within the intercritical temperature range to partially reaustenitize, and again liquid quenched. On
completion of the austenitizing/quenching cycles, tempering at a temperature between 1100°F [595°C] and the lower critical
temperature shall follow.
NOTE 2—Although liquid quenching from the austenitizing temperatures is more effective in enhancing impact properties, air cooling from the
austenitizing temperatures is also beneficial and may be used instead of the normalizing procedure in 6.2.
7. Chemical Composition
7.1 Heat Analysis—The heat analysis obtained from sampling in accordance with Specification A 788/A 788M shall comply
with Table 1 except that the additional features of Supplementary Requirements S11 and S12 shall also apply as individually
specified in the ordering information.
7.2 Product Analysis—The purchaser may use the product analysis provision of Specification A 788/A 788M to obtain a
product analysis from a forging representing each heat or multiple heat.
8. Mechanical Properties
8.1 General Requirements—Except when otherwise specified in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S2, the material
shall conform to the requirements for mechanical properties prescribed in Table 2 when tested in accordance with the latest issue
of Test Methods and DefinitionsA 370. The largest obtainable tension test specimen as specified in Test Methods and Definitions
A 370 shall be used.
8.1.1 Except when otherwise specified in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S2, the longitudinal axis of the
specimens shall be parallel to the direction of major working of the forging. For upset-disc forgings, the longitudinal axis of the
test specimen shall be in the tangential direction.
8.1.1.1 The longitudinal axis of the specimen shall be located midway between the parallel surfaces of the test extension if
added to the periphery of disks or midway between the center and surface of solid forgings. For hollow forgings, the longitudinal
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
Grades 1 and 2 Grade 3 Grade 4
Carbon, max 0.30 0.35 0.30
Manganese 0.40–1.05 0.80–1.35 0.80–1.35
Phosphorus, max 0.025 0.025 0.025
Sulfur, max 0.025 0.025 0.025
Silicon 0.15–0.35 0.15–0.35 0.15–0.35
A 266/A 266M – 03a (2008)
TABLE 2 Tensile Requirements
Grade 1 Grades Grade 3
2 and 4
Tensile strength, min, ksi 60–85 70–95 75–100
[MPa] [415–585] [485–655] [515–690]
Yield strength (0.2 % offset), 30 36 37.5
min, ksi [MPa] [205] [250] [260]
Elongation in 2 in. or 50 23 20 19
mm, min, %
Reduction of area, min, % 38 33 30
axisofthespecimensshallbelocatedmidwaybetweenthecenterandoutersurfacesofthewall.Whenseparatelyforgedtestblocks
are employed as defined in 8.1.3, the tension test specimens shall be taken from a location that represents the midwall of the
heaviestsectionoftheproductionforgings.Whenspecimensarerequiredfromoppositeends,theyshallbetakenfromthediagonal
corners of an axial plane.
8.1.2 Except as specified herein, tests for acceptance shall be made after heat treatment has been completed. When the ends of
the cylindrical forgings are closed in by reforging, the cylindrical forgings may be annealed, normalized, or normalized and
temperedandtestedpriortoreforging.Afterreforging,theentireforgingshallbereheat-treatedinthesamemannerandatthesame
temperature range as employed when the forging was heat-treated prior to certification testing.
8.1.3 When mutually agreed upon between manufacturer and purchaser, test specimens may be machined from a speciall
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.