ASTM F2348-04(2017)
(Specification)Standard Performance Specification for Privacy Padlocks
Standard Performance Specification for Privacy Padlocks
ABSTRACT
This performance specification covers the functional, operational, and security requirements, as well as the function descriptions, operational tests, forcing tests, and surreptitious entry tests for privacy padlocks that offer limited protection to forced attack similar to that provided by tamper-indicative security seals. The types of padlocks covered here are as follows: Type P01—key operated; Type P02—combination operated; Type P03—frangible element operated; Type P04—replaceable frangible element operated; and Type P05—independent custody operated. Four levels of performance are described in this specification with Grade 0 the lowest and Grade 3 the highest.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers functional, operational, and security requirements for padlocks. Included are function descriptions, operational tests, forcing tests, and surreptitious entry tests.
1.2 This specification describes and grades various levels of performance to provide users of the specification with criteria upon which to select suitable padlocks.
1.3 Tests described are laboratory tests, and although they simulate field conditions as to attacks, they do not duplicate these conditions. Tests described are repeatable in the laboratory.
1.4 Some users of this specification may wish to use padlocks that have special attributes not related to security.
1.5 This specification describes and grades various levels of performance provided by limited dual custody operation.
1.6 The specific padlocks included have shackles of limited diameter, permitting attachment to existing zipper slides and zipper pulls and other devices provided for closure.
1.7 These padlocks are considered “privacy padlocks” offering limited protection to forced attack similar to that provided by tamper-indicative security seals. A successful forced attack would be indicated by the damage done to the padlock. For padlocks offering greater protection to forced attack, the user is directed to Performance Specification F883.
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are provided for information only.
1.9 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portions, Sections 8 – 11, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:F2348 −04 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Performance Specification for
Privacy Padlocks
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2348; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This specification covers functional, operational, and 2.1 ASTM Standards:
security requirements for padlocks. Included are function F883 Performance Specification for Padlocks
descriptions, operational tests, forcing tests, and surreptitious
3. Terminology
entry tests.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.2 This specification describes and grades various levels of
3.1.1 acceptance testing, v—to assure by documented test-
performance to provide users of the specification with criteria
ingthatapadlockmeetsspecifictestsofSpecificationF2348as
upon which to select suitable padlocks.
agreed to by the buyer and seller.
1.3 Tests described are laboratory tests, and although they
3.1.2 case, n—housing or body of a lock or latch.
simulate field conditions as to attacks, they do not duplicate
3.1.3 certified, v—to assure by documented testing that a
these conditions. Tests described are repeatable in the labora-
tory. padlock meets all test requirements appropriate to its grading.
3.1.4 combination lock, n—lock that is operated by local
1.4 Some users of this specification may wish to use
input of a specific series or sequence of numbers or letters.
padlocks that have special attributes not related to security.
3.1.5 cylinder, n—complete operating unit which usually
1.5 This specification describes and grades various levels of
consists of the plug, shell, tumblers, springs, plug retainer, a
performance provided by limited dual custody operation.
cam/tailpiece or other actuating device, and all other necessary
1.6 The specific padlocks included have shackles of limited
operating parts.
diameter, permitting attachment to existing zipper slides and
3.1.6 cylinder bitting, n—group of numbers that represent
zipper pulls and other devices provided for closure.
the bitting of a key or the tumblers, or both, of a lock or
1.7 These padlocks are considered “privacy padlocks” of-
cylinder.
fering limited protection to forced attack similar to that
3.1.7 decode, v—to determine a key combination by physi-
provided by tamper-indicative security seals. A successful
cal measurement of a key or cylinder parts, or both.
forced attack would be indicated by the damage done to the
3.1.8 heel, n—part of a padlock shackle that normally is
padlock. For padlocks offering greater protection to forced
retained in the case when in the unlocked position.
attack, the user is directed to Performance Specification F883.
3.1.9 independent dual custody, adj—function of a mecha-
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
nism that allows access by two different people with different
standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are
credentials.
provided for information only.
