ASTM D7147-05
(Specification)Standard Specification for Testing and Establishing Allowable Loads of Joist Hangers
Standard Specification for Testing and Establishing Allowable Loads of Joist Hangers
ABSTRACT
This specification covers a procedure for evaluating metal devices used for wood-to-wood, wood-to-concrete, wood-to-concrete masonry, and wood-to-steel joist, beam, and girder connections. It describes test methods for evaluating the capacities of joist hangers subject to vertical and torsional loading. Also, this specification provides a method of assigning allowable loads to joist hangers based on measured strength and deformation characteristics. Test specimens consisting of a length of joist supported by joist hangers attached to two headers are subjected to a vertical load by a suitable testing machine, while the vertical load and corresponding deflection of the joist are measured and recorded to provide load-slip data.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers a procedure for evaluating metal devices used for wood-to-wood, wood-to-concrete, wood-to-concrete masonry, and wood-to-steel connections. This method is intended for use with devices used to connect joists, beams, and girders together. These devices are commonly described as joist hangers.
1.2 This specification describes test methods for evaluating the capacities of joist hangers subject to vertical and torsional loading.
1.3 This specification provides a method of assigning allowable loads to joist hangers based on measured strength and deformation characteristics. Information obtained by the provisions of this specification is applicable to design when using the Allowable Stress Design method.
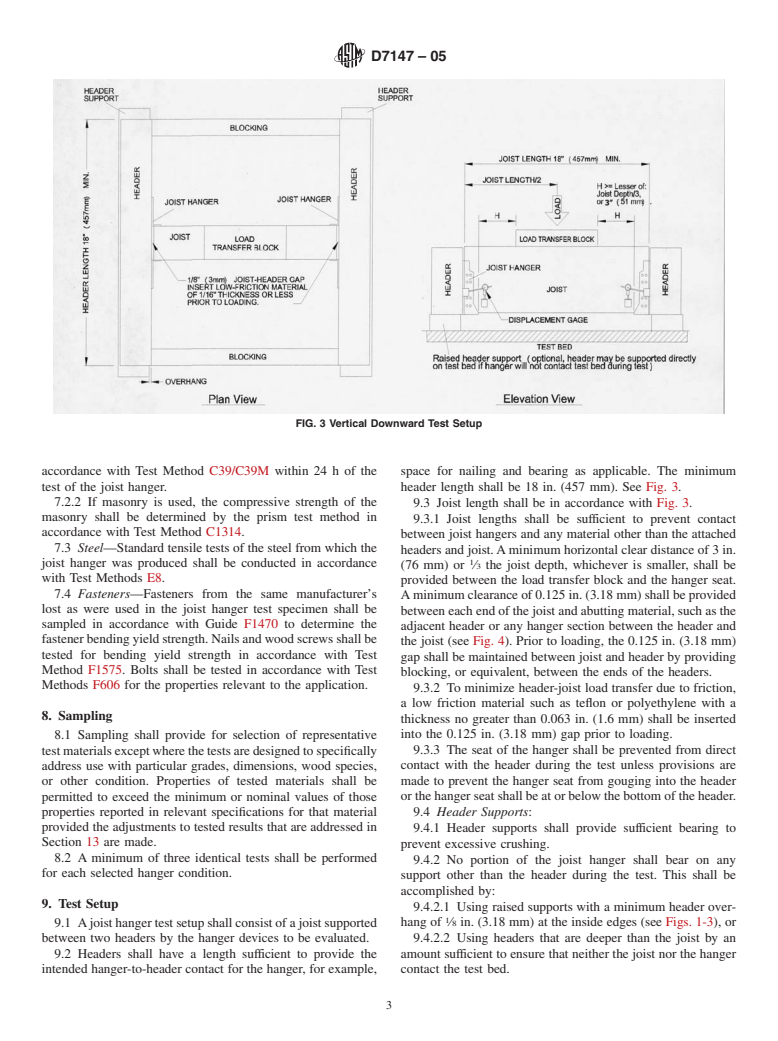
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7147 – 05
Standard Specification for
Testing and Establishing Allowable Loads of Joist Hangers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7147; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Wood-Based Materials
D3737 Practice for Establishing Allowable Properties for
1.1 This specification covers a procedure for evaluating
Structural Glued Laminated Timber (Glulam)
metal devices used for wood-to-wood, wood-to-concrete,
D4442 Test Methods for Direct Moisture Content Measure-
wood-to-concrete masonry, and wood-to-steel connections.
