ASTM B446-23
(Specification)Standard Specification for Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Niobium Alloy, Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Silicon Alloy, and Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Tungsten Alloy Rod and Bar
Standard Specification for Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Niobium Alloy, Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Silicon Alloy, and Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Tungsten Alloy Rod and Bar
ABSTRACT
This specification covers nickel-chromium-molybdenum-columbium (UNS N06625), nickel-chromium-molybdenum-silicon alloy (UNS N06219), and nickel-chromium-molybdenum-tungsten alloy (UNS N06650) in the form of hot-worked rod and bar and cold-worked rod. The matreial shall conform to the required chemical composition for carbon, manganese, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chromium, columbium, tantalum, cobalt, molybdenum, iorn, aluminum, titanium, copper, nickel, tungsten, and nitrogen. The materials shall conform to the the heat treatment and room temperature tensile properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation. Dimensions of the alloys such as diameter, thickness, or width, length and straightness shall also be determined.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers nickel-chromium-molybdenum-niobium alloy (UNS N06625), nickel-chromium-molybdenum-silicon alloy (UNS N06219), and Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Tungsten Alloy (UNS N06650)2 in the form of both hot-worked and cold-worked rod and bar in the conditions shown in Table 1.
1.1.1 UNS N06625 products are furnished in three grades of different heat-treated conditions:
1.1.1.1 Grade 1 (Annealed)—Material is normally employed in service temperatures up to 1100 °F (593 °C).
1.1.1.2 Grade 2 (Solution Annealed)—Material is normally employed in service temperatures above 1100 °F (593 °C) when resistance to creep and rupture is required.
Note 1: Hot-working or reannealing may change properties significantly, depending on working history and temperatures.
1.1.1.3 Grade 3 (Solution Annealed and Cold Worked)—Material is normally employed in services where higher strengths are needed.
1.1.2 Alloys UNS N06219 and UNS N06650 are supplied in solution annealed condition only.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 12, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: B446 − 23
Standard Specification for
Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Niobium Alloy, Nickel-
Chromium-Molybdenum-Silicon Alloy, and Nickel-Chromium-
1
Molybdenum-Tungsten Alloy Rod and Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B446; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* those identified in the appropriate Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for
this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to
1.1 This specification covers nickel-chromium-
establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental
molybdenum-niobium alloy (UNS N06625), nickel-chromium-
practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limi-
molybdenum-silicon alloy (UNS N06219), and Nickel-
2 tations prior to use.
Chromium-Molybdenum-Tungsten Alloy (UNS N06650) in
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
the form of both hot-worked and cold-worked rod and bar in
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
the conditions shown in Table 1.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
1.1.1 UNS N06625 products are furnished in three grades of
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
different heat-treated conditions:
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.1.1.1 Grade 1 (Annealed)—Material is normally em-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ployed in service temperatures up to 1100 °F (593 °C).
1.1.1.2 Grade 2 (Solution Annealed)—Material is normally
2. Referenced Documents
employed in service temperatures above 1100 °F (593 °C)
3
when resistance to creep and rupture is required. 2.1 ASTM Standards:
B443 Specification for Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-
NOTE 1—Hot-working or reannealing may change properties
Columbium Alloy and Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-
significantly, depending on working history and temperatures.
Silicon Alloy Plate, Sheet, and Strip
1.1.1.3 Grade 3 (Solution Annealed and Cold Worked)—
B880 Specification for General Requirements for Chemical
Material is normally employed in services where higher
Check Analysis Limits for Nickel, Nickel Alloys and
strengths are needed.
Cobalt Alloys
1.1.2 Alloys UNS N06219 and UNS N06650 are supplied in
B899 Terminology Relating to Non-ferrous Metals and Al-
solution annealed condition only.
loys
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
E8/E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Ma-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
terials
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
and are not considered standard.
Determine Conformance with Specifications
E1473 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel,
1.3 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
Cobalt, and High-Temperature Alloys
test methods portion, Section 12, of this specification: This
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
3. Terminology
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this specification,
refer to Terminology B899.