3.1.10 keyway, n—the opening in a lock or cylinder that is
1.9 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
shaped to accept a key bit or blade of a proper configuration.
testmethodportions,Sections8–11,ofthisspecification: This
standard does not purport to address the safety concerns, if
3.1.11 manipulate, v—dialing process typically used with
any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user combination locks to determine operational status of the lock,
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
potential combinations, or attempt to free the mechanism.
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
3.1.12 manipulation, n—opening method for mechanical
tions prior to use.
combination locks that uses the tolerances of that lock to
determine an opening combination.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F12 on
Security Systems and Equipmentand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F12.50 on Locking Devices. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved March 1, 2017. Published March 2017. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2004. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as F2348 – 04 (2010). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/F2348-04R17. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F2348−04 (2017)
3.1.13 padlock, n—detachable and portable lock with a 4.3.4 Option D—Combination operated with key control.
shackle that locks into its case.
5. General Requirements
3.1.14 pick, v—to manipulate tumblers in a keyed lock
mechanism through the keyway, without obvious damage, by
5.1 Inferences—Cylinderpicking,rapping,anddecodingare
means other than the specifically designed key.
described in this specification. Since the skill of the person
doing the testing has a direct bearing on the results of the tests,
3.1.15 plug, n—part of a cylinder that contains the keyway,
one of each test shall be conducted by three different persons
with tumbler chambers usually corresponding to those in the
having experience of not less than one year of approximately
cylinder shell.
the same skill level and the results averaged for determining
3.1.16 rap, v—to unlock a padlock shackle from its case by
relative levels of performance.
striking the case to disengage the locking mechanism.
5.2 Tolerances:
3.1.17 removable cylinder, n—cylinder that can be removed
5.2.1 Fixture Tolerances—All tolerances shall follow stan-
from a locking device by a key or tool, or both.
dard machining practices unless otherwise specified.
3.1.18 shackle, n—part of a padlock that passes through an
5.2.2 Test Setup Tolerances:
opening in an object or fits around an object and is ultimately
5.2.2.1 Force: 0.5 % of working range.
locked into the case.
5.2.2.2 Height: 63 mm (0.12 in.)
3.1.19 tamper-indicative device (tid), n—mechanical device
5.2.2.3 Torque: 4.0 % of reading.
whose physical change in state is an obvious indication of
5.3 Temperature—All tests shall be conducted between 16
tamper
and 27°C (61 and 81°F).
3.1.20 toe, n—part of a padlock shackle that is normally
5.4 Test Reports—All test reports shall be dated.
released from the case in the unlocked position.
3.1.21 tumbler, n—movable obstruction of varying size and
6. Test Specimens
configuration in a lock or cylinder that makes direct contact
6.1 Select specimens for test at random from the manufac-
with the key or another tumbler and prevents an incorrect key
turers’ finished stock of each size and model being certified by
or torquing device from activating the lock or other mecha-
the manufacturer.
nism.
6.2 Padlocks may be used for multiple tests if previous tests
3.1.22 zipper slide, n—movable device that opens and
would not influence subsequent test results.
closes a zipper.
3.1.23 zipper pull, n—element attached to a zipper slide to 6.3 Select four padlocks for the forcing tests. For surrepti-
facilitate movement. tious entry tests, select five padlocks for each test required.
Select one padlock for the cycle test.
4. Classification of Functions
4.1 Types of Padlocks: 7. Preparation of Apparatus
4.1.1 Type P01—Key operated.
7.1 Tensile Loading Device—Provide a tensile loading de-
4.1.2 Type P02—Combination operated.
vice having a load and force measuring capacity of 1142 to
4.1.3 Type P03—Frangible element operated.
2855 mm/N (200 to 500 in./lb).
4.1.4 Type P04—Replaceable frangible element operated.
4.1.5 Type P05—Independent custody operated.
8. Test Methods
4.2 Grades—Four levels of performance are described in
8.1 Forcing Tests (see Table 1)
this specification with Grade 0 the lowest and Grade 3 the
8.1.1 Tensile Test
highest.
