ASTM B564-06
(Specification)Standard Specification for Nickel Alloy Forgings
Standard Specification for Nickel Alloy Forgings
SCOPE
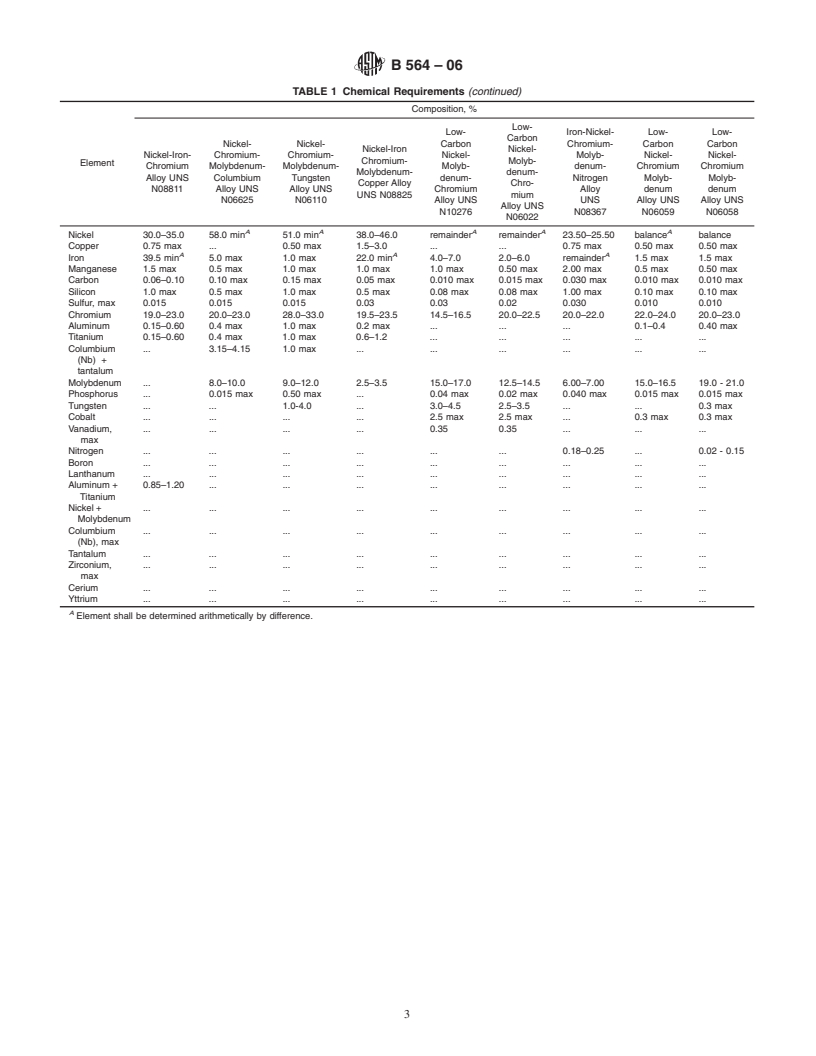
1.1 This specification covers forgings of nickel alloy UNS N02200, Ni-Cu alloy UNS N04400, Ni-Cr-Fe alloys UNS N06600, UNS N06603, and UNS N06690, Ni-Cr-Mo-Nb alloy UNS N06625, Ni-Cr-Mo-Si alloy UNS N06219, low-carbon Ni-Mo-Cr alloys UNS N10276 and UNS N06022, Ni-Cr-Mo-W alloy UNS N06110, low-carbon Ni-Cr-Mo-W alloy UNS N06686, Ni-Fe-Cr-Mo-Cu alloy UNS N08825, Fe-Ni-Cr-Mo-N alloy UNS N08367, low-carbon Ni-Cr-Mo alloys UNS N06035, UNS N06058, and UNS N06059, low carbon Ni-Cr-Mo-Cu alloy UNS N06200, Ni-Mo-Cr-Fe alloy UNS N10242, Ni-Mo alloys UNS N10665 and UNS N10675, low-carbon Ni-Fe-Cr-Mo-Cu alloy UNS N08031, Ni-Cr-W-Mo alloy UNS N06230, Ni-Cr-Co-Mo alloy UNS N06617, Ni-Co-Cr-Si alloy UNS N12160, Ni-Fe-Cr alloys, Ni-Mo alloy UNS N10629, Ni-Cr-Fe-Al alloy UNS N06025, Ni-Cr-Fe-Si alloy UNS N06045, Low-Carbon Ni-Mo-Cr-Ta alloy UNS N06210, Ni-Mo-Cr-Fe alloy UNS N10624, and low-carbon Cr-Ni-Fe-N alloy UNS R20033*.