1
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
B02.07 on Refined Nickel and Cobalt and Their Alloys.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2023. Published November 2023. Originally
3
approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as B446 – 19. DOI: For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
10.1520/B0446-23. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
2
Designation (UNS N06650) was established in accordance with Practice E527 Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
and SAE J 1086, Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS). the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B446 − 23
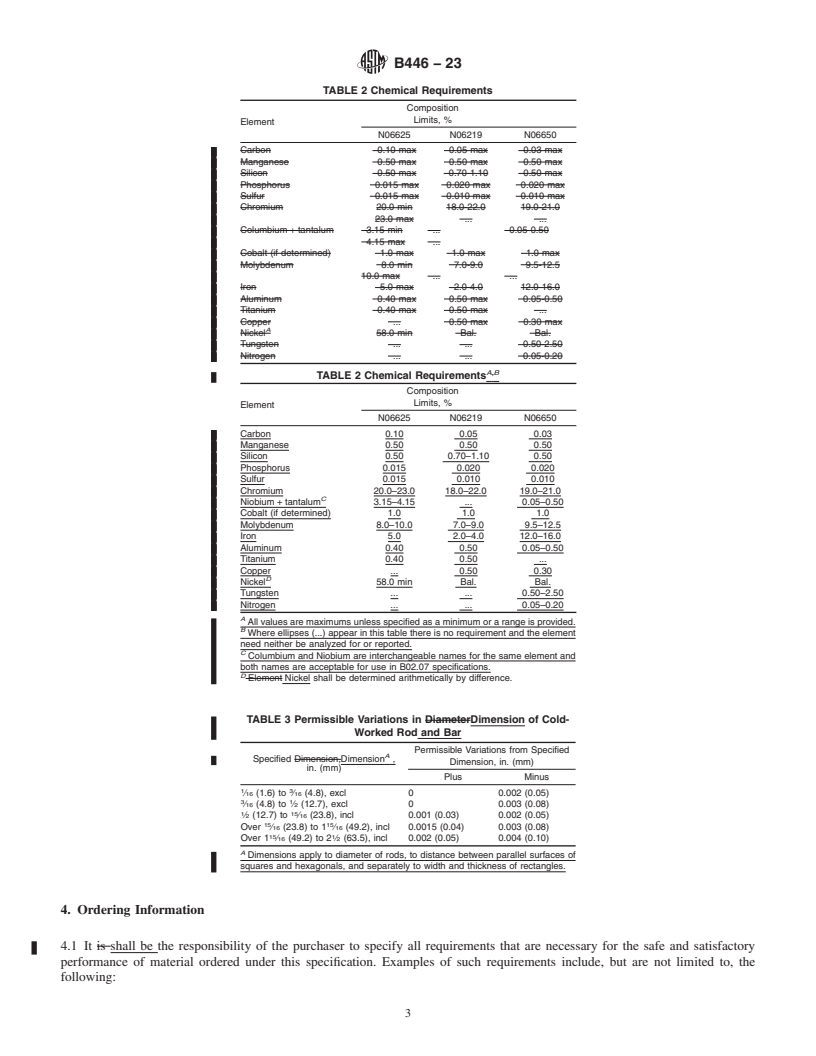
TABLE 1 Conditions for Hot-Worked and Cold-Worked Rod and TABLE 3 Permissible Variations in Dimension of Cold-Wo
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B446 − 19 B446 − 23
Standard Specification for
Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Columbium Alloy (UNS
N06625), Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Silicon Alloy (UNS
N06219), Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Niobium Alloy,
Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Silicon Alloy, and Nickel-
Chromium-Molybdenum-Tungsten Alloy (UNS N06650) Rod
1
and Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B446; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers nickel-chromium-molybdenum-columbium nickel-chromium-molybdenum-niobium alloy (UNS
N06625), nickel-chromium-molybdenum-silicon alloy (UNS N06219), and Nickel-Chromium-Molybdenum-Tungsten Alloy
2
(UNS N06650) in the form of both hot-worked and cold-worked rod and bar and cold-worked rod in the conditions shown in Table
1.
1.1.1 UNS N06625 products are furnished in twothree grades of different heat-treated conditions:
1.1.1.1 Grade 1 (Annealed)—Material is normally employed in service temperatures up to 1100°F (593°C).1100 °F (593 °C).
1.1.1.2 Grade 2 (Solution Annealed)—Material is normally employed in service temperatures above 1100°F (593°C)1100 °F
(593 °C) when resistance to creep and rupture is required.
NOTE 1—Hot-working or reannealing may change properties significantly, depending on working history and temperatures.
1.1.1.3 Grade 3 (Solution Annealed and Cold Worked)—Material is normally employed in services where higher strengths are
needed.
1.1.2 Alloys UNS N06219 and UNS N06650 are supplied in solution annealed condition only.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 12, of this specification: cThisThis
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B02.07 on Refined
Nickel and Cobalt and Their Alloys.
Current edition approved April 1, 2019Nov. 1, 2023. Published April 2019November 2023. Originally approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 20142019 as
B446B446 – 19.– 03 (2014). DOI: 10.1520/B0446-19. DOI: 10.1520/B0446-23.
2
Designation (UNS N06650) was established in accordance with Practice E527 and SAE J 1086, Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS).
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B446 − 23
TABLE 1 Conditions for Hot-Worked and Cold-Worked Rod and
A
Bar and Cold-Worked Rod
Tensile Yield Elongation
Diameter or Distance
Strength Strength in 2 in. or
Between Parallel Surfaces,
min, ksi (0.2 % offset), 50 mm or
in. (mm)
(MPa) min, ksi (MPa) 4D, min, %
B
UNS N06625 Grade 1 (Annealed)
Up to 4 (102), incl 120 (827) 60 (414) 30
Over 4 (102) to 10 (254), 110 (758) 50 (345) 25
incl
C
UNS N06625 Grade 2 (Solution Annealed)
All sizes 100 (690) 40 (276) 30
UNS N06625 Grade 3 (Solution Annealed and Cold-Worked)
Up to 2.5 in. (63 mm) 135 (930) 100 (690) 25
UNS N06219 All (Solution Annealed)
All sizes 96 (660) 39 (270) 50
UNS N06650 All (Solution Annealed)
All sizes 116 (800) 58 (400) 45
A
Forging quality is furnished to chemical requirements and surface inspection
only. No tensile properties are required. Forging stock is typically supplied in the
hot worked condition, (see X1.1.5).
B
Annealed 1600°F (871°C)1600 °F (871 °C) minimum.
C
Solution annealed at 2000°F (1093°C)2000 °F (1093 °C) minimum, with or
without subsequent stabilization anneal at 1800°F (982°C)1800 °F (982 °C) mini-
mum to increase resistance to sensitization.
of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for this
product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmenta
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.