ment of Wood and Wood-Base Materials
This method is intended for use with devices used to connect
D4444 Test Method for Laboratory Standardization and
joists, beams, and girders together. These devices are com-
Calibration of Hand-Held Moisture Meters
monly described as joist hangers.
D5055 Specification for Establishing and Monitoring Struc-
1.2 This specification describes test methods for evaluating
tural Capacities of Prefabricated Wood I-Joists
the capacities of joist hangers subject to vertical and torsional
D5456 SpecificationforEvaluationofStructuralComposite
loading.
Lumber Products
1.3 Thisspecificationprovidesamethodofassigningallow-
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
able loads to joist hangers based on measured strength and
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
deformation characteristics. Information obtained by the pro-
E575 Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of
visions of this specification is applicable to design when using
Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and As-
the Allowable Stress Design method.
semblies
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
F606 Test Methods for Determining the Mechanical Prop-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
erties of Externally and Internally Threaded Fasteners,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Washers, Direct Tension Indicators, and Rivets
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
F1470 Practice for Fastener Sampling for Specified Me-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
chanical Properties and Performance Inspection
2. Referenced Documents F1575 Test Method for Determining Bending Yield Mo-
ment of Nails
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2.2 Other Standards:
C31/C31M Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test
ANSI/AF&PANDS-2001 National Design Specificationfor
Specimens in the Field
Wood Construction
C39/C39M Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cy-
ANSI/ASME B18.2.1 Square and Hex Bolts and Screws
lindrical Concrete Specimens
(Inch Series), 1996
C90 Specification for Loadbearing Concrete Masonry Units
Specification and Commentary for the Design of Cold-
C270 Specification for Mortar for Unit Masonry
Formed Steel Structural Members, 1996
C1314 Test Method for Compressive Strength of Masonry
Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, 1989
Prisms
D9 Terminology Relating to Wood and Wood-Based Prod-
3. Terminology
ucts
3.1 The following section defines terms used in this speci-
D245 Practice for Establishing Structural Grades and Re-
fication. See Terminology D9 for other terminology.
lated Allowable Properties for Visually Graded Lumber
3.2 Definitions:
D2395 Test Methods for Specific Gravity of Wood and
1 3
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D07 on Wood Available from American Forest and Paper Association (AF&PA), 1111 19th
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D07.05 on Wood Assemblies. St., NW, Suite 800, Washington, DC 20036.
Current edition approved April 1, 2005. Published April 2005. DOI: 10.1520/ Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
D7147-05. International Headquarters, Three Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990.
2 5
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI), 1101 17th St., NW,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Suite 1300, Washington, DC 20036.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC), One E.
the ASTM website. Wacker Dr., Suite 3100, Chicago, IL 60601-2001.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D7147 – 05
3.2.1 header—amembersupportingajoisthanger.Aheader
may also be referred to as a “supporting” member.
3.2.2 joist—a bending member supported by a joist hanger.
A joist may also be referred to as a “supported” member.
3.2.3 joist hanger—a metal device, usually cold-formed
from light-gage steel sheet or welded from steel plate, used to
transfer loads from a joist to a header member or wall in
building construction. Face-mount joist hangers contact the
side surface of the header and do not contact the top of the
header. Top-mount hangers are joist hangers that contact the
side and top surface of the header.
3.2.4 structural composite lumber—see Specification
D5456.
3.2.5 structural glued laminated timber—see Practice
D3737.
3.2.6 wood I-joists—see Specification D5055.