8.1.1.1 Scope—The subject privacy class of padlock is not a
4.3 Options: security padlock. Any can be forced using simple well-known
4.3.1 Option A—Key is captive in cylinder when padlock is attack methods. It is important that any successful forcing
unlocked. attack leaves clear evidence of the event.
4.3.2 Option B—Not used in this specification. 8.1.1.2 Significance and Use—The forcing tests to be per-
4.3.3 Option C—Non-changeable combination. formed establish grade levels for tensile (pulling the shackle
TABLE 1
Grade per ASTM F2348
Description Units 0 P1 P2 P3
Shackle Diameter mm <3.0 3.0 4.0 5.0
TABLE 1 Forcing Tests Required Values Units 0 F1 F2 F3
Forcing tests Tensile Test lb <200 200 350 500
Shackle Cutting Test lb <500 500 1000 2000
Evidence of Forced Attack no yes yes yes
Non-Functioning after Forced Attack no yes yes yes
F2348−04 (2017)
TABLE 2
TABLE 2 Surreptitious Entry Tests Units 0 S1S2S3
Required Values
Surreptitious Entry Tests Picking or Manipulating Test s <30 30 100 180
Rap Test s <5 5 10 20
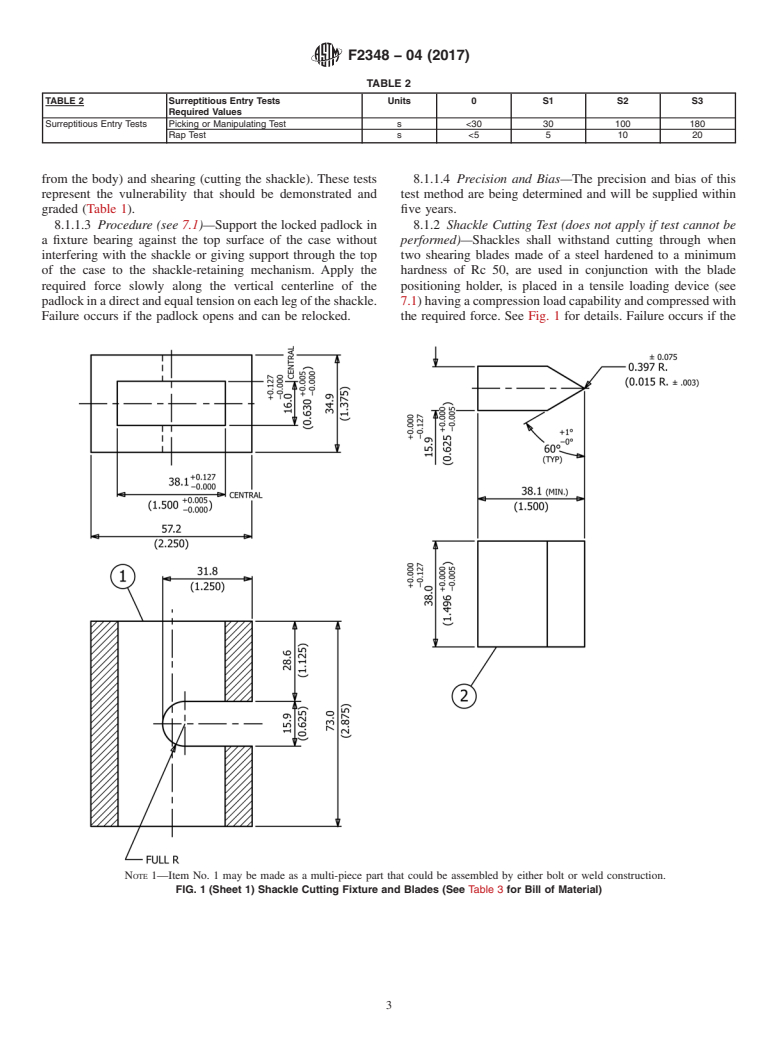
from the body) and shearing (cutting the shackle). These tests 8.1.1.4 Precision and Bias—The precision and bias of this
represent the vulnerability that should be demonstrated and test method are being determined and will be supplied within
graded (Table 1). five years.
8.1.1.3 Procedure (see 7.1)—Suppo
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.