1.1.1 The nickel-iron-chromium alloys are UNS N08120, UNS N08800, UNS N08810, and UNS N08811. Alloy UNS N08800 is normally employed in service temperatures up to and including 1100F (593C). Alloys UNS N08810, N08120, and UNS N08811 are normally employed in service temperatures above 1100F where resistance to creep and rupture is required, and are annealed to develop controlled grain size for optimum properties in this temperature range.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety and health practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B 564 – 06
Standard Specification for
1
Nickel Alloy Forgings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 564; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate
2
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material
1.1 This specification covers forgings of nickel alloy UNS
as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate
N02200, Ni-Cu alloy UNS N04400, Ni-Cr-Fe alloys UNS
safety and health practices, and determine the applicability of
N06600, UNS N06603, and UNS N06690, Ni-Cr-Mo-Nb alloy
regulatory limitations prior to use.
UNS N06625, Ni-Cr-Mo-Si alloy UNS N06219, low-carbon
Ni-Mo-Cr alloys UNS N10276 and UNS N06022, Ni-Cr-
2. Referenced Documents
Mo-W alloy UNS N06110, low-carbon Ni-Cr-Mo-W alloy
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
UNSN06686,Ni-Fe-Cr-Mo-CualloyUNSN08825,Fe-Ni-Cr-
B 880 SpecificationforGeneralRequirementsforChemical
Mo-N alloy UNS N08367, low-carbon Ni-Cr-Mo alloys UNS
Check Analysis Limits for Nickel, Nickel Alloys and
N06035, UNS N06058, and UNS N06059, low carbon Ni-Cr-
Cobalt Alloys
Mo-Cu alloy UNS N06200, Ni-Mo-Cr-Fe alloy UNS N10242,
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
Ni-Mo alloys UNS N10665 and UNS N10675, low-carbon
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
Ni-Fe-Cr-Mo-Cu alloy UNS N08031, Ni-Cr-W-Mo alloy UNS
Determine Conformance with Specifications
N06230, Ni-Cr-Co-Mo alloy UNS N06617, Ni-Co-Cr-Si alloy
E76 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Nickel-Copper
UNS N12160, Ni-Fe-Cr alloys, Ni-Mo alloy UNS N10629,
4
Alloys
Ni-Cr-Fe-Al alloy UNS N06025, Ni-Cr-Fe-Si alloy UNS
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
N06045, Low-Carbon Ni-Mo-Cr-Ta alloy UNS N06210, Ni-
E 350 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Carbon Steel,
Mo-Cr-Fe alloy UNS N10624, and low-carbon Cr-Ni-Fe-N
Low-Alloy Steel, Silicon Electrical Steel, Ingot Iron, and
alloy UNS R20033*.
Wrought Iron
1.1.1 The nickel-iron-chromium alloys are UNS N08120,
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
UNS N08800, UNS N08810, and UNS N08811. Alloy UNS
E 1473 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel,
N08800 is normally employed in service temperatures up to
Cobalt, and High-Temperature Alloys
and including 1100°F (593°C).Alloys UNS N08810, N08120,
5
2.2 Military Standards:
and UNS N08811 are normally employed in service tempera-
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
tures above 1100°F where resistance to creep and rupture is
MIL-STD-271 Nondestructive Testing Requirements for
required, and are annealed to develop controlled grain size for
Metals
optimum properties in this temperature range.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3. Ordering Information
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
and are not considered standard.
specification. Examples of such requirements include, but are
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
not limited to, the following:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.1 Alloy (Table 1).
responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar
3.1.2 Condition (Table 2).
3.1.3 Quantity (mass or number of pieces).
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
3
B02.07 on Refined Nickel and Cobalt and Their Alloys. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved July 1, 2006. Published July 2006. Originally approved contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as B 564 – 04. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi- the ASTM website.
4
cation SB-564 in Section II of that Code. Withdrawn.
5
* New designations established in accordance with ASTM E 527 and SAE Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
J1086, Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS). Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.