FIG. 2 Typical Uplift Test Setup
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Joist hangers are used to transfer vertical loads from a
joist to a header in building construction. In addition to vertical
5.1.2 Loads applied vertically upward with reference to the
load transfer, joist hangers may provide torsional resistance for
intended application of the joist hanger, shall be classified as
the ends of a joist. The performance of this connection is
uplift (see Fig. 2).
influenced by a number of variables, such as the properties of
5.2 Torsional Moment Test (optional)—A test method is
the hanger, the joist material, the header material, and the
provided in Appendix X1 for torsional moment capacity
fasteners. The test described in this specification provide for
evaluation of hangers. This test consists of a joist supported by
consistency in evaluating the performance of such assembled
two joist hangers attached to headers (see Figs. X1.1 and
units.
X1.2).The movement of the joist with respect to the headers is
measured and recorded to provide data for calculating angular
5. Summary of Test Method
rotation and load-deflection relationships.
5.1 Vertical Load Test—Test specimens consisting of a
length of joist supported by joist hangers attached to two
6. Apparatus
headers are subjected to a vertical load by a suitable testing
6.1 Testing Machine—A testing machine that is capable of
machine (see Figs. 1-3), while the vertical load and corre-
operationataconstantrateofmotionofthemovablecrosshead
sponding deflection of the joist are measured and recorded to
or a constant rate of loading and a force-measuring device that
provide load-slip data.
is calibrated in accordance with Practices E4.
5.1.1 Loads applied vertically downward with reference to
6.2 Displacement Gage—All tests shall use a dial gage(s),
the intended application of the joist hanger, shall be classified
or equivalent, to measure the relative movement between the
as downward (see Fig. 1).
joist and header. Devices used for this purpose shall have a
least reading of 0.001 in. (0.02 mm).
7. Test Materials
7.1 Wood—All wood materials shall be of structural quality
with allowable values substantiated by accepted procedures,
such as those found in Section 2. The specific gravity and
moisture content of the joists and headers shall be determined
in accordance with Test Methods D2395 and D4442 or D4444,
respectively. All specific gravities shall be reported on an
oven-dry basis in accordance with Test Methods D2395.
Specificgravitymeasurementstakenatmoisturecontentsother
than oven-dry shall be adjusted to the oven-dry moisture
content in accordance with Appendix X1 of Test Methods
D2395.
7.2 Concrete or Masonry:
7.2.1 If concrete is used, a minimum of two concrete test
cylinders shall be prepared, stored, and cured in accordance
with Practice C31/C31M from the same batch of concrete used
FIG. 1 Typical Vertical Downward Test Setup in the joist hanger test specimen. Cylinders shall be tested in
D7147 – 05
FIG. 3 Vertical Downward Test Setup
accordance with Test Method C39/C39M within 24 h of the space for nailing and bearing as applicable. The minimum
test of the joist hanger. header length shall be 18 in. (457 mm). See Fig. 3.
7.2.2 If masonry is used, the compressive strength of the
9.3 Joist length shall be in accordance with Fig. 3.
masonry shall be determined by the prism test method in
9.3.1 Joist lengths shall be sufficient to prevent contact
accordance with Test Method C1314.
between joist hangers and any material other than the attached
7.3 Steel—Standard tensile tests of the steel from which the
headers and joist.Aminimum horizontal clear distance of 3 in.
joist hanger was produced shall be conducted in accordance
(76 mm) or ⁄3 the joist depth, whichever is smaller, shall be
with Test Methods E8.
provided between the load transfer block and the hanger seat.
7.4 Fasteners—Fasteners from the same manufacturer’s
Aminimum clearance of 0.125 in. (3.18 mm) shall be provided
lost as were used in the joist hanger test specimen shall be
between each end of the joist and abutting material, such as the
sampled in accordance with Guide F1470 to determine the
adjacent header or any hanger section between the header and
fastenerbendingyieldstrength.Nailsandwoodscrewsshallbe
the joist (see Fig. 4). Prior to loading, the 0.125 in. (3.18 mm)
tested for bending yield strength in accordance with Test
gap shall be maintained between joist and header by providing
Method F1575. Bolts shall be tested in accordance with Test
blocking, or equivalent, between the ends of the headers.
Methods F606 for the properties relevant to the application.
9.3.2 To minimize header-joist load transfer due to friction,
a low friction material such as teflon or polyethylene with a
8. Sampling
thickness no greater than 0.063 in. (1.6 mm) shall be inserted
into the 0.125 in. (3.18 mm) gap prior to loading.
8.1 Sampling shall provide for selection of representative
testmaterialsexceptwherethetestsaredesignedtospecifically 9.3.3 The seat of the hanger shall be prevented from direct
contact with the header during the test unless provisions are
address use with particular grades, dimensions, wood species,
or other condition. Properties of tested materials shall be made to prevent the hanger seat from gouging into the header
orthehangerseatshallbeatorbelowthebottomoftheheader.
permitted to exceed the minimum or nominal values of those
properties reported in relevant specifications for that material 9.4 Header Supports:
provided the adjustments to tested results that are addressed in
9.4.1 Header supports shall provide sufficient bearing to
Section 13 are made.
prevent excessive crushing.
8.2 A minimum of three identical tests shall be performed
9.4.2 No portion of the joist hanger shall bear on any
for each selected hanger condition.
support other than the header during the test. This shall be
accomplished by:
9. Test Setup
9.4.2.1 Using raised supports with a minimum header over-
hang of ⁄8 in. (3.18 mm) at the inside edges (see Figs. 1-3), or
9.1 Ajoisthangertestsetupshallconsistofajoistsupported
between two headers by the hanger devices to be evaluated. 9.4.2.2 Using headers that are deeper than the joist by an
9.2 Headers shall have a length sufficient to provide the amount sufficient to ensure that neither the joist nor the hanger
intended hanger-to-header contact for the hanger, for example, contact the test bed.
D7147 – 05
FIG. 4 Required Gap When Portion of Joist Hanger Exists Between Header and Joist
9.4.3 The test bed or any header supports shall not contact 11. Procedure
the joist or joist hanger at any time during the test.
11.1 The following properties must be determined for ma-
terials used in the test:
NOTE 1—A ⁄8-in. overhang of the header beyond the inside edge of the
support has historically been provided to ensure contact does not occur
(1) tensile strength of hanger steel,
between the joist hanger and the header support.
(2) specific gravity of wood materials as outlined in 13.5.2-
9.5 Reinforcement of joist members at the area of load
13.5.4, and
application shall be permitted to prevent member failure in
(3) bending yield strength of the fasteners.
bending, shear, or compression perpendicular-to-grain at the
11.2 Vertical movement of the joist with respect to each
applied load, so as to produce a failure in the joist hanger, or of
header shall be measured with a minimum of two dial gages or
the fasteners between the joist hanger and the joist or header
other suitable device as depicted in Fig. 3. The dial gage shall
member(s)orajoistbearingfailureatthehanger.Thelengthof
measure movement of any point along the depth of the joist
joist reinforcement shall be no closer than 2 in. (51 mm) from
(top, bottom, or side) located within 1.5 in. (38 mm) from the
the end of each hanger.
end of the joist. Dial gage bases shall be attached to the bottom
9.6 Blockingbetweentheheadersoralternatemethodsshall
half of the header to the center of the gage base or attached to
be provided to prevent rotation of the headers inward towards
the test machine bed.
the joist. Tensile reinforcement between the headers shall be
11.2.1 Exception—Whenthejoistsetupisinvertedforuplift
permittedtopreventrotationoftheheadersoutwardawayfrom
testing, the dial gage or other suitable device shall be located
the joist. Such reinforcement shall not contact the joist hangers
on the joist within 1 in. (25 mm) from the end of the hanger
or otherwise interfere with their performance.
seat.
9.7 Where a hanger device is of a design that is not
11.3 The load shall be centered over the joist and be
adaptable to the test setup described above, necessary depar-
transferredfromthecrossheadtothetestspecimeninamanner
tures shall be permitted, provided the altered setup will
thatwillassureequaldistributionoftheloadtobothendsofthe
perform the essential function of testing the joist hanger
joist. The load shall be applied over a sufficient joist length to
device, and provided that such departures are reported in the
prevent excessive crushing under the loading head and shall
test report in detail.
conform to the requirements of Section 9.
10. Conditioning 11.4 For downward